Cmos oscillator
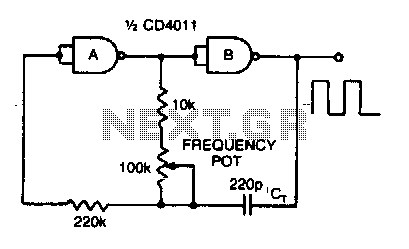
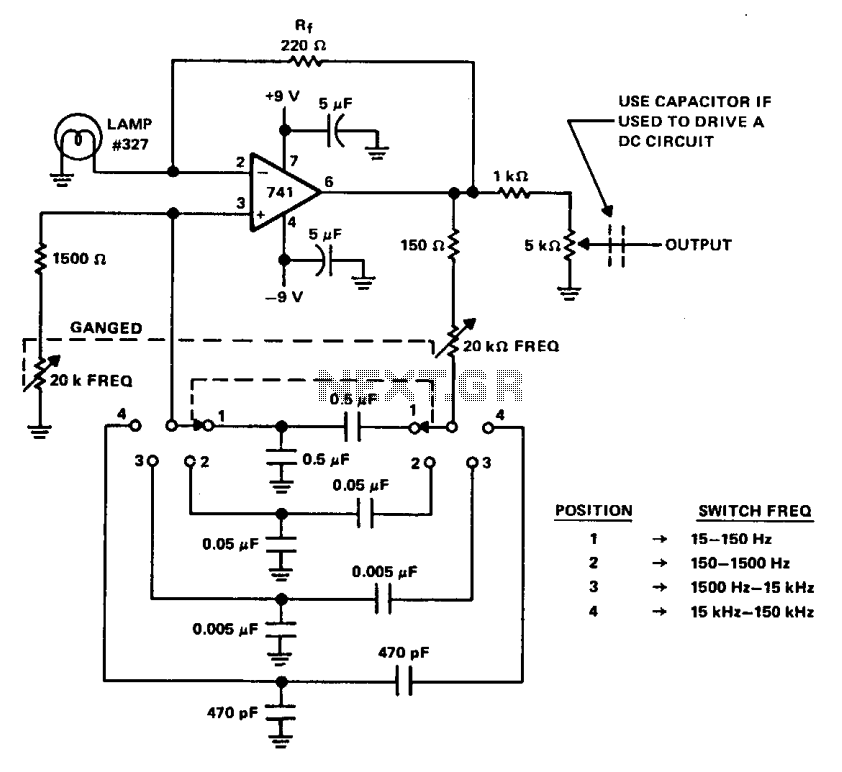
Adjusting the 100 K ohm potentiometer modifies the discharge rate of capacitor Ct, thereby affecting the output frequency. A square wave output is produced. The maximum frequency achievable with CMOS technology is constrained to 2 MHz.
The circuit described involves a timing configuration where a capacitor (Ct) is discharged through a variable resistor (100 K ohm potentiometer). This setup is typically used in oscillator circuits to generate square wave signals. The frequency of the output square wave is inversely related to the discharge time of the capacitor; as the resistance of the potentiometer is increased, the discharge rate of the capacitor decreases, leading to a lower frequency output. Conversely, reducing the resistance allows for a quicker discharge, resulting in a higher frequency.
In a CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) implementation, the maximum frequency output is limited to 2 MHz due to the inherent switching speed of the CMOS transistors and the time constants associated with the RC (resistor-capacitor) network formed by the potentiometer and the capacitor. The design must consider these limitations to ensure reliable operation within the specified frequency range.
For practical applications, the circuit can be utilized in various timing and waveform generation scenarios, such as clock signals for digital circuits, tone generation in audio applications, or as part of a more complex modulation scheme. Proper selection of the capacitor value and the potentiometer's resistance range will allow for fine-tuning of the frequency output to meet specific application requirements.Varying the 100 K pot changes the discharge rate of Ct and hence the frequency. A square wave output is generated The maximum frequency using CMOS is limited to 2 MHz.
The circuit described involves a timing configuration where a capacitor (Ct) is discharged through a variable resistor (100 K ohm potentiometer). This setup is typically used in oscillator circuits to generate square wave signals. The frequency of the output square wave is inversely related to the discharge time of the capacitor; as the resistance of the potentiometer is increased, the discharge rate of the capacitor decreases, leading to a lower frequency output. Conversely, reducing the resistance allows for a quicker discharge, resulting in a higher frequency.
In a CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) implementation, the maximum frequency output is limited to 2 MHz due to the inherent switching speed of the CMOS transistors and the time constants associated with the RC (resistor-capacitor) network formed by the potentiometer and the capacitor. The design must consider these limitations to ensure reliable operation within the specified frequency range.
For practical applications, the circuit can be utilized in various timing and waveform generation scenarios, such as clock signals for digital circuits, tone generation in audio applications, or as part of a more complex modulation scheme. Proper selection of the capacitor value and the potentiometer's resistance range will allow for fine-tuning of the frequency output to meet specific application requirements.Varying the 100 K pot changes the discharge rate of Ct and hence the frequency. A square wave output is generated The maximum frequency using CMOS is limited to 2 MHz.