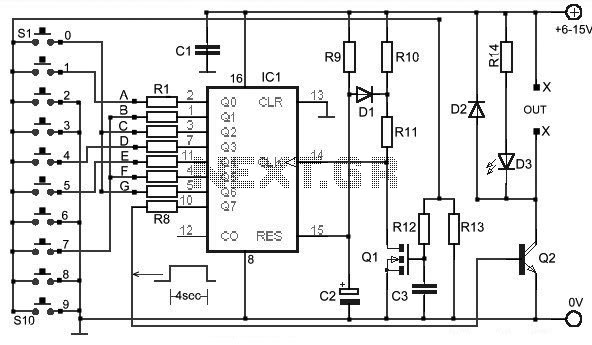
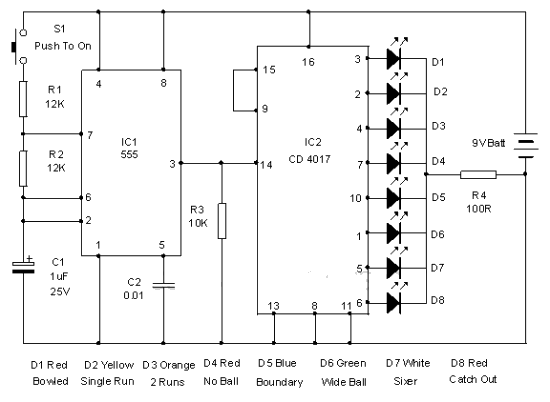
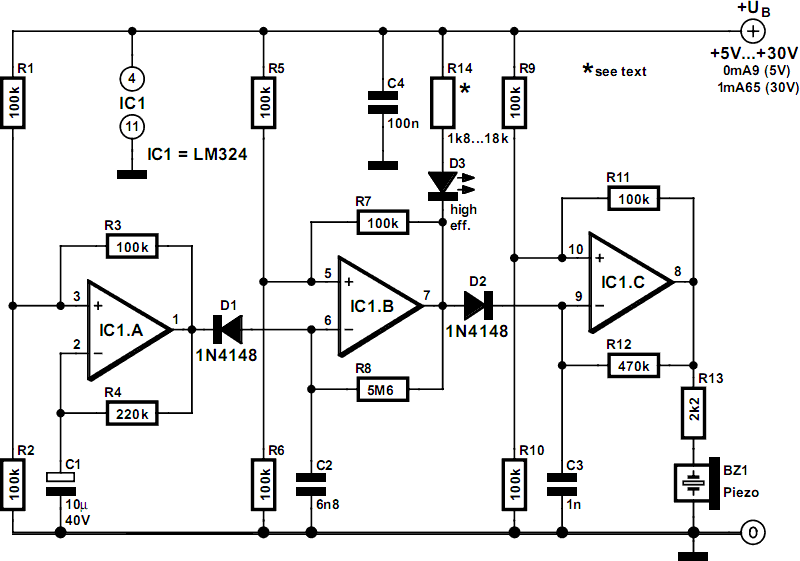
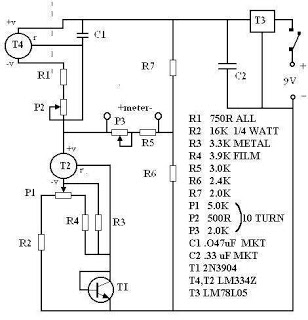
Electronic keyer
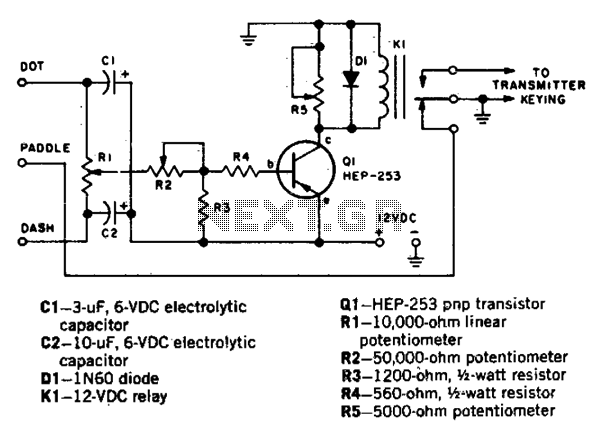
This circuit automatically generates Morse code dots and dashes determined by time constants involving C1 and C2. R1 establishes the dot/dash ratio, while R2 controls the speed. Additionally, R5 determines the relay drop-out point.
The circuit functions by utilizing capacitors C1 and C2 to create specific time delays that correspond to the duration of Morse code signals. The values of these capacitors, in conjunction with the resistors R1 and R2, allow for precise control over the timing characteristics of the generated signals. R1's role in setting the dot/dash ratio is crucial, as it defines the relative lengths of dots and dashes in Morse code, which are typically represented by short and long pulses, respectively.
R2's function as a speed regulator is equally important, as it adjusts the overall rate at which the Morse code is transmitted. By varying the resistance of R2, the operator can increase or decrease the transmission speed, accommodating different communication needs or preferences.
The inclusion of R5 as a relay drop-out point adds another layer of functionality to the circuit. This resistor sets a threshold at which the relay will disengage, effectively controlling how long the Morse code signals are maintained before the system resets or pauses. This feature is essential for ensuring that the circuit can operate in a loop, continuously generating Morse code signals without manual intervention.
Overall, the design of this circuit allows for a versatile and adjustable Morse code generator, making it suitable for various applications in communication systems where Morse code is utilized. The careful selection of component values will directly influence the performance and reliability of the generated Morse code signals.This circuit automatically produces Morse code dots and dashes set by time constants involving Cl and C2. Rl sets dot/dash ratio and R2 sets the speed R5 sets the relay drop-out point.
The circuit functions by utilizing capacitors C1 and C2 to create specific time delays that correspond to the duration of Morse code signals. The values of these capacitors, in conjunction with the resistors R1 and R2, allow for precise control over the timing characteristics of the generated signals. R1's role in setting the dot/dash ratio is crucial, as it defines the relative lengths of dots and dashes in Morse code, which are typically represented by short and long pulses, respectively.
R2's function as a speed regulator is equally important, as it adjusts the overall rate at which the Morse code is transmitted. By varying the resistance of R2, the operator can increase or decrease the transmission speed, accommodating different communication needs or preferences.
The inclusion of R5 as a relay drop-out point adds another layer of functionality to the circuit. This resistor sets a threshold at which the relay will disengage, effectively controlling how long the Morse code signals are maintained before the system resets or pauses. This feature is essential for ensuring that the circuit can operate in a loop, continuously generating Morse code signals without manual intervention.
Overall, the design of this circuit allows for a versatile and adjustable Morse code generator, making it suitable for various applications in communication systems where Morse code is utilized. The careful selection of component values will directly influence the performance and reliability of the generated Morse code signals.This circuit automatically produces Morse code dots and dashes set by time constants involving Cl and C2. Rl sets dot/dash ratio and R2 sets the speed R5 sets the relay drop-out point.