Drive A Relay Using A 1-Wire Addressable Switch

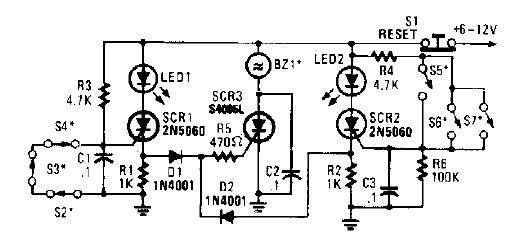
The 1-Wire Net, or MicroLAN (by Maxim-Dallas), is a straightforward method for connecting slow devices such as sensors, relay drivers, and switches using basic components. These components include a 1-Wire protocol handler, an interface to the external world, and often a parasitic power supply. A long string of 1-Wire components can be created by distributing them along a high-quality twisted-pair copper wire. A controller at one end of the string can supply power to the entire configuration. A common application for this setup is controlling relays to activate electrical loads. The DS2405, a 1-Wire flip-flop with an open drain output, is a suitable choice for this purpose. However, the parasitic power harvested from the 1-Wire cable may not suffice for power-hungry loads like relay solenoids or photocoupler LEDs. It is important to avoid connecting the 1-Wire reference to the relay driver reference, as the 1-Wire can be sensitive. A dc-dc converter could provide galvanic isolation for the relay driver, but these converters tend to be costly. The circuit illustrated in Figure 1 employs a single transistor and a transformer to achieve the necessary galvanic insulation for operating a relay without interfering with the 1-Wire Net. Q1 and T1 form a Hartley oscillator, with the load on the transformer influencing the oscillator's operation. The oscillator ceases when the DS2405 is closed due to excessive load on T1’s secondary coil. The oscillations, detected by diodes D4, D5, and D6, increase the voltage at Q1’s base, thereby engaging the relay. Consequently, when the DS2405’s output is open, the relay is engaged, and when its output is closed, the relay is released. With the specified component values, the oscillation frequency is approximately 300 kHz. Figure 2 presents the Spice-simulated timing diagram of the voltages across the relay coil and the I/O pin of the DS2405, showing a negligible delay between input and output.
The 1-Wire Net system is designed for effective communication and control of low-speed devices in various applications. The architecture allows for the integration of multiple devices while minimizing the complexity of wiring and connections. The use of twisted-pair copper wire enhances the reliability of the signal transmission, reducing noise and interference.
In the described circuit, the DS2405 operates as a digital switch, controlling the state of the relay through its open-drain output. The Hartley oscillator, composed of the transistor (Q1) and the transformer (T1), generates oscillations that are essential for the relay's operation. The transformer provides isolation between the 1-Wire Net and the relay circuit, ensuring that any disturbances in the relay operation do not affect the 1-Wire communication.
The diodes (D4, D5, and D6) play a crucial role in detecting the presence of oscillations. When the relay is activated, the oscillation frequency stabilizes, allowing for reliable operation. The feedback mechanism ensures that the relay remains engaged as long as the DS2405 output is open, providing a straightforward and efficient control method.
The choice of a 300 kHz oscillation frequency is significant, as it balances the need for rapid switching with the limitations of the components used. The timing diagram generated through Spice simulation offers insights into the performance of the circuit, confirming that the input from the DS2405 and the output to the relay coil are well synchronized.
This configuration is particularly useful in applications where remote control of electrical loads is required, such as in home automation systems, industrial control systems, and sensor networks. The 1-Wire protocol's simplicity and the circuit's effective isolation mechanism make it a practical solution for diverse electronic control tasks.The 1-Wire Net, or MicroLAN (by Maxim-Dallas), is a simple way to connect slow devices (such as sensors, relay drivers, switches, and so on) using simple components. These components contain the 1-Wire protocol handler, some type of interface to the external world, and often a parasitic power supply.
You may build a very long string of 1-Wire comp onents by just distributing them in a string over a good quality twisted-pair copper wire. The controller connected to one string end can supply the power for the entire string. A common use of such a string is to control relays to activate some electrical loads. For this purpose, the DS2405 (1-Wire flip-flop with open drain output) is a good choice. Of course, the parasitic power you can steal from the 1-Wire cable isn`t enough to operate some power-hungry load, like a relay solenoid (or a photocoupler LED). Obviously, you don`t want to connect the 1-Wire reference to the relay driver reference because 1-Wire can be very touchy.
