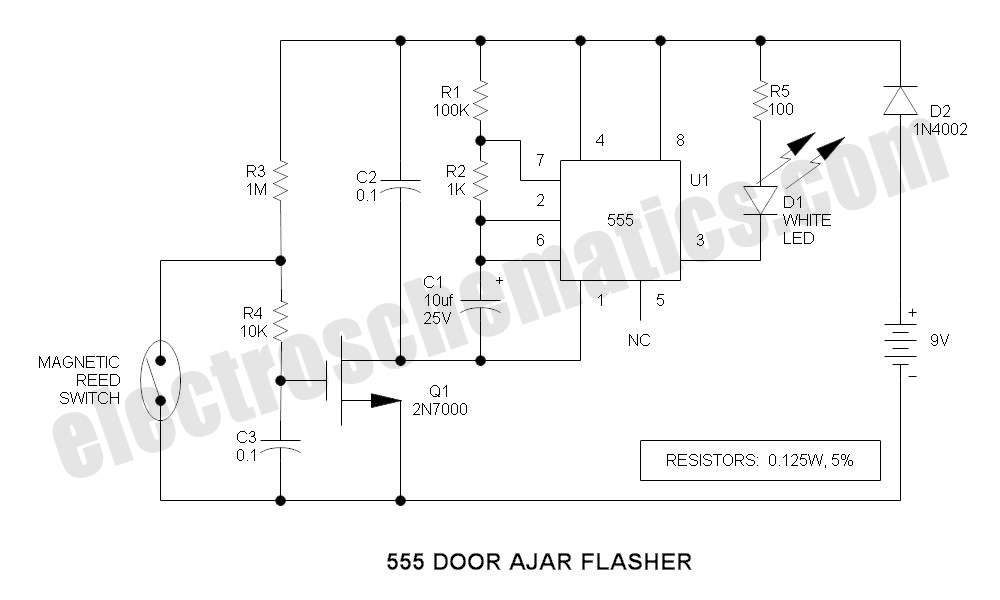
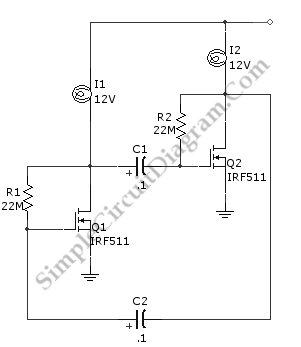
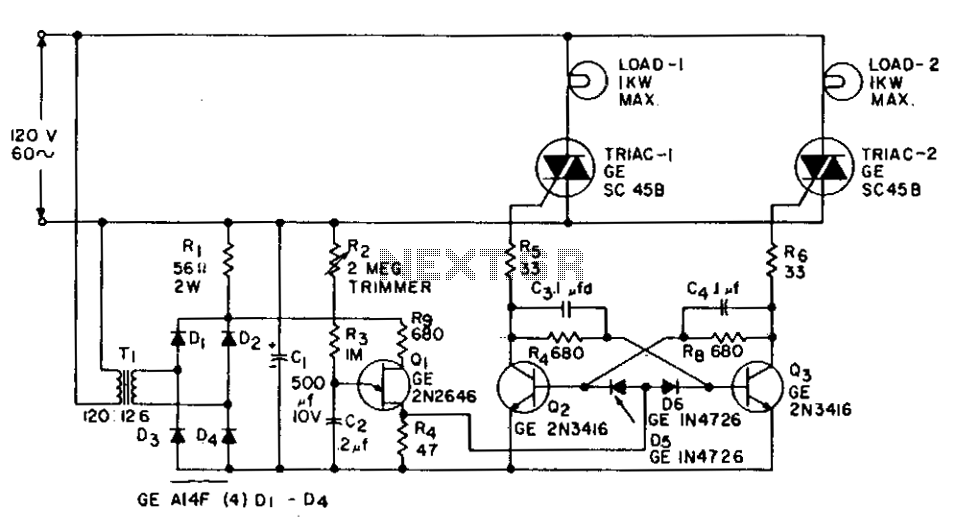
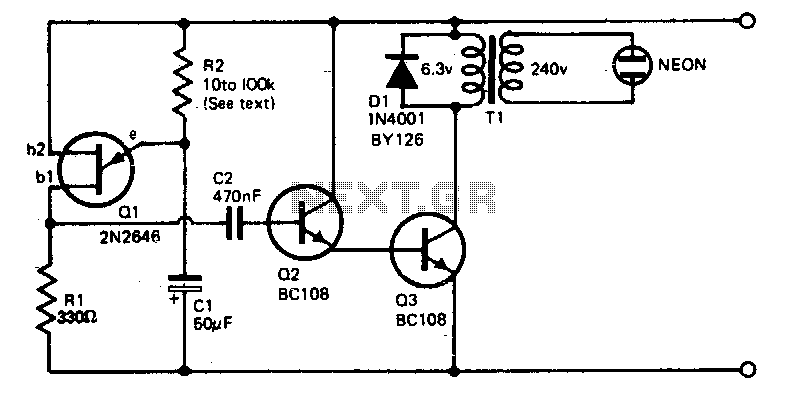
Flip-flop flasher
