FET Audio Mixer and Switch
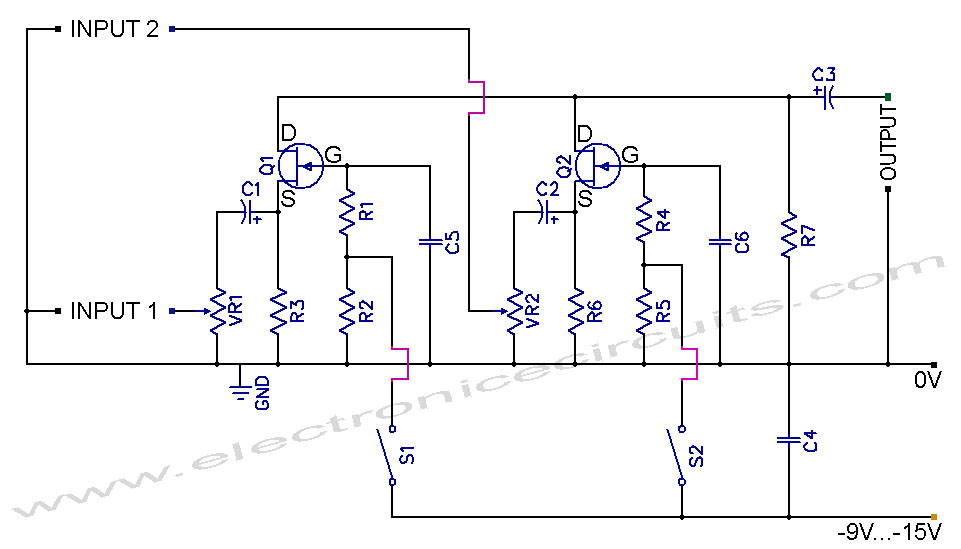
Instructions for building a FET audio mixer and switch circuit. The parts list includes: R1 - 1MΩ, R2 - 47kΩ, R3 - 47kΩ, R4 - 1MΩ, R5 - 47kΩ, R6 - 47kΩ, R7 - 47kΩ, VR1 - 50kΩ, VR2 - 50kΩ, C1, C2, C3 - 4.7µF 16V, C4 - 100nF (104), C5 - 47nF (473), C6 - 47nF (473), Q1 - BF245 or 2N3819, Q2 - BF245 or 2N3819, S1, S2 - switches. Junction FETs such as the BF245 or 2N3819 are commonly used in high-frequency circuits but can also be applied to low-frequency circuits.
The FET audio mixer and switch circuit utilizes field-effect transistors (FETs) to achieve efficient audio signal mixing and switching. The circuit design incorporates various resistors (R1 to R7) and variable resistors (VR1 and VR2) to control gain and balance across audio channels. Capacitors (C1 to C6) are strategically placed to filter and couple audio signals, ensuring that the frequency response is optimized for both low-frequency (LF) and high-frequency (HF) applications.
The use of junction FETs, specifically the BF245 or 2N3819, is critical in this circuit due to their low noise characteristics and high input impedance, making them suitable for audio applications. The switches (S1 and S2) allow for manual selection between different audio sources or channels, enhancing flexibility in audio routing.
The circuit operates by allowing audio signals to pass through the FETs, which act as variable resistors controlled by the gate voltage. This configuration provides low distortion and high fidelity, essential for audio mixing applications. The values of the resistors and capacitors can be adjusted to tailor the circuit's performance to specific audio requirements, such as adjusting the mixing levels or the frequency response.
Overall, the FET audio mixer and switch circuit is a versatile design that can be adapted for various audio processing tasks, making it a valuable tool for audio engineers and enthusiasts alike.How to built a FET Audio Mixer and Switch Circuit. PARTS LIST, R1 1MΩ, R2 47kΩ, R3 47kΩ, R4 1MΩ, R5 47kΩ, R6 47kΩ, R7 47kΩ, VR1 50kΩ, VR2 50kΩ, C1, C2, C3 4.7µF 16V, C4 100nF (104), C5 47nF (473), C6 47nF (473), Q1 BF245 or 2N3819, Q2 BF245 or 2N3819, S1, S2 Switch, Junction-FETs such as the BF245 or 2N3819 already popular in HF circuits but it can also applied to LF circuits. 🔗 External reference
The FET audio mixer and switch circuit utilizes field-effect transistors (FETs) to achieve efficient audio signal mixing and switching. The circuit design incorporates various resistors (R1 to R7) and variable resistors (VR1 and VR2) to control gain and balance across audio channels. Capacitors (C1 to C6) are strategically placed to filter and couple audio signals, ensuring that the frequency response is optimized for both low-frequency (LF) and high-frequency (HF) applications.
The use of junction FETs, specifically the BF245 or 2N3819, is critical in this circuit due to their low noise characteristics and high input impedance, making them suitable for audio applications. The switches (S1 and S2) allow for manual selection between different audio sources or channels, enhancing flexibility in audio routing.
The circuit operates by allowing audio signals to pass through the FETs, which act as variable resistors controlled by the gate voltage. This configuration provides low distortion and high fidelity, essential for audio mixing applications. The values of the resistors and capacitors can be adjusted to tailor the circuit's performance to specific audio requirements, such as adjusting the mixing levels or the frequency response.
Overall, the FET audio mixer and switch circuit is a versatile design that can be adapted for various audio processing tasks, making it a valuable tool for audio engineers and enthusiasts alike.How to built a FET Audio Mixer and Switch Circuit. PARTS LIST, R1 1MΩ, R2 47kΩ, R3 47kΩ, R4 1MΩ, R5 47kΩ, R6 47kΩ, R7 47kΩ, VR1 50kΩ, VR2 50kΩ, C1, C2, C3 4.7µF 16V, C4 100nF (104), C5 47nF (473), C6 47nF (473), Q1 BF245 or 2N3819, Q2 BF245 or 2N3819, S1, S2 Switch, Junction-FETs such as the BF245 or 2N3819 already popular in HF circuits but it can also applied to LF circuits. 🔗 External reference