You could use a dc-dc converter to galvanically insulate the relay driver, but these converters are expensive. The circuit shown in Figure 1 uses a single transistor and a transformer to supply the required galvanic insulation to operate a relay without disturbing the 1-Wire Net.
Q1 and T1 form a Hartley oscillator. And, the load on the transformer affects the oscillator operation. It stops oscillating when the DS2405 is closed due to the excessive load on T1`s secondary coil. The presence of oscillations, detected by D4, D5, and D6, increases the voltage on Q1`s base, engaging the relay. Therefore, when the DS2405`s output is open, the relay is engaged. Conversely, when its output is closed, the relay is re-leased. With the indicated values, the oscillation frequency is about 300 kHz. Figure 2 shows the (Spice simulated) timing diagram of the voltages on the relay coil and on the I/O pin of the DS2405.
There`s a negligible delay between input and output. 🔗 External reference
The 1-Wire Net system is designed for effective communication and control of low-speed devices in various applications. The architecture allows for the integration of multiple devices while minimizing the complexity of wiring and connections. The use of twisted-pair copper wire enhances the reliability of the signal transmission, reducing noise and interference.
In the described circuit, the DS2405 operates as a digital switch, controlling the state of the relay through its open-drain output. The Hartley oscillator, composed of the transistor (Q1) and the transformer (T1), generates oscillations that are essential for the relay's operation. The transformer provides isolation between the 1-Wire Net and the relay circuit, ensuring that any disturbances in the relay operation do not affect the 1-Wire communication.
The diodes (D4, D5, and D6) play a crucial role in detecting the presence of oscillations. When the relay is activated, the oscillation frequency stabilizes, allowing for reliable operation. The feedback mechanism ensures that the relay remains engaged as long as the DS2405 output is open, providing a straightforward and efficient control method.
The choice of a 300 kHz oscillation frequency is significant, as it balances the need for rapid switching with the limitations of the components used. The timing diagram generated through Spice simulation offers insights into the performance of the circuit, confirming that the input from the DS2405 and the output to the relay coil are well synchronized.
This configuration is particularly useful in applications where remote control of electrical loads is required, such as in home automation systems, industrial control systems, and sensor networks. The 1-Wire protocol's simplicity and the circuit's effective isolation mechanism make it a practical solution for diverse electronic control tasks.The 1-Wire Net, or MicroLAN (by Maxim-Dallas), is a simple way to connect slow devices (such as sensors, relay drivers, switches, and so on) using simple components. These components contain the 1-Wire protocol handler, some type of interface to the external world, and often a parasitic power supply.
You may build a very long string of 1-Wire comp onents by just distributing them in a string over a good quality twisted-pair copper wire. The controller connected to one string end can supply the power for the entire string. A common use of such a string is to control relays to activate some electrical loads. For this purpose, the DS2405 (1-Wire flip-flop with open drain output) is a good choice. Of course, the parasitic power you can steal from the 1-Wire cable isn`t enough to operate some power-hungry load, like a relay solenoid (or a photocoupler LED). Obviously, you don`t want to connect the 1-Wire reference to the relay driver reference because 1-Wire can be very touchy.
You could use a dc-dc converter to galvanically insulate the relay driver, but these converters are expensive. The circuit shown in Figure 1 uses a single transistor and a transformer to supply the required galvanic insulation to operate a relay without disturbing the 1-Wire Net.
Q1 and T1 form a Hartley oscillator. And, the load on the transformer affects the oscillator operation. It stops oscillating when the DS2405 is closed due to the excessive load on T1`s secondary coil. The presence of oscillations, detected by D4, D5, and D6, increases the voltage on Q1`s base, engaging the relay. Therefore, when the DS2405`s output is open, the relay is engaged. Conversely, when its output is closed, the relay is re-leased. With the indicated values, the oscillation frequency is about 300 kHz. Figure 2 shows the (Spice simulated) timing diagram of the voltages on the relay coil and on the I/O pin of the DS2405.
There`s a negligible delay between input and output. 🔗 External reference