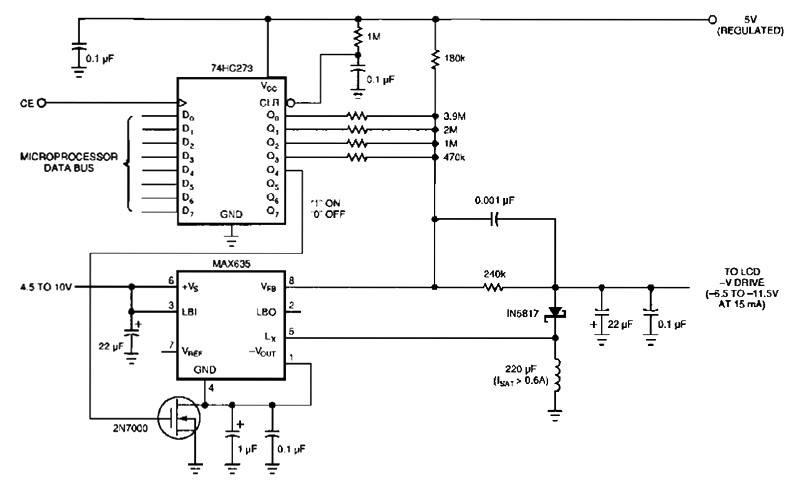
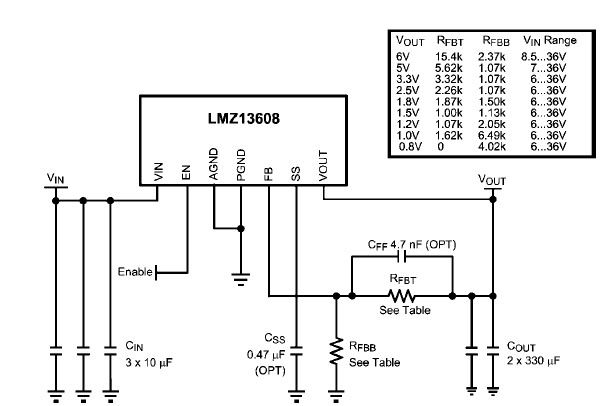
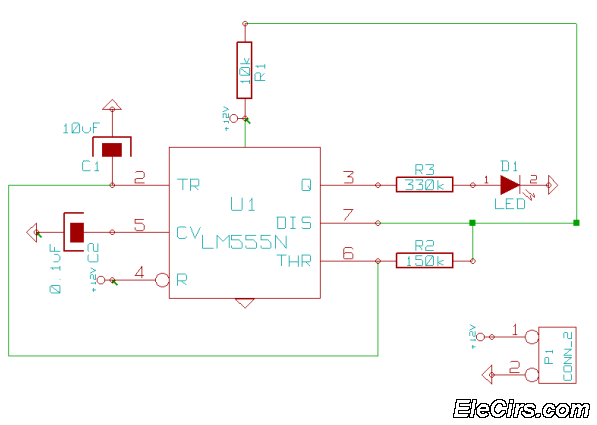
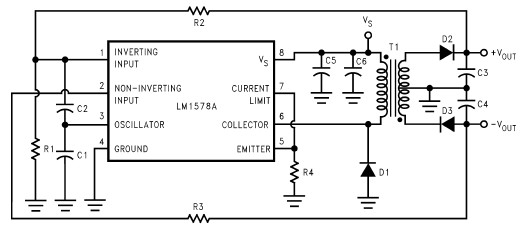
Discrete PWM Generator Circuit
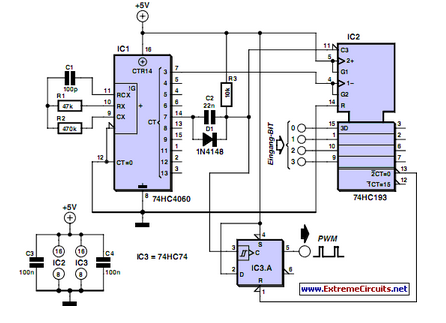
PWM waveforms are frequently utilized to regulate the speed of DC motors. The duty cycle of the digital waveform can be defined using an adjustable parameter.
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) is a technique employed to control the power delivered to electrical devices, particularly in applications involving DC motors. In this context, PWM allows for efficient speed control by varying the duty cycle of the waveform. The duty cycle, expressed as a percentage, represents the proportion of time the signal is in a high state (on) compared to the low state (off) within a given period.
To implement PWM for controlling a DC motor, a microcontroller or dedicated PWM controller generates the waveform. The frequency of the PWM signal must be chosen carefully, generally in the range of a few kilohertz, to ensure smooth motor operation without audible noise. The adjustable parameter, often set via a potentiometer or a digital input, allows the user to modify the duty cycle dynamically.
When the duty cycle is increased, the motor receives more power, resulting in higher speed. Conversely, reducing the duty cycle decreases the power supplied to the motor, leading to a slower speed. This method of control is advantageous because it minimizes power loss compared to other methods, such as resistive control, allowing for more efficient operation and heat management.
In practical applications, additional components may be included in the circuit, such as transistors or MOSFETs, to handle the higher currents required by the motor, as well as diodes for back EMF protection. Proper design considerations, including the selection of appropriate components and the layout of the circuit, are crucial for achieving optimal performance and reliability in PWM-controlled DC motor applications.PWM waveforms are commonly used to control the speed of DC motors. The mark/space ratio of the digital wave-form can be defined either by using an adjusta.. 🔗 External reference
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) is a technique employed to control the power delivered to electrical devices, particularly in applications involving DC motors. In this context, PWM allows for efficient speed control by varying the duty cycle of the waveform. The duty cycle, expressed as a percentage, represents the proportion of time the signal is in a high state (on) compared to the low state (off) within a given period.
To implement PWM for controlling a DC motor, a microcontroller or dedicated PWM controller generates the waveform. The frequency of the PWM signal must be chosen carefully, generally in the range of a few kilohertz, to ensure smooth motor operation without audible noise. The adjustable parameter, often set via a potentiometer or a digital input, allows the user to modify the duty cycle dynamically.
When the duty cycle is increased, the motor receives more power, resulting in higher speed. Conversely, reducing the duty cycle decreases the power supplied to the motor, leading to a slower speed. This method of control is advantageous because it minimizes power loss compared to other methods, such as resistive control, allowing for more efficient operation and heat management.
In practical applications, additional components may be included in the circuit, such as transistors or MOSFETs, to handle the higher currents required by the motor, as well as diodes for back EMF protection. Proper design considerations, including the selection of appropriate components and the layout of the circuit, are crucial for achieving optimal performance and reliability in PWM-controlled DC motor applications.PWM waveforms are commonly used to control the speed of DC motors. The mark/space ratio of the digital wave-form can be defined either by using an adjusta.. 🔗 External reference