dc to dc converter
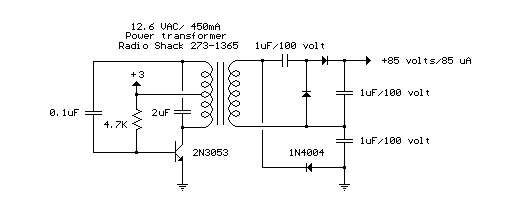
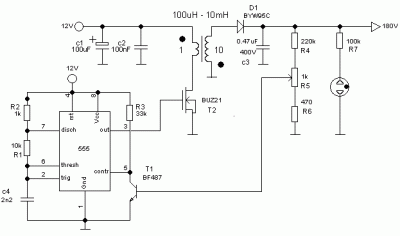
The circuit is a DC to DC converter utilizing a standard 12 VAC center-tapped power transformer configured as a blocking oscillator. Although the circuit exhibits low efficiency, it generates a high voltage suitable for low power applications. The input battery voltage is increased by a factor of 10 across the transformer and further elevated by a voltage tripler comprising three capacitors and diodes connected to the high voltage side of the transformer.
The described DC to DC converter circuit operates by employing a center-tapped transformer, which is a critical component in this design. The transformer is energized by a blocking oscillator, a circuit configuration that allows for the conversion of direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) and subsequently back into a higher DC voltage. The blocking oscillator works by rapidly switching the current flow, causing the transformer to generate an alternating voltage on its secondary winding.
The center-tapped transformer provides two equal voltage outputs from its secondary winding, which facilitates the generation of a high voltage by utilizing half of the winding. The output voltage is further amplified through a voltage tripler circuit. This voltage tripler consists of three capacitors and three diodes arranged in a specific configuration that allows the circuit to effectively multiply the voltage output from the transformer.
During operation, the first diode conducts during the positive half-cycle of the AC voltage from the transformer, charging the first capacitor. In the subsequent half-cycle, the second diode conducts, allowing the second capacitor to charge while the first capacitor retains its charge. The third diode then allows for the combination of the charges from the first two capacitors, effectively tripling the input voltage. The final output voltage is available for low power applications, making this circuit suitable for devices that require a high voltage supply but do not demand high current.
It is important to note that while this circuit is capable of producing high voltages, its overall efficiency is limited. Factors contributing to this inefficiency include losses in the transformer, voltage drops across the diodes, and the inherent capacitance and leakage currents in the capacitors. Despite these limitations, the circuit remains a viable solution for applications where high voltage is necessary, but where efficiency is not the primary concern. Proper design considerations, such as selecting appropriate component ratings and ensuring adequate heat dissipation, are essential for reliable operation.The circuit is a DC to DC converter using a standard 12 VAC center tapped power transformer wired as a blocking oscillator. The circuit is not very efficient but will produce a high voltage usable for low power applications. The input battery voltage is raised by a factor of 10 across the transformer and further raised by a voltage tripler consisting of three capacitors and diodes connected to the high voltage side of the transformer..
🔗 External reference
The described DC to DC converter circuit operates by employing a center-tapped transformer, which is a critical component in this design. The transformer is energized by a blocking oscillator, a circuit configuration that allows for the conversion of direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) and subsequently back into a higher DC voltage. The blocking oscillator works by rapidly switching the current flow, causing the transformer to generate an alternating voltage on its secondary winding.
The center-tapped transformer provides two equal voltage outputs from its secondary winding, which facilitates the generation of a high voltage by utilizing half of the winding. The output voltage is further amplified through a voltage tripler circuit. This voltage tripler consists of three capacitors and three diodes arranged in a specific configuration that allows the circuit to effectively multiply the voltage output from the transformer.
During operation, the first diode conducts during the positive half-cycle of the AC voltage from the transformer, charging the first capacitor. In the subsequent half-cycle, the second diode conducts, allowing the second capacitor to charge while the first capacitor retains its charge. The third diode then allows for the combination of the charges from the first two capacitors, effectively tripling the input voltage. The final output voltage is available for low power applications, making this circuit suitable for devices that require a high voltage supply but do not demand high current.
It is important to note that while this circuit is capable of producing high voltages, its overall efficiency is limited. Factors contributing to this inefficiency include losses in the transformer, voltage drops across the diodes, and the inherent capacitance and leakage currents in the capacitors. Despite these limitations, the circuit remains a viable solution for applications where high voltage is necessary, but where efficiency is not the primary concern. Proper design considerations, such as selecting appropriate component ratings and ensuring adequate heat dissipation, are essential for reliable operation.The circuit is a DC to DC converter using a standard 12 VAC center tapped power transformer wired as a blocking oscillator. The circuit is not very efficient but will produce a high voltage usable for low power applications. The input battery voltage is raised by a factor of 10 across the transformer and further raised by a voltage tripler consisting of three capacitors and diodes connected to the high voltage side of the transformer..
🔗 External reference