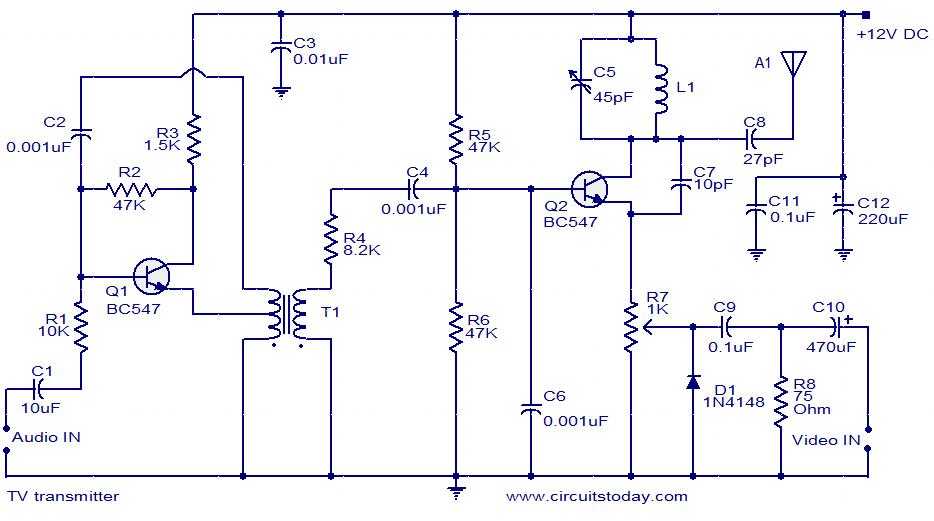
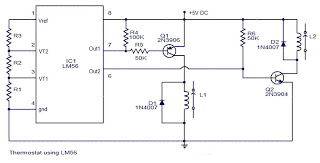
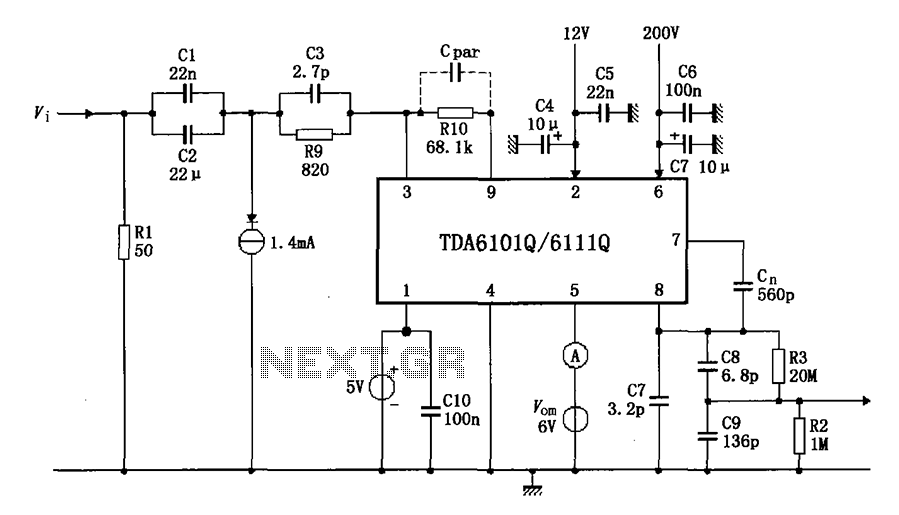
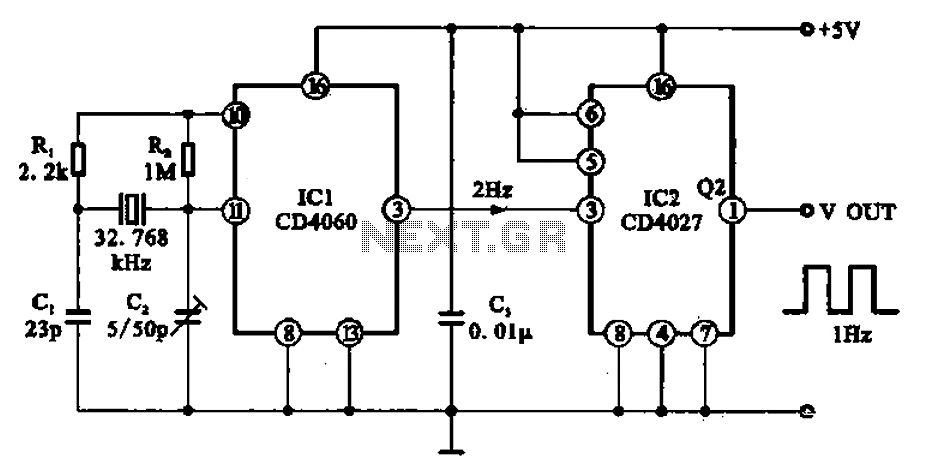
Differential amplifier circuit has a constant current source
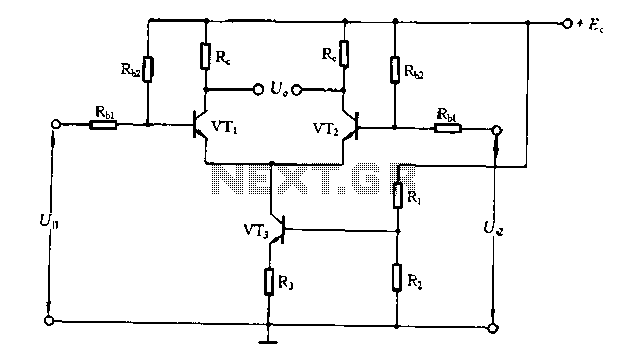
The differential amplifier circuit features a constant current source.
The differential amplifier is a fundamental building block in analog electronics, utilized for amplifying the difference between two input voltages while rejecting any signals that are common to both inputs. Central to its operation is the constant current source, which provides a stable biasing current to the transistors in the circuit. This ensures that the amplifier maintains consistent performance across varying conditions.
In a typical configuration, the differential amplifier consists of two input transistors, often bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) or field-effect transistors (FETs), arranged in a complementary manner. The constant current source is connected to the emitters (in the case of BJTs) or sources (for FETs) of the input transistors, allowing for precise control over the quiescent operating point of the amplifier.
The output of the differential amplifier can be taken from the collectors (for BJTs) or drains (for FETs) of the input transistors. The differential gain of the amplifier is primarily determined by the load resistors connected to these outputs and the transconductance of the input devices. To enhance the common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR), additional stages or feedback mechanisms may be employed, improving the overall performance of the amplifier in real-world applications.
