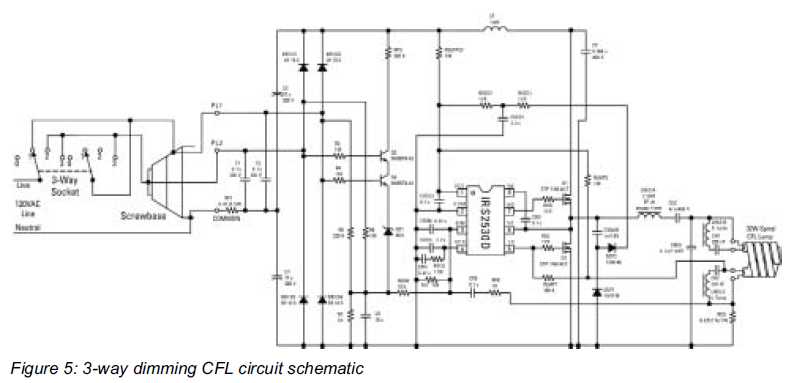
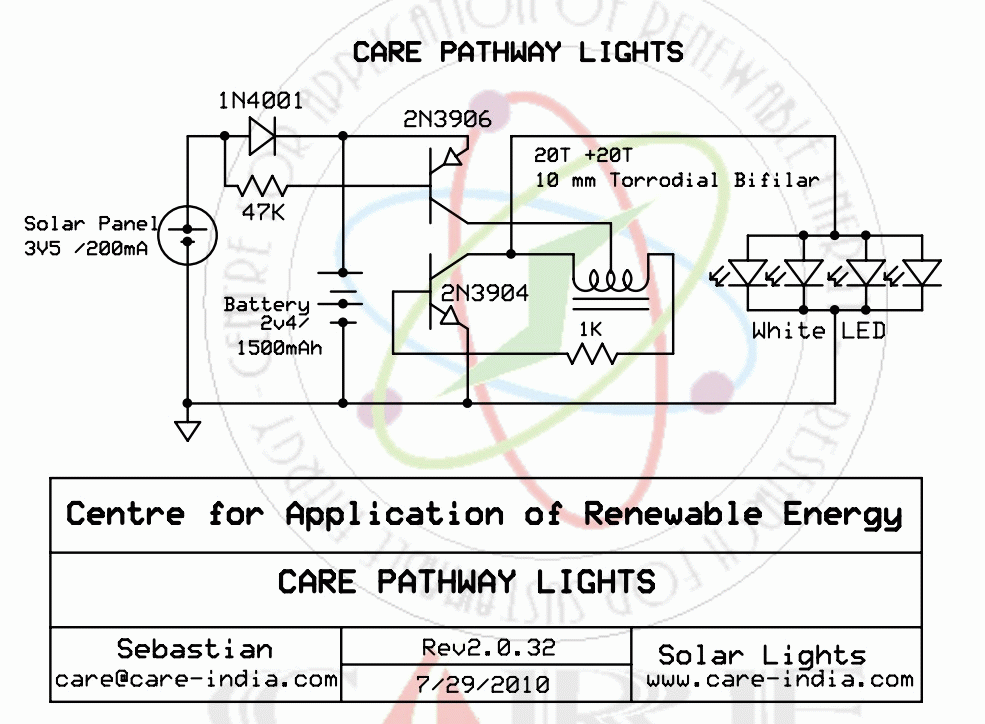
eec247 Information on compact fluorescent lighting
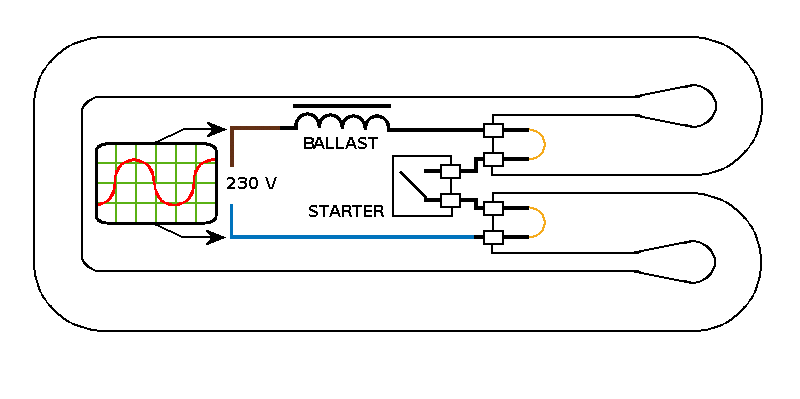
The magnetic field generated in the ballast collapses rapidly, resulting in a high voltage across the tube, which causes the internal gas to conduct. This process can be likened to gradually inflating a balloon and then puncturing it with a pin.
