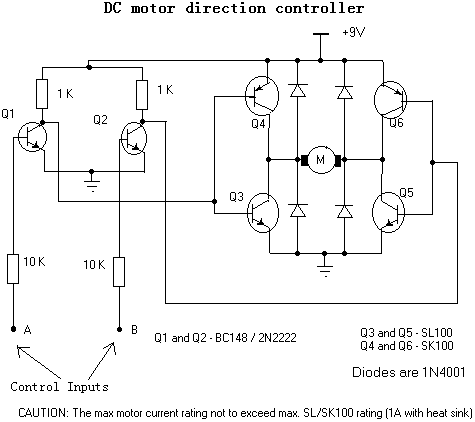
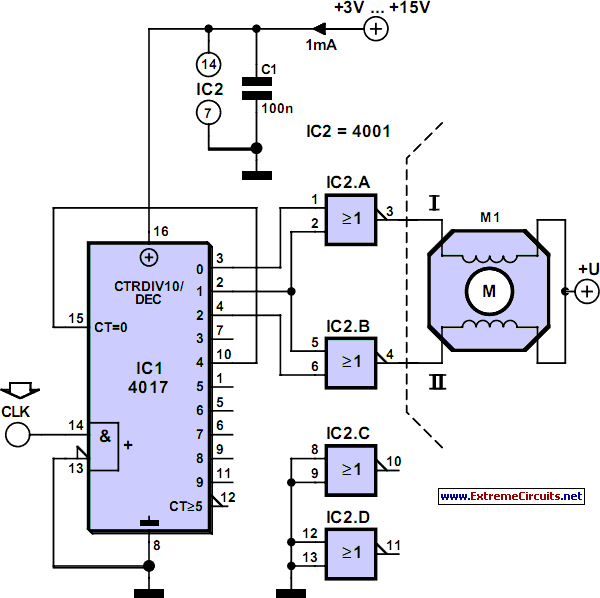
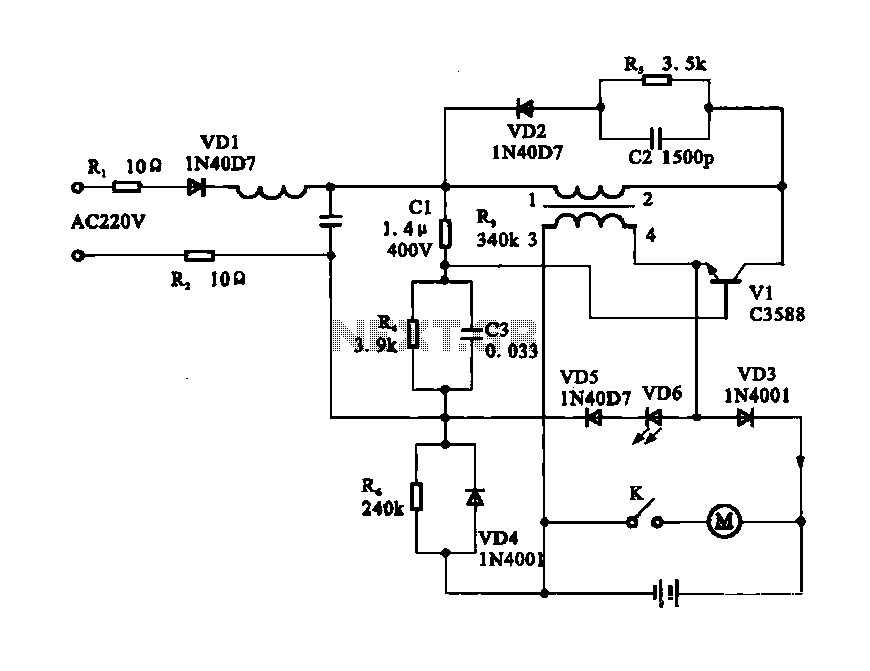
dc servo motor controller

The A3952S integrated circuit, designed by Allegro MicroSystems, can be utilized to create straightforward and effective motor driver circuits. A previous article discussed a basic bipolar stepper motor driver circuit that employs two A3952S circuits. The A3952S is capable of continuous output currents of up to 2 A and can operate at voltages ranging up to 50 V. This document presents a simple DC servo motor application suitable for various electronic projects. The DC servo motor driver schematic utilizes only one integrated circuit along with a few additional electronic components. For bidirectional DC servo motors, the PHASE terminal facilitates mechanical direction control. Similar to dynamic braking of the motor, abrupt changes in the direction of a rotating motor generate a current due to back EMF, with the magnitude of this current being dependent on the mode of operation.
