DIY Homemade Signal Generator with Pulse Width Modulation

Construct a signal generator using readily available components. It should produce a square wave with variable frequency and adjustable pulse width. This device can be utilized for various applications, including DC motor speed regulation, dimming of lamps or LEDs, transformer drivers, ignition coil circuits, and other high-voltage power supply units.
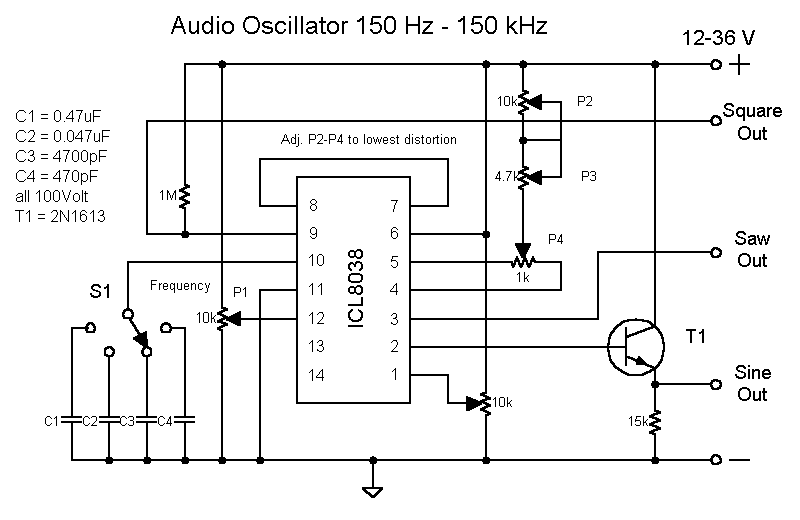
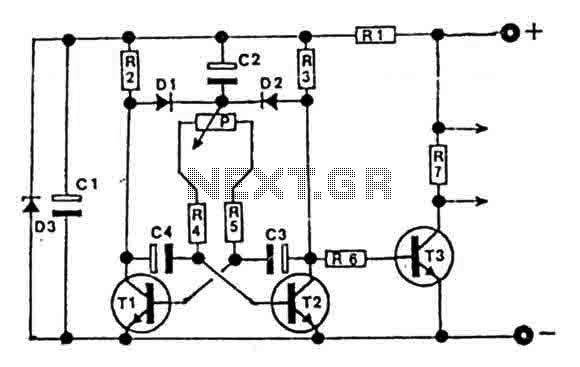
To create a versatile signal generator capable of producing square wave signals with variable frequency and pulse width, a configuration based on a 555 timer IC can be employed. The 555 timer, in astable mode, is particularly suitable for generating continuous square wave signals.
The circuit typically consists of the following components: a 555 timer IC, resistors, capacitors, and a potentiometer for frequency and pulse width adjustment. The frequency of the output signal is determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors connected to the timer. To achieve variable frequency, one of the resistors can be replaced with a potentiometer, allowing for manual adjustment.
For pulse width modulation, the duty cycle of the output signal can be manipulated by adjusting the resistance values in the timing circuit. By using a second potentiometer, the pulse width can be varied independently of the frequency, providing greater control over the output signal characteristics.
The output of the 555 timer can be connected to various loads, such as DC motors, lamps, or LEDs, allowing for applications like speed control or dimming. Additionally, the output can be interfaced with high-voltage circuits, such as ignition coils or transformer drivers, by incorporating suitable driver circuits that can handle the necessary voltage and current levels.
To ensure stability and reliability, decoupling capacitors should be placed close to the power supply pins of the 555 timer. A filtering capacitor may also be used at the output to smoothen the signal if required.
Overall, this signal generator circuit is a practical solution for producing adjustable square wave signals for a wide range of electronic applications, making it an invaluable tool for both hobbyists and professionals in the field of electronics.Make a signal generator from easily obtainable parts. Square wave, variable frequency, variable pulse width. This can be used for many things such as DC motor speed control, lamp or LED dimming, Transformer drivers. Ignition coil circuits and other high voltage PSU`s.. 🔗 External reference
To create a versatile signal generator capable of producing square wave signals with variable frequency and pulse width, a configuration based on a 555 timer IC can be employed. The 555 timer, in astable mode, is particularly suitable for generating continuous square wave signals.
The circuit typically consists of the following components: a 555 timer IC, resistors, capacitors, and a potentiometer for frequency and pulse width adjustment. The frequency of the output signal is determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors connected to the timer. To achieve variable frequency, one of the resistors can be replaced with a potentiometer, allowing for manual adjustment.
For pulse width modulation, the duty cycle of the output signal can be manipulated by adjusting the resistance values in the timing circuit. By using a second potentiometer, the pulse width can be varied independently of the frequency, providing greater control over the output signal characteristics.
The output of the 555 timer can be connected to various loads, such as DC motors, lamps, or LEDs, allowing for applications like speed control or dimming. Additionally, the output can be interfaced with high-voltage circuits, such as ignition coils or transformer drivers, by incorporating suitable driver circuits that can handle the necessary voltage and current levels.
To ensure stability and reliability, decoupling capacitors should be placed close to the power supply pins of the 555 timer. A filtering capacitor may also be used at the output to smoothen the signal if required.
Overall, this signal generator circuit is a practical solution for producing adjustable square wave signals for a wide range of electronic applications, making it an invaluable tool for both hobbyists and professionals in the field of electronics.Make a signal generator from easily obtainable parts. Square wave, variable frequency, variable pulse width. This can be used for many things such as DC motor speed control, lamp or LED dimming, Transformer drivers. Ignition coil circuits and other high voltage PSU`s.. 🔗 External reference