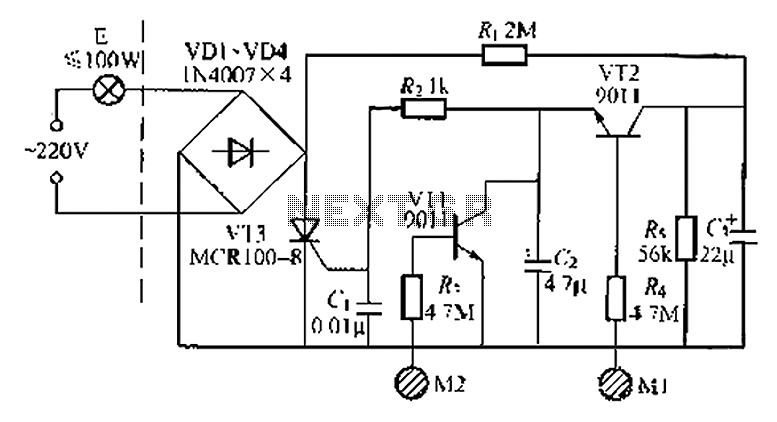
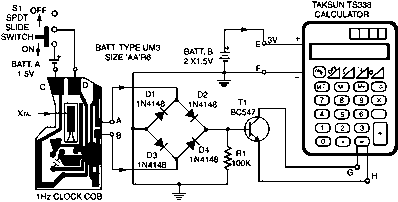
Doubling rectifier circuit in negative ion generator application circuit
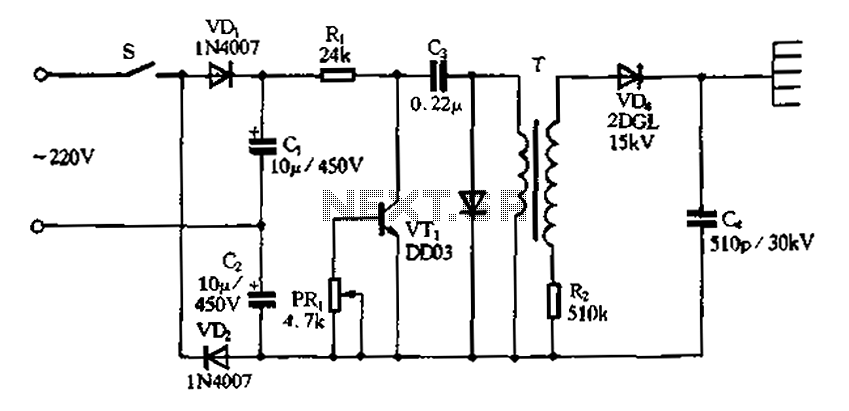
Doubling rectifier circuit in a negative ion generator application circuit.
The doubling rectifier circuit is an essential component in negative ion generator applications, where it plays a crucial role in converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) while also increasing the voltage level. This circuit typically utilizes a combination of diodes and capacitors to achieve its rectification and voltage doubling functions.
In a standard configuration, the circuit consists of two diodes arranged in a full-wave rectifier setup. The input AC voltage is applied to the anodes of the diodes, which allows current to flow through them during both halves of the AC cycle. The output from the cathodes of the diodes is then smoothed by a capacitor, which helps to reduce the ripple in the DC output.
To achieve voltage doubling, an additional capacitor is employed to store energy during the rectification process. When the AC voltage reaches its peak, the first diode conducts and charges the capacitor. During the next half cycle, the second diode becomes forward-biased, allowing the capacitor to discharge and effectively doubling the output voltage.
This configuration is particularly advantageous in negative ion generator circuits, as it provides the high voltage necessary for ionization processes while maintaining a compact design. The use of high-voltage rated diodes and capacitors is critical to ensure reliability and efficiency in the circuit operation.
Overall, the doubling rectifier circuit is integral to the performance of negative ion generators, enabling them to produce the desired ion concentration levels for various applications, including air purification and environmental enhancement. Proper selection of components and careful circuit design are essential to optimize the performance and longevity of the system.Doubling rectifier circuit in negative ion generator application circuit
The doubling rectifier circuit is an essential component in negative ion generator applications, where it plays a crucial role in converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) while also increasing the voltage level. This circuit typically utilizes a combination of diodes and capacitors to achieve its rectification and voltage doubling functions.
In a standard configuration, the circuit consists of two diodes arranged in a full-wave rectifier setup. The input AC voltage is applied to the anodes of the diodes, which allows current to flow through them during both halves of the AC cycle. The output from the cathodes of the diodes is then smoothed by a capacitor, which helps to reduce the ripple in the DC output.
To achieve voltage doubling, an additional capacitor is employed to store energy during the rectification process. When the AC voltage reaches its peak, the first diode conducts and charges the capacitor. During the next half cycle, the second diode becomes forward-biased, allowing the capacitor to discharge and effectively doubling the output voltage.
This configuration is particularly advantageous in negative ion generator circuits, as it provides the high voltage necessary for ionization processes while maintaining a compact design. The use of high-voltage rated diodes and capacitors is critical to ensure reliability and efficiency in the circuit operation.
Overall, the doubling rectifier circuit is integral to the performance of negative ion generators, enabling them to produce the desired ion concentration levels for various applications, including air purification and environmental enhancement. Proper selection of components and careful circuit design are essential to optimize the performance and longevity of the system.Doubling rectifier circuit in negative ion generator application circuit