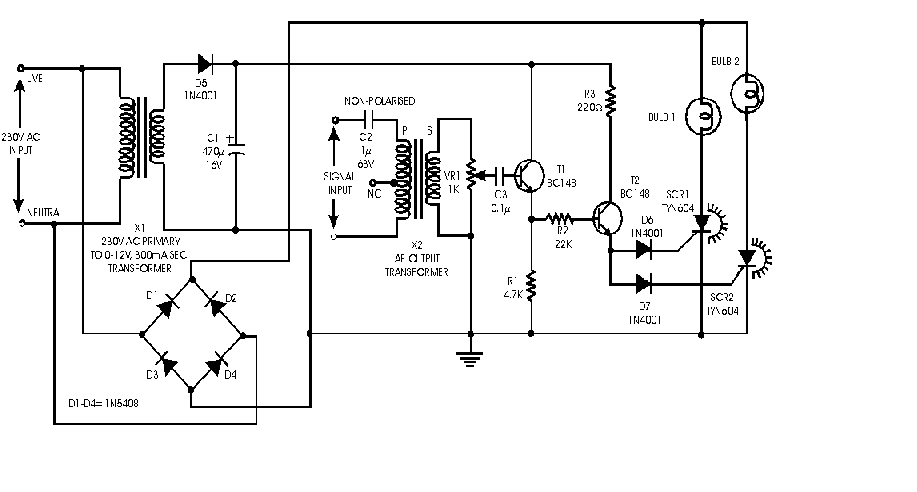
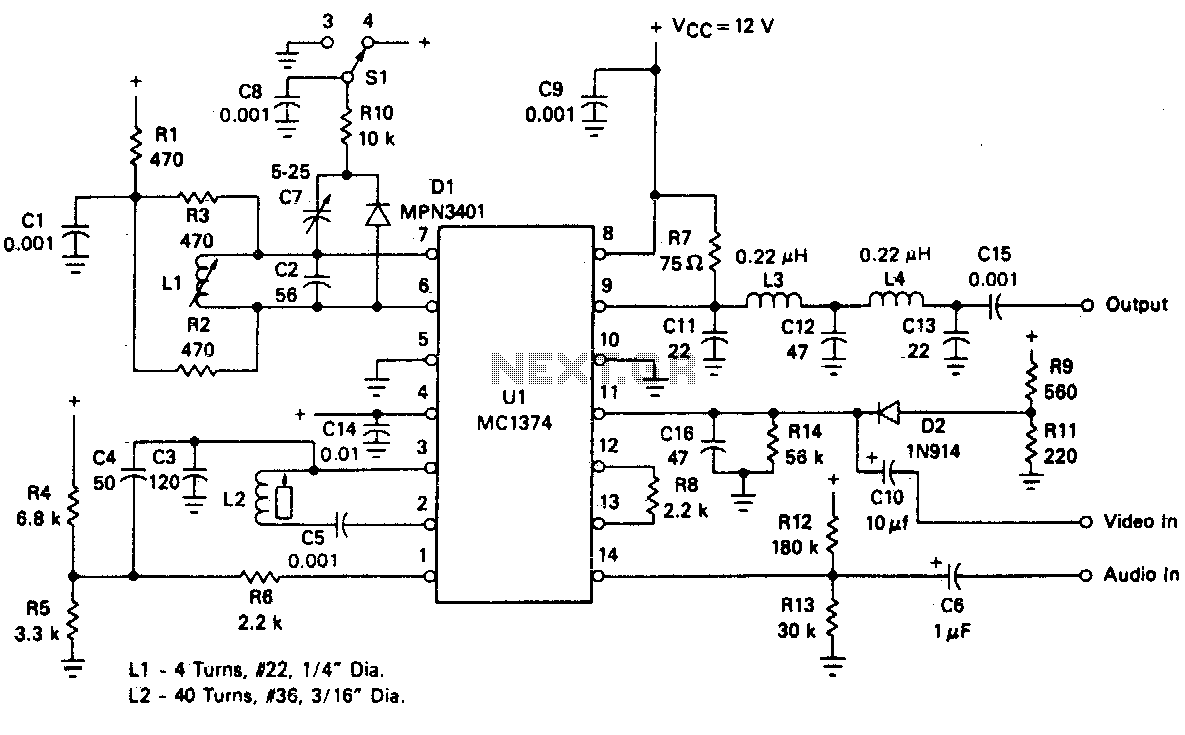
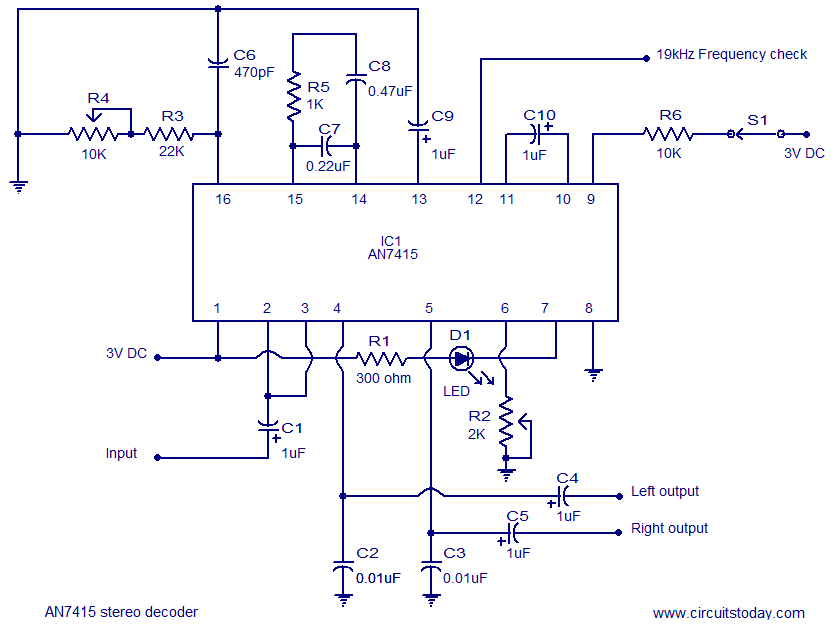
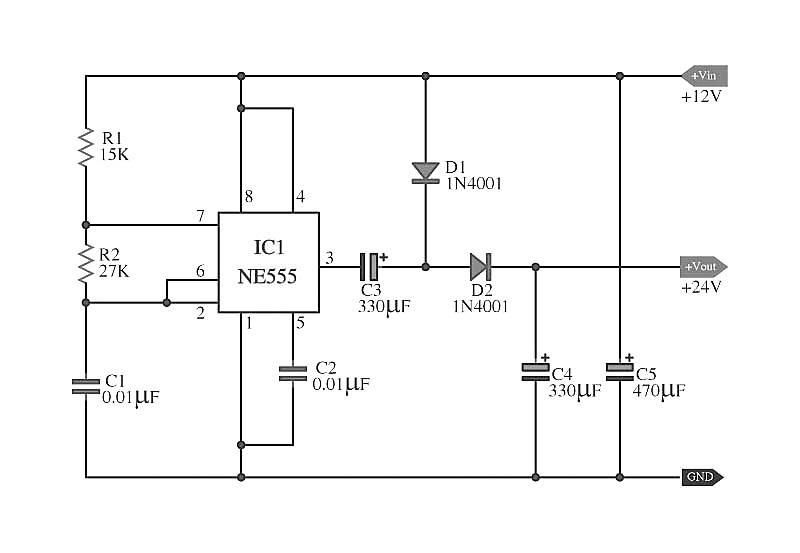
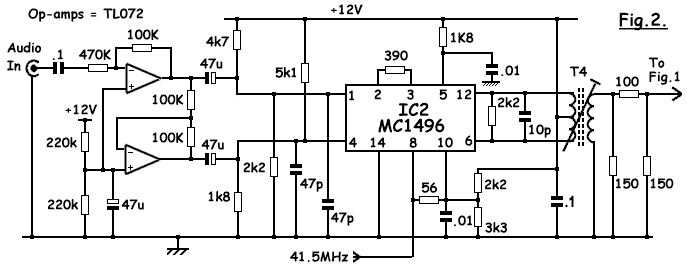
DOUBLE SIDEBAND SUPPRESSED CARRIER MODULATOR

The basic current allows no carrier to be present in the output. By adding offsets to the carrier differential pairs, controlled amounts of carrier appear at the output. The amplitude becomes a function of the modulation signal—AM modulation.
In a typical AM modulation circuit, the fundamental principle involves the modulation of a carrier signal's amplitude in accordance with the information signal, which is often audio. The circuit consists of a carrier generator, typically an oscillator, which produces a high-frequency sine wave. This carrier signal is then mixed with the baseband signal, which contains the information to be transmitted.
The configuration of differential pairs is crucial in this setup, as it allows for precise control over the carrier signal's presence in the output. By applying specific offsets to these pairs, the circuit can introduce controlled amounts of the carrier signal into the output. This modulation can be fine-tuned to achieve the desired amplitude levels of the carrier, effectively allowing for the transmission of the audio signal over a radio frequency.
The modulation index, which is the ratio of the amplitude of the modulating signal to the amplitude of the carrier signal, plays a vital role in determining the quality and fidelity of the transmitted signal. Properly managing this index ensures that the output retains the integrity of the original audio signal while allowing the carrier to be appropriately modulated.
In summary, the design of an AM modulation circuit requires careful consideration of the carrier signal's amplitude and its interaction with the information signal. By utilizing differential pairs and applying offsets, the circuit can achieve the necessary modulation characteristics for effective communication.The basic current allows no carrier to be present in the output. By adding offsets to the carrier differential pairs, controlled amounts of carrier appear at the output. The amplitude becomes a function of the modulation signal-AM modulation. 🔗 External reference