The A3952S integrated circuit is a versatile solution for motor control applications, particularly in the context of DC servo motors. This IC integrates several functions that simplify the design of motor driver circuits. The primary features of the A3952S include its ability to handle continuous output currents up to 2 A and operate within a voltage range of 8 V to 50 V, making it suitable for a wide array of applications.
In the schematic for the DC servo motor driver, the A3952S is connected to the motor, power supply, and various passive components. The circuit typically includes resistors and capacitors for filtering and stability, ensuring that the motor operates smoothly without unwanted oscillations. The PHASE terminal is crucial for controlling the direction of the motor. By toggling this terminal, the user can reverse the motor's direction, which is essential for applications requiring bidirectional motion.
In addition to direction control, the A3952S provides features such as current sensing and thermal shutdown, which enhance the reliability of the motor driver circuit. The back EMF generated during abrupt direction changes necessitates careful consideration of the circuit design to prevent damage to the components. The design must accommodate the transient currents that occur, especially when switching directions, to ensure the longevity of the integrated circuit and the motor.
Overall, the A3952S offers a compact and efficient solution for controlling DC servo motors, making it an excellent choice for hobbyists and professionals alike in various electronic projects.As we presented in another article the A3952S integrated circuit ( designed by Allegro MicroSystems ) can be used to design very simple and useful motor driver circuits. In the precedent article was presented a simple bipolar stepper motor driver circuit that use two A3952S circuits.
As we presented in that article, the A3952S is capable of cont inuous output currents up to 2 A and operating voltages range up to 50 V. This circuit presents a simple DC servo motor application that can be used in various electronic projects. As you can see in the circuit schematic this Dc servo motor driver schematic circuit use just one integrated circuit and other few external electronic components.
With bidirectional dc servo motors, the PHASE terminal can be used for mechanical direction control. Similar to when braking the motor dynamically, abrupt changes in the direction of a rotating motor produce a current generated by the back EMF. The current generated will depend on the mode of operation. 🔗 External reference
The A3952S integrated circuit is a versatile solution for motor control applications, particularly in the context of DC servo motors. This IC integrates several functions that simplify the design of motor driver circuits. The primary features of the A3952S include its ability to handle continuous output currents up to 2 A and operate within a voltage range of 8 V to 50 V, making it suitable for a wide array of applications.
In the schematic for the DC servo motor driver, the A3952S is connected to the motor, power supply, and various passive components. The circuit typically includes resistors and capacitors for filtering and stability, ensuring that the motor operates smoothly without unwanted oscillations. The PHASE terminal is crucial for controlling the direction of the motor. By toggling this terminal, the user can reverse the motor's direction, which is essential for applications requiring bidirectional motion.
In addition to direction control, the A3952S provides features such as current sensing and thermal shutdown, which enhance the reliability of the motor driver circuit. The back EMF generated during abrupt direction changes necessitates careful consideration of the circuit design to prevent damage to the components. The design must accommodate the transient currents that occur, especially when switching directions, to ensure the longevity of the integrated circuit and the motor.
Overall, the A3952S offers a compact and efficient solution for controlling DC servo motors, making it an excellent choice for hobbyists and professionals alike in various electronic projects.As we presented in another article the A3952S integrated circuit ( designed by Allegro MicroSystems ) can be used to design very simple and useful motor driver circuits. In the precedent article was presented a simple bipolar stepper motor driver circuit that use two A3952S circuits.
As we presented in that article, the A3952S is capable of cont inuous output currents up to 2 A and operating voltages range up to 50 V. This circuit presents a simple DC servo motor application that can be used in various electronic projects. As you can see in the circuit schematic this Dc servo motor driver schematic circuit use just one integrated circuit and other few external electronic components.
With bidirectional dc servo motors, the PHASE terminal can be used for mechanical direction control. Similar to when braking the motor dynamically, abrupt changes in the direction of a rotating motor produce a current generated by the back EMF. The current generated will depend on the mode of operation. 🔗 External reference