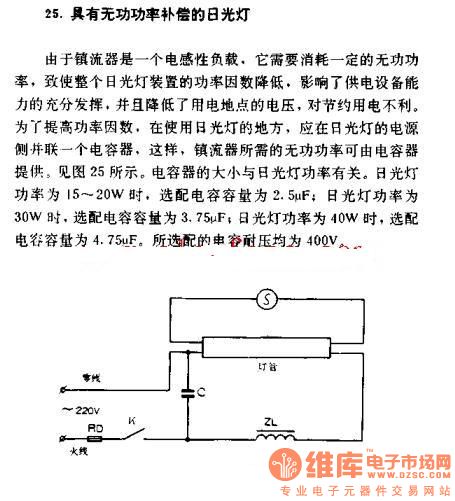
In this circuit, the ballast serves as a critical component that stabilizes the current flowing through a gas discharge tube, such as a fluorescent lamp. When the lamp is initially powered, the ballast generates a magnetic field as current flows through its coils. This field is essential for maintaining the proper operating conditions for the gas within the tube.
As the gas in the tube begins to ionize, it creates a conductive path for the current. When the power supply is interrupted or switched off, the magnetic field in the ballast collapses rapidly. The collapse induces a high voltage across the terminals of the tube due to the principles of electromagnetic induction. This high voltage is sufficient to ionize the gas further, allowing it to conduct electricity momentarily.
The analogy of inflating a balloon and then piercing it illustrates the sudden release of energy when the circuit is disrupted. Just as the balloon bursts and releases air rapidly, the collapse of the magnetic field results in a high-voltage spike that can lead to a brief but intense conduction through the gas, allowing the lamp to illuminate momentarily even after the power has been cut.
This phenomenon is crucial in applications where a quick burst of light is required, such as in flashes for photography or in certain types of lighting systems. The design of the ballast and the gas discharge tube must be carefully calibrated to ensure that the voltage levels and timing are appropriate for the desired application, optimizing performance and longevity while minimizing the risk of damage due to excessive voltage spikes.The magnetic field built up in the ballast collapses quickly, producing a high voltage across the tube and causing the internal gas to conduct. It`s a bit like slowly blowing up a balloon and sticking a pin in it. 🔗 External reference
In this circuit, the ballast serves as a critical component that stabilizes the current flowing through a gas discharge tube, such as a fluorescent lamp. When the lamp is initially powered, the ballast generates a magnetic field as current flows through its coils. This field is essential for maintaining the proper operating conditions for the gas within the tube.
As the gas in the tube begins to ionize, it creates a conductive path for the current. When the power supply is interrupted or switched off, the magnetic field in the ballast collapses rapidly. The collapse induces a high voltage across the terminals of the tube due to the principles of electromagnetic induction. This high voltage is sufficient to ionize the gas further, allowing it to conduct electricity momentarily.
The analogy of inflating a balloon and then piercing it illustrates the sudden release of energy when the circuit is disrupted. Just as the balloon bursts and releases air rapidly, the collapse of the magnetic field results in a high-voltage spike that can lead to a brief but intense conduction through the gas, allowing the lamp to illuminate momentarily even after the power has been cut.
This phenomenon is crucial in applications where a quick burst of light is required, such as in flashes for photography or in certain types of lighting systems. The design of the ballast and the gas discharge tube must be carefully calibrated to ensure that the voltage levels and timing are appropriate for the desired application, optimizing performance and longevity while minimizing the risk of damage due to excessive voltage spikes.The magnetic field built up in the ballast collapses quickly, producing a high voltage across the tube and causing the internal gas to conduct. It`s a bit like slowly blowing up a balloon and sticking a pin in it. 🔗 External reference