In a typical AM modulation circuit, the fundamental principle involves the modulation of a carrier signal's amplitude in accordance with the information signal, which is often audio. The circuit consists of a carrier generator, typically an oscillator, which produces a high-frequency sine wave. This carrier signal is then mixed with the baseband signal, which contains the information to be transmitted.
The configuration of differential pairs is crucial in this setup, as it allows for precise control over the carrier signal's presence in the output. By applying specific offsets to these pairs, the circuit can introduce controlled amounts of the carrier signal into the output. This modulation can be fine-tuned to achieve the desired amplitude levels of the carrier, effectively allowing for the transmission of the audio signal over a radio frequency.
The modulation index, which is the ratio of the amplitude of the modulating signal to the amplitude of the carrier signal, plays a vital role in determining the quality and fidelity of the transmitted signal. Properly managing this index ensures that the output retains the integrity of the original audio signal while allowing the carrier to be appropriately modulated.
In summary, the design of an AM modulation circuit requires careful consideration of the carrier signal's amplitude and its interaction with the information signal. By utilizing differential pairs and applying offsets, the circuit can achieve the necessary modulation characteristics for effective communication.The basic current allows no carrier to be present in the output. By adding offsets to the carrier differential pairs, controlled amounts of carrier appear at the output. The amplitude becomes a function of the modulation signal-AM modulation. 🔗 External reference