In summary, the differential amplifier circuit with a constant current source is designed to provide high accuracy and stability in amplifying differential signals, making it suitable for applications such as instrumentation, signal conditioning, and audio processing.Differential amplifier circuit has a constant current source road
The differential amplifier is a fundamental building block in analog electronics, utilized for amplifying the difference between two input voltages while rejecting any signals that are common to both inputs. Central to its operation is the constant current source, which provides a stable biasing current to the transistors in the circuit. This ensures that the amplifier maintains consistent performance across varying conditions.
In a typical configuration, the differential amplifier consists of two input transistors, often bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) or field-effect transistors (FETs), arranged in a complementary manner. The constant current source is connected to the emitters (in the case of BJTs) or sources (for FETs) of the input transistors, allowing for precise control over the quiescent operating point of the amplifier.
The output of the differential amplifier can be taken from the collectors (for BJTs) or drains (for FETs) of the input transistors. The differential gain of the amplifier is primarily determined by the load resistors connected to these outputs and the transconductance of the input devices. To enhance the common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR), additional stages or feedback mechanisms may be employed, improving the overall performance of the amplifier in real-world applications.
In summary, the differential amplifier circuit with a constant current source is designed to provide high accuracy and stability in amplifying differential signals, making it suitable for applications such as instrumentation, signal conditioning, and audio processing.Differential amplifier circuit has a constant current source road