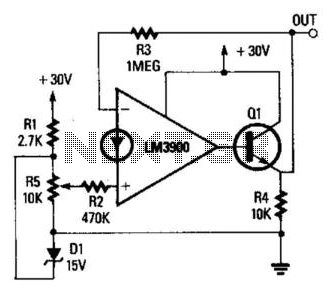
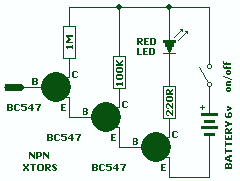
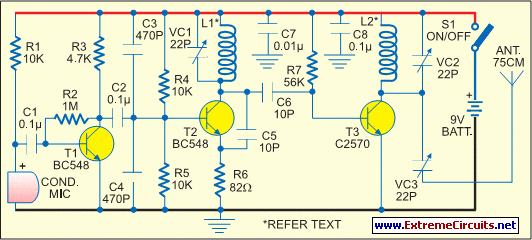
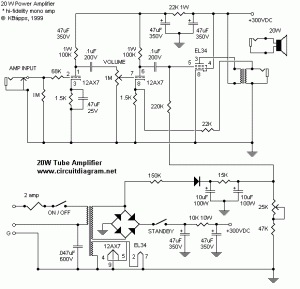
Fixed Voltage Power Supply
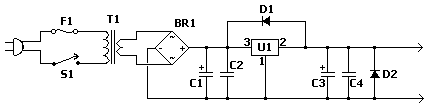
The fixed voltage power supply is useful in applications where an adjustable output is not required. This supply is simple, but very flexible as the voltage it outputs is dependent only on the regulator and transformer you choose. The maximum output current is 1.5A.
A fixed voltage power supply typically consists of a transformer, a rectifier, a filter capacitor, and a voltage regulator. The transformer steps down the AC mains voltage to a lower AC voltage suitable for the desired output. The choice of transformer is critical, as it determines the output voltage and current capabilities.
The rectifier, often implemented using a bridge configuration with diodes, converts the AC voltage from the transformer into pulsating DC voltage. This pulsating DC is not suitable for most applications, so a filter capacitor is used to smooth the output voltage. The capacitor charges and discharges to reduce voltage ripple, providing a more stable DC voltage output.
The voltage regulator is responsible for maintaining a constant output voltage despite variations in load current or input voltage. Common types of voltage regulators for fixed voltage applications include linear regulators, such as the 78xx series, and low-dropout (LDO) regulators. The selection of the regulator will depend on the desired output voltage, current rating, and efficiency requirements.
In this design, the maximum output current is specified as 1.5A. This indicates that the components, particularly the transformer and regulator, must be rated to handle this current without overheating or failing. Proper heat dissipation measures, such as heat sinks, may be necessary for the voltage regulator to ensure reliable operation.
Overall, the fixed voltage power supply is an essential component in many electronic devices, providing a stable and reliable power source for various applications.The fixed voltage power supply is useful in applications where an adjustable output is not required. This supply is simple, but very flexable as the voltage it outputs is dependant only on the regulator and transformer you choose. The maximum output current is 1.5A. 🔗 External reference
A fixed voltage power supply typically consists of a transformer, a rectifier, a filter capacitor, and a voltage regulator. The transformer steps down the AC mains voltage to a lower AC voltage suitable for the desired output. The choice of transformer is critical, as it determines the output voltage and current capabilities.
The rectifier, often implemented using a bridge configuration with diodes, converts the AC voltage from the transformer into pulsating DC voltage. This pulsating DC is not suitable for most applications, so a filter capacitor is used to smooth the output voltage. The capacitor charges and discharges to reduce voltage ripple, providing a more stable DC voltage output.
The voltage regulator is responsible for maintaining a constant output voltage despite variations in load current or input voltage. Common types of voltage regulators for fixed voltage applications include linear regulators, such as the 78xx series, and low-dropout (LDO) regulators. The selection of the regulator will depend on the desired output voltage, current rating, and efficiency requirements.
In this design, the maximum output current is specified as 1.5A. This indicates that the components, particularly the transformer and regulator, must be rated to handle this current without overheating or failing. Proper heat dissipation measures, such as heat sinks, may be necessary for the voltage regulator to ensure reliable operation.
Overall, the fixed voltage power supply is an essential component in many electronic devices, providing a stable and reliable power source for various applications.The fixed voltage power supply is useful in applications where an adjustable output is not required. This supply is simple, but very flexable as the voltage it outputs is dependant only on the regulator and transformer you choose. The maximum output current is 1.5A. 🔗 External reference