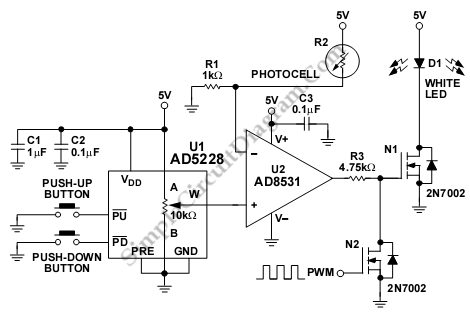
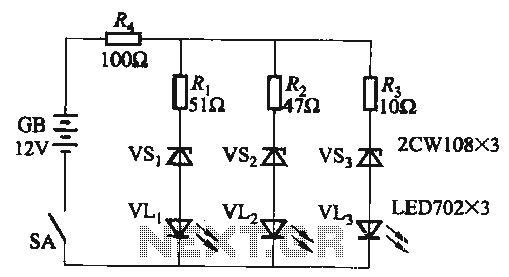
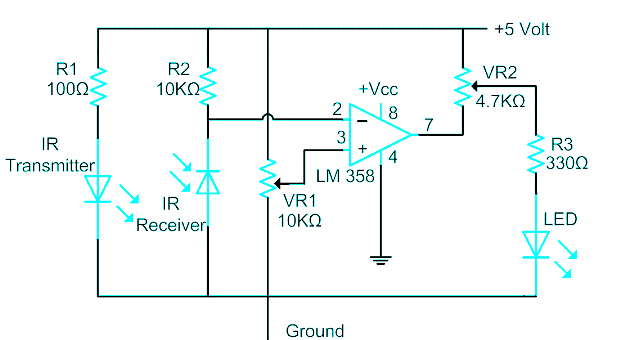
DTMF infrared remote control circuit
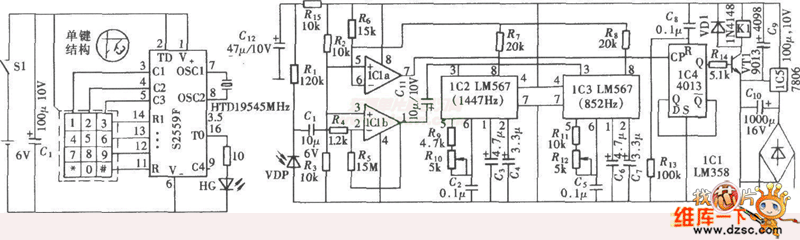
The DTMF infrared remote control circuit utilizes a DTMF encoded signal that can be decoded by a specialized decoder and the PLL audio decoder LM567. However, a DTMF encoded signal decoded by a single decoder yields only one frequency. A complete control signal is formed by combining the outputs from two decoder frequencies. The infrared remote control signal generated by this system...
The DTMF (Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency) infrared remote control circuit is designed to facilitate wireless control through the transmission of DTMF signals, which are commonly used in telephone dialing. The circuit incorporates a DTMF decoder that interprets the dual-tone signals emitted by a keypad or other input device. The LM567 phase-locked loop (PLL) audio decoder is a critical component that enhances the circuit's ability to accurately decode audio frequencies, enabling reliable signal processing.
In operation, the circuit generates a DTMF encoded signal, which consists of two simultaneous audio frequencies that correspond to the keypad buttons pressed. Each button on the keypad produces a unique combination of these frequencies, allowing for a wide range of control commands. When the signal reaches the DTMF decoder, it analyzes the frequency components and outputs a corresponding digital signal that represents the specific command.
However, it is essential to note that a single decoder can only process one frequency at a time. To create a complete control signal, the circuit must utilize two decoders working in tandem. By combining the outputs from both decoders, the system can generate a more complex control command that encompasses multiple actions or functions.
The infrared remote control signal produced by this circuit is transmitted via an infrared LED, which emits the encoded signal as light pulses. A compatible infrared receiver detects these light pulses and converts them back into electrical signals, which can then be processed by a microcontroller or another control system. This design allows for versatile applications, including remote operation of electronic devices, automation systems, and more.
Overall, the DTMF infrared remote control circuit represents an effective solution for wireless control applications, leveraging the reliability of DTMF signaling and the efficiency of infrared communication technology.The DTMF infrared remote control circuit. The DTMF encoded signal can be decoded by the special decoder and the PLL audio decoder LM567. But the DTMF encoded signal which is decoded by only one decoder, has only one frequency, one group of control signal is composed by two decoder`s output frequency. The infrared remote control signal which is produced by th.. 🔗 External reference
The DTMF (Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency) infrared remote control circuit is designed to facilitate wireless control through the transmission of DTMF signals, which are commonly used in telephone dialing. The circuit incorporates a DTMF decoder that interprets the dual-tone signals emitted by a keypad or other input device. The LM567 phase-locked loop (PLL) audio decoder is a critical component that enhances the circuit's ability to accurately decode audio frequencies, enabling reliable signal processing.
In operation, the circuit generates a DTMF encoded signal, which consists of two simultaneous audio frequencies that correspond to the keypad buttons pressed. Each button on the keypad produces a unique combination of these frequencies, allowing for a wide range of control commands. When the signal reaches the DTMF decoder, it analyzes the frequency components and outputs a corresponding digital signal that represents the specific command.
However, it is essential to note that a single decoder can only process one frequency at a time. To create a complete control signal, the circuit must utilize two decoders working in tandem. By combining the outputs from both decoders, the system can generate a more complex control command that encompasses multiple actions or functions.
The infrared remote control signal produced by this circuit is transmitted via an infrared LED, which emits the encoded signal as light pulses. A compatible infrared receiver detects these light pulses and converts them back into electrical signals, which can then be processed by a microcontroller or another control system. This design allows for versatile applications, including remote operation of electronic devices, automation systems, and more.
Overall, the DTMF infrared remote control circuit represents an effective solution for wireless control applications, leveraging the reliability of DTMF signaling and the efficiency of infrared communication technology.The DTMF infrared remote control circuit. The DTMF encoded signal can be decoded by the special decoder and the PLL audio decoder LM567. But the DTMF encoded signal which is decoded by only one decoder, has only one frequency, one group of control signal is composed by two decoder`s output frequency. The infrared remote control signal which is produced by th.. 🔗 External reference