Double five-band equalizer circuit
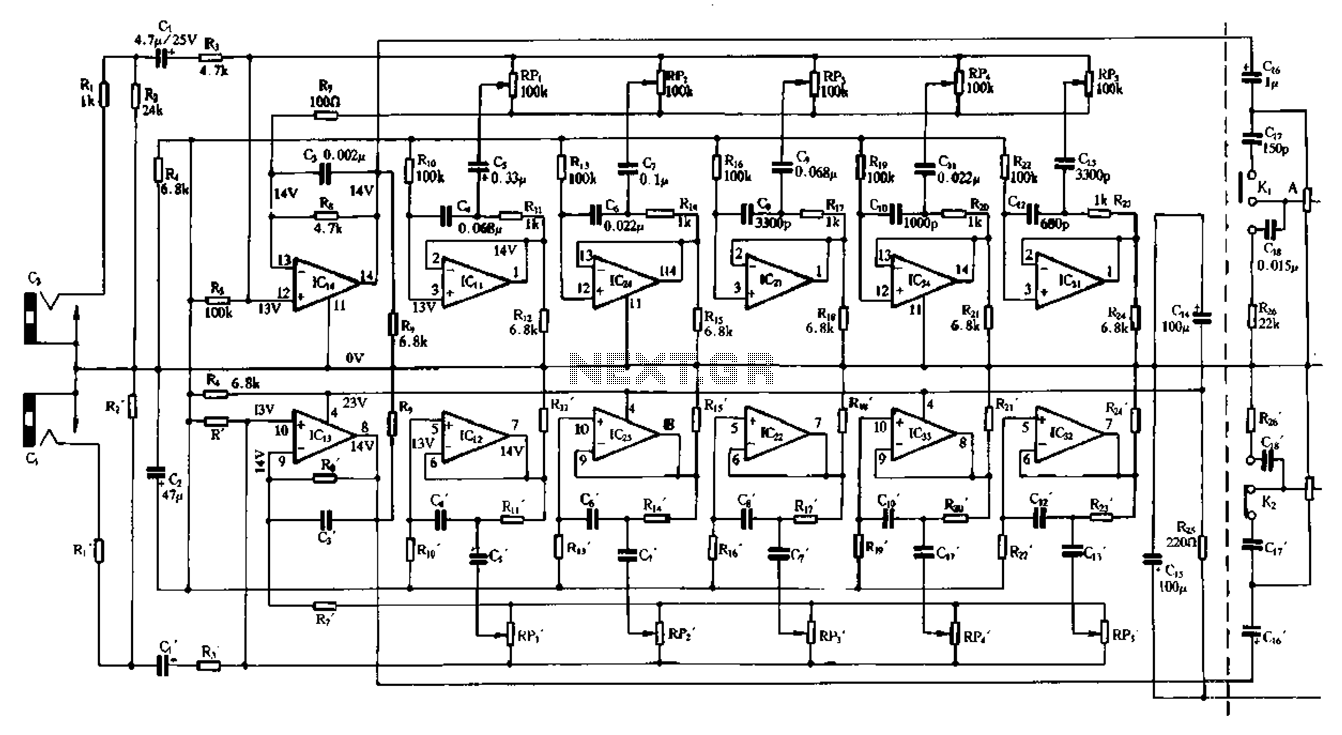
Figure 1-98 illustrates a double five-band equalizer circuit featuring a secondary connection. In this configuration, IC1 and IC14 serve as voltage amplifiers for each channel of the equalizer. The circuit also includes IC11, IC24, IC2, IC34, IC31, IC12, IC23, IC22, IC33, and IC32, which comprise a two-channel analog inductor network. Capacitors C7, C9, C11, and C13 correspond to the components shown in Figure 1-93(a) as C1, while capacitors C4, C6, C8, and C10 through C12 are related to the bar. Resistor R2 is fixed at 1 kΩ, and resistor R1 is fixed at 100 kΩ.
The double five-band equalizer circuit depicted in Figure 1-98 is designed to provide precise control over audio frequency response across two channels. The voltage amplifiers, represented by IC1 and IC14, amplify the input audio signals, allowing for enhanced signal processing capabilities. Each channel features a series of operational amplifiers (IC11, IC24, IC2, etc.) that work in tandem to adjust the gain and frequency response of the audio signals.
The analog inductor network formed by the various ICs (IC34, IC31, IC12, IC23, IC22, IC33, and IC32) plays a crucial role in shaping the equalization curve. By manipulating the inductance values, the circuit can effectively boost or cut specific frequency bands, allowing for tailored sound quality based on user preferences or specific audio environments.
Capacitors C7, C9, C11, and C13 are integral to the frequency response characteristics, as they interact with the resistors and inductors to create the desired filter characteristics. The design references Figure 1-93(a) for component values, ensuring compatibility and consistency in performance. The fixed resistor R2, set at 1 kΩ, stabilizes the circuit, while R1, set at 100 kΩ, aids in controlling the gain across the equalizer stages.
Overall, this double five-band equalizer circuit is an essential tool for audio processing, enabling users to achieve optimal sound quality through precise frequency adjustments.Figure 1-98 is a double five-band equalizer circuit composed of a second connection. FIG IC1 IC14 respectively equalizer per channel utility voltage amplifier; ICLl, IC24, IC 2 1, IC 34, IC31 and IC12.Ic23.IC22, IC33, Ic32 were two-channel analog inductor body; Island, C7, C9.Cll.C13 correspond to Figure 1-93 (a) of C1; C4, C6, C8.cIo -C12 correspond bar. R2 is fixed at 1kfl, Ri fixed 100koo
The double five-band equalizer circuit depicted in Figure 1-98 is designed to provide precise control over audio frequency response across two channels. The voltage amplifiers, represented by IC1 and IC14, amplify the input audio signals, allowing for enhanced signal processing capabilities. Each channel features a series of operational amplifiers (IC11, IC24, IC2, etc.) that work in tandem to adjust the gain and frequency response of the audio signals.
The analog inductor network formed by the various ICs (IC34, IC31, IC12, IC23, IC22, IC33, and IC32) plays a crucial role in shaping the equalization curve. By manipulating the inductance values, the circuit can effectively boost or cut specific frequency bands, allowing for tailored sound quality based on user preferences or specific audio environments.
Capacitors C7, C9, C11, and C13 are integral to the frequency response characteristics, as they interact with the resistors and inductors to create the desired filter characteristics. The design references Figure 1-93(a) for component values, ensuring compatibility and consistency in performance. The fixed resistor R2, set at 1 kΩ, stabilizes the circuit, while R1, set at 100 kΩ, aids in controlling the gain across the equalizer stages.
Overall, this double five-band equalizer circuit is an essential tool for audio processing, enabling users to achieve optimal sound quality through precise frequency adjustments.Figure 1-98 is a double five-band equalizer circuit composed of a second connection. FIG IC1 IC14 respectively equalizer per channel utility voltage amplifier; ICLl, IC24, IC 2 1, IC 34, IC31 and IC12.Ic23.IC22, IC33, Ic32 were two-channel analog inductor body; Island, C7, C9.Cll.C13 correspond to Figure 1-93 (a) of C1; C4, C6, C8.cIo -C12 correspond bar. R2 is fixed at 1kfl, Ri fixed 100koo