Electronic fishing shrimp machine circuit diagram 2
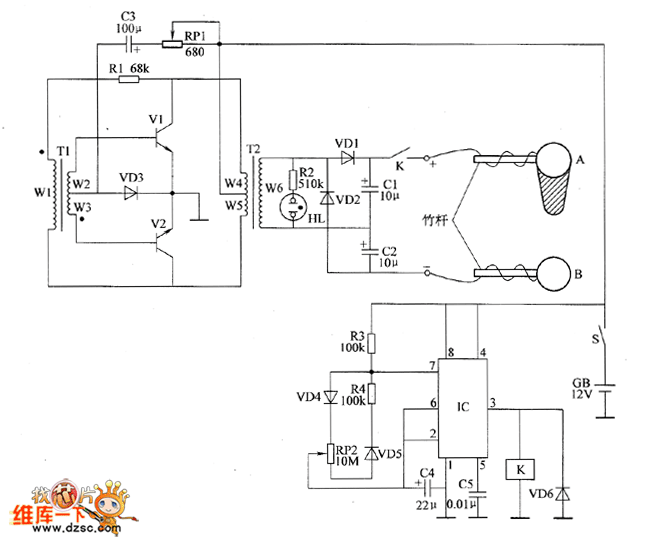
The electronic fishing shrimp machine circuit consists of an astable oscillator, an inverter circuit, and a high-voltage output circuit, as depicted in Figure 20. The astable oscillator circuit includes a time-base integrated circuit (IC), resistors R3 and R4, a potentiometer (RP2), diodes VD4 and VD5, and capacitors C4 and C5. The inverter circuit is made up of transistors V1 and V2, transformers T1 and T2, resistor R1, potentiometer RP1, diode VD3, and capacitor C3. The high-voltage output circuit comprises transformer T2, relay K, diodes VD1, VD2, and VD6, resistor R2, capacitors C1 and C2, a neon light (HL), and electrodes A and B. The resistance of RP1 can be adjusted to change the oscillation frequency of the inverter circuit.
The electronic fishing shrimp machine operates through a carefully designed circuit that integrates multiple components to achieve its functionality. The astable oscillator serves as the timing mechanism, generating a continuous square wave output. This is accomplished by configuring the time-base integrated circuit along with the associated resistors and capacitors, which determine the frequency of oscillation. The inclusion of diodes in this section ensures that the circuit operates efficiently by managing the direction of the current flow.
The inverter circuit plays a crucial role in converting the low voltage signals from the oscillator into high voltage signals suitable for driving the high-voltage output circuit. Transistors V1 and V2 act as switches, modulating the current through transformers T1 and T2, which step up the voltage levels. The use of a potentiometer (RP1) in this section allows for fine-tuning of the inverter's output frequency, enabling the user to adjust the performance of the machine based on specific fishing conditions.
The high-voltage output circuit is responsible for generating the electrical signals that attract shrimp. Transformer T2 increases the voltage to a level that can energize the relay (K), which in turn controls the flow of current to the output components. Diodes VD1, VD2, and VD6 protect the circuit from back EMF generated by the inductive loads, ensuring longevity and reliability. The capacitors (C1 and C2) filter the output signal, smoothing out any fluctuations and providing a stable output. The neon light (HL) serves as an indicator, illuminating when the circuit is active, while electrodes A and B are positioned to create the electric field necessary for attracting shrimp.
In summary, the electronic fishing shrimp machine circuit is a complex assembly of components working in unison to create an effective device for attracting marine life. Each section of the circuit is designed to perform specific functions that contribute to the overall operation of the machine, allowing for adjustments to be made to optimize performance in various aquatic environments.The ectronic fishing shrimp machine circuit is composed of the astable oscillator, inverter circuit, high voltage output circuit, and the circuit is shown as the figure 20. Astable oscillator circuit is composed of the time-base integrated circuit IC, resistors R3, R4, potentiometer RP2, diodes VD4, VD5 and capacitors C4, C5.
Inverter circuit is c omposed of the transistors V1, V2, transformers T1, T2, resistor R1, potentiometer RP1, diode VD3 and capacitor C3. High-voltage output circuit consists of the transformer T2, relay K, diodes VD1, VD2, VD6, resistor R2, capacitors C1, C2, neon light HL and the electrodes A, B.
Adjusting the resistance of RP1 can change the oscillation frequency of the inverter circuit. 🔗 External reference
The electronic fishing shrimp machine operates through a carefully designed circuit that integrates multiple components to achieve its functionality. The astable oscillator serves as the timing mechanism, generating a continuous square wave output. This is accomplished by configuring the time-base integrated circuit along with the associated resistors and capacitors, which determine the frequency of oscillation. The inclusion of diodes in this section ensures that the circuit operates efficiently by managing the direction of the current flow.
The inverter circuit plays a crucial role in converting the low voltage signals from the oscillator into high voltage signals suitable for driving the high-voltage output circuit. Transistors V1 and V2 act as switches, modulating the current through transformers T1 and T2, which step up the voltage levels. The use of a potentiometer (RP1) in this section allows for fine-tuning of the inverter's output frequency, enabling the user to adjust the performance of the machine based on specific fishing conditions.
The high-voltage output circuit is responsible for generating the electrical signals that attract shrimp. Transformer T2 increases the voltage to a level that can energize the relay (K), which in turn controls the flow of current to the output components. Diodes VD1, VD2, and VD6 protect the circuit from back EMF generated by the inductive loads, ensuring longevity and reliability. The capacitors (C1 and C2) filter the output signal, smoothing out any fluctuations and providing a stable output. The neon light (HL) serves as an indicator, illuminating when the circuit is active, while electrodes A and B are positioned to create the electric field necessary for attracting shrimp.
In summary, the electronic fishing shrimp machine circuit is a complex assembly of components working in unison to create an effective device for attracting marine life. Each section of the circuit is designed to perform specific functions that contribute to the overall operation of the machine, allowing for adjustments to be made to optimize performance in various aquatic environments.The ectronic fishing shrimp machine circuit is composed of the astable oscillator, inverter circuit, high voltage output circuit, and the circuit is shown as the figure 20. Astable oscillator circuit is composed of the time-base integrated circuit IC, resistors R3, R4, potentiometer RP2, diodes VD4, VD5 and capacitors C4, C5.
Inverter circuit is c omposed of the transistors V1, V2, transformers T1, T2, resistor R1, potentiometer RP1, diode VD3 and capacitor C3. High-voltage output circuit consists of the transformer T2, relay K, diodes VD1, VD2, VD6, resistor R2, capacitors C1, C2, neon light HL and the electrodes A, B.
Adjusting the resistance of RP1 can change the oscillation frequency of the inverter circuit. 🔗 External reference