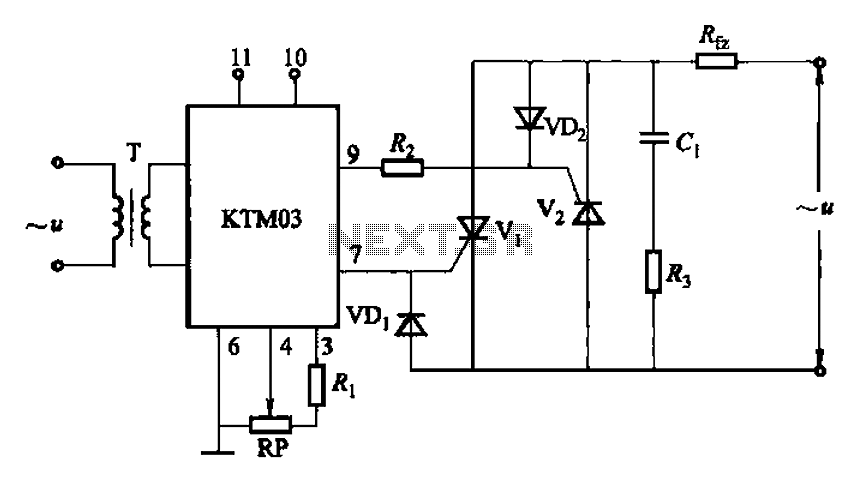
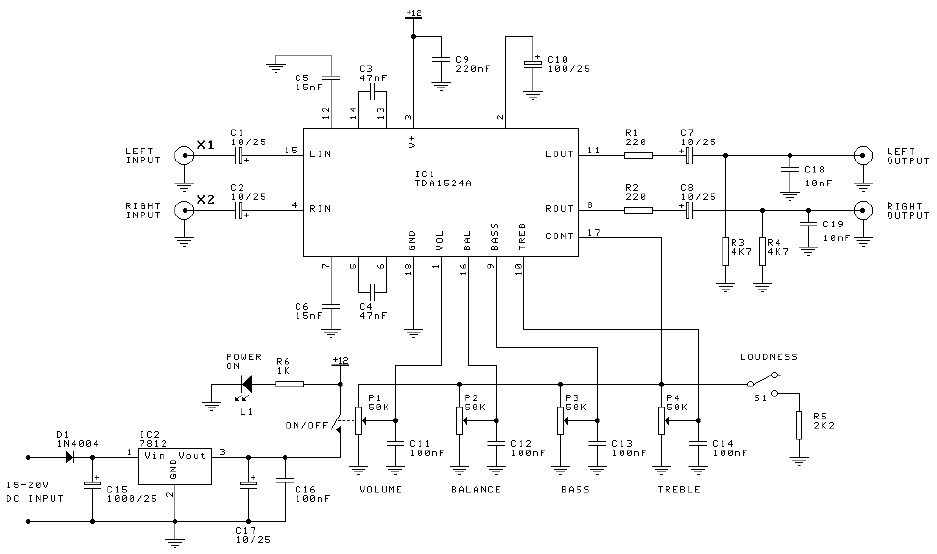
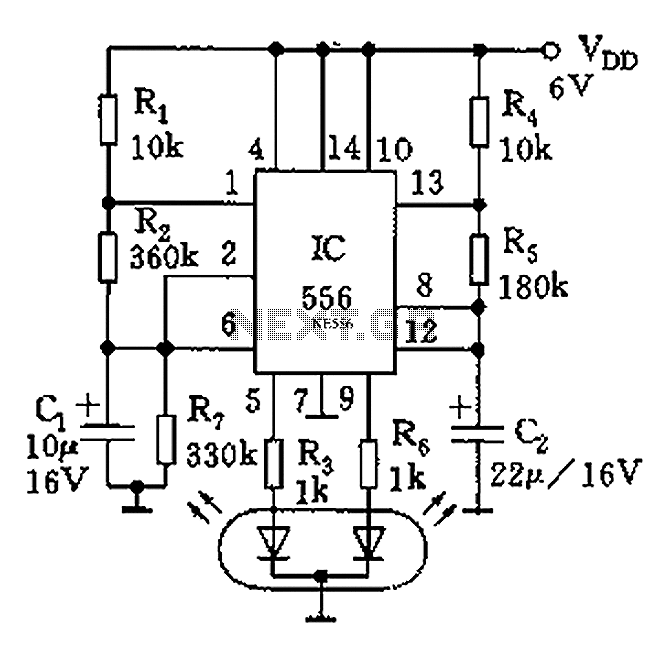
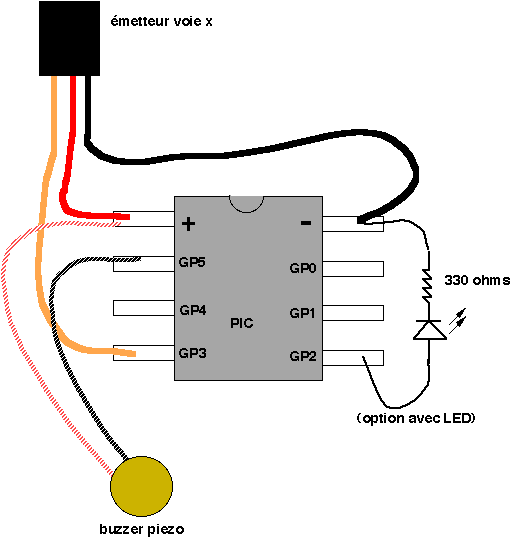
DIY Crystal Oscillator Circuit
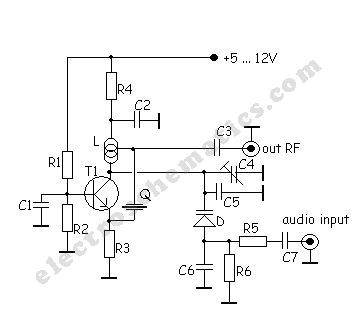
A very simple DIY crystal oscillator circuit that uses a quartz crystal for frequency stability and a suitable RF transistor. It employs a second or third harmonic crystal for operation.
This DIY crystal oscillator circuit is designed to generate stable oscillations using a quartz crystal, which is known for its excellent frequency stability. The circuit typically consists of a few key components, including a quartz crystal, an RF transistor, resistors, and capacitors.
The choice of using a second or third harmonic crystal is crucial, as it allows the oscillator to operate at higher frequencies than the fundamental frequency of the crystal. The RF transistor amplifies the oscillations produced by the crystal, ensuring that the output signal is strong enough for further applications.
In constructing this circuit, the quartz crystal is connected in a feedback loop with the RF transistor. The feedback network comprises resistors and capacitors, which help to stabilize the oscillation frequency and control the gain of the oscillator. Proper selection of these passive components is essential for achieving the desired frequency output and maintaining signal integrity.
The oscillator can be powered by a DC voltage source, typically ranging from a few volts to a maximum specified by the transistor's ratings. The output can be taken from the collector of the transistor, which provides a high-frequency signal suitable for various applications, including signal generation, clock pulses, or as a local oscillator in RF applications.
Overall, this simple DIY crystal oscillator circuit serves as an excellent introduction to oscillator design, demonstrating the principles of frequency stability and amplification in a straightforward and accessible manner.A very simple DIY crystal oscillator circuit which use a quartz for frequency stability and a good rf transistor. Use a 2-nd or 3-rd harmonic crystal, for.. 🔗 External reference
This DIY crystal oscillator circuit is designed to generate stable oscillations using a quartz crystal, which is known for its excellent frequency stability. The circuit typically consists of a few key components, including a quartz crystal, an RF transistor, resistors, and capacitors.
The choice of using a second or third harmonic crystal is crucial, as it allows the oscillator to operate at higher frequencies than the fundamental frequency of the crystal. The RF transistor amplifies the oscillations produced by the crystal, ensuring that the output signal is strong enough for further applications.
In constructing this circuit, the quartz crystal is connected in a feedback loop with the RF transistor. The feedback network comprises resistors and capacitors, which help to stabilize the oscillation frequency and control the gain of the oscillator. Proper selection of these passive components is essential for achieving the desired frequency output and maintaining signal integrity.
The oscillator can be powered by a DC voltage source, typically ranging from a few volts to a maximum specified by the transistor's ratings. The output can be taken from the collector of the transistor, which provides a high-frequency signal suitable for various applications, including signal generation, clock pulses, or as a local oscillator in RF applications.
Overall, this simple DIY crystal oscillator circuit serves as an excellent introduction to oscillator design, demonstrating the principles of frequency stability and amplification in a straightforward and accessible manner.A very simple DIY crystal oscillator circuit which use a quartz for frequency stability and a good rf transistor. Use a 2-nd or 3-rd harmonic crystal, for.. 🔗 External reference