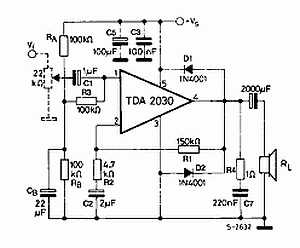
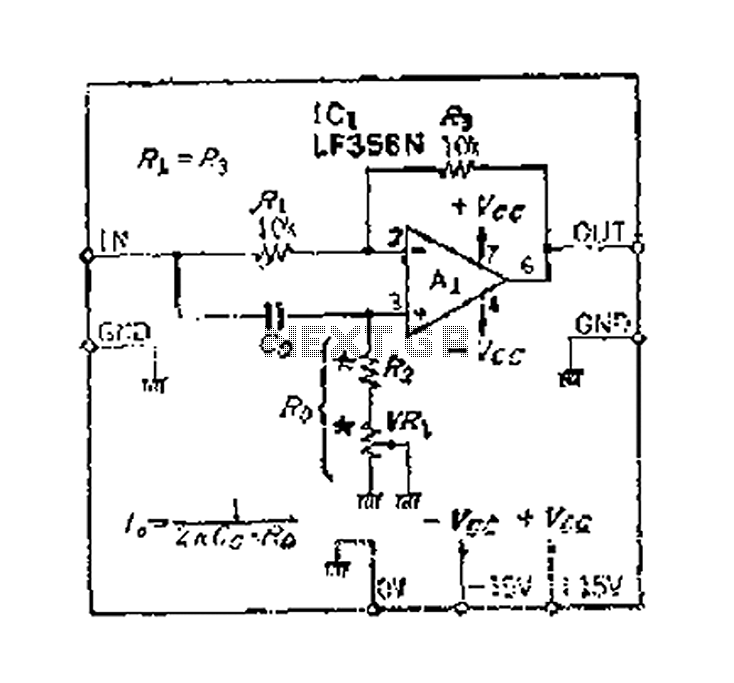
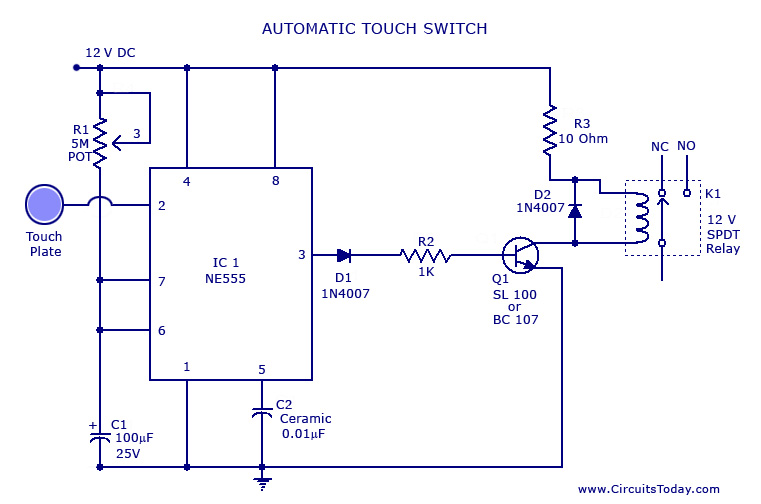
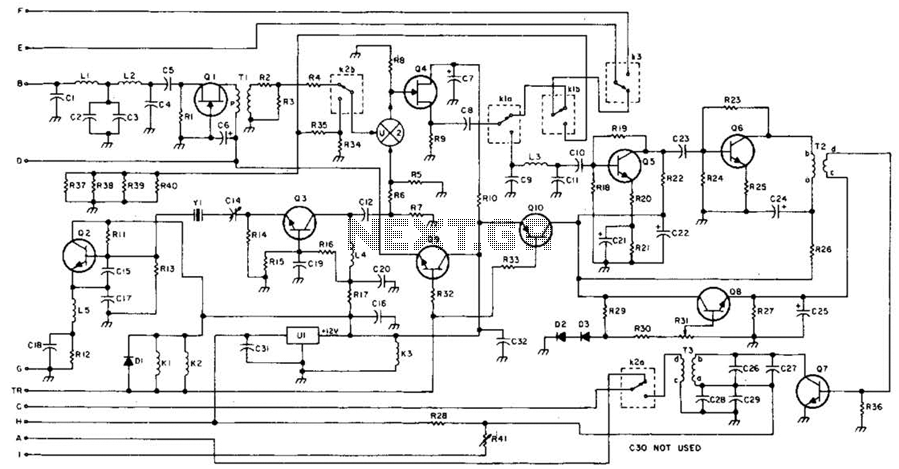
Crystal Controlled Frequency Converter Circuit
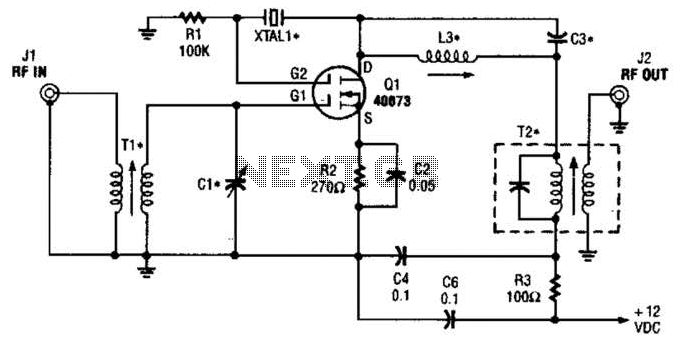
The second gate (G2) of a MOSFET can be utilized to integrate a crystal oscillator within the same stage as a frequency mixer. While this technique is common in tube technology, it is rarely implemented in dual-gate MOSFET circuits. Components L3, C3, and X1 constitute the crystal oscillator, while T2 serves as an intermediate frequency (IF) output transformer. T1 and C1 are tuned to the converter input frequency. This circuit is expected to operate effectively up to approximately 25 MHz, or even higher when using third-overtone crystals.
The described circuit leverages the unique characteristics of dual-gate MOSFETs, particularly their ability to handle multiple inputs and provide enhanced gain control. The integration of a crystal oscillator at the second gate (G2) facilitates precise frequency control, which is critical in applications such as radio frequency (RF) mixing.
In this configuration, L3 acts as an inductor that, together with C3, forms a resonant tank circuit with X1, which is the crystal oscillator. The choice of crystal type is vital, as third-overtone crystals can significantly extend the operational frequency range, allowing the circuit to function efficiently beyond 25 MHz.
T1 and C1 are essential for ensuring that the input frequency to the converter is accurately tuned. This tuning process is crucial for maximizing the mixer’s performance and minimizing signal distortion. The output from the mixer is then processed through T2, which is designed to efficiently transfer the intermediate frequency signal to the next stage of the circuit.
Overall, this design exemplifies a sophisticated approach to RF signal processing, merging traditional techniques with modern semiconductor technology to achieve high-frequency performance in compact circuitry. The careful selection of components and their configurations is vital for optimizing the circuit's functionality and reliability in practical applications. The second gate (G2) of a MOSFET can be used to incorporate a crystal oscillator into the same stage as a frequency mixer. Although old hat with tubes, this scheme is seldom seen in dual-gate MOSFET circuitry. L3, 03, and XI form the crystal oscillator, and T2 is an IF output transformer. T1 and 01 are tuned to the converter input frequency. This circuit should be useable up to 25 MHz or so, or higher with third- overtone crystals.
The described circuit leverages the unique characteristics of dual-gate MOSFETs, particularly their ability to handle multiple inputs and provide enhanced gain control. The integration of a crystal oscillator at the second gate (G2) facilitates precise frequency control, which is critical in applications such as radio frequency (RF) mixing.
In this configuration, L3 acts as an inductor that, together with C3, forms a resonant tank circuit with X1, which is the crystal oscillator. The choice of crystal type is vital, as third-overtone crystals can significantly extend the operational frequency range, allowing the circuit to function efficiently beyond 25 MHz.
T1 and C1 are essential for ensuring that the input frequency to the converter is accurately tuned. This tuning process is crucial for maximizing the mixer’s performance and minimizing signal distortion. The output from the mixer is then processed through T2, which is designed to efficiently transfer the intermediate frequency signal to the next stage of the circuit.
Overall, this design exemplifies a sophisticated approach to RF signal processing, merging traditional techniques with modern semiconductor technology to achieve high-frequency performance in compact circuitry. The careful selection of components and their configurations is vital for optimizing the circuit's functionality and reliability in practical applications. The second gate (G2) of a MOSFET can be used to incorporate a crystal oscillator into the same stage as a frequency mixer. Although old hat with tubes, this scheme is seldom seen in dual-gate MOSFET circuitry. L3, 03, and XI form the crystal oscillator, and T2 is an IF output transformer. T1 and 01 are tuned to the converter input frequency. This circuit should be useable up to 25 MHz or so, or higher with third- overtone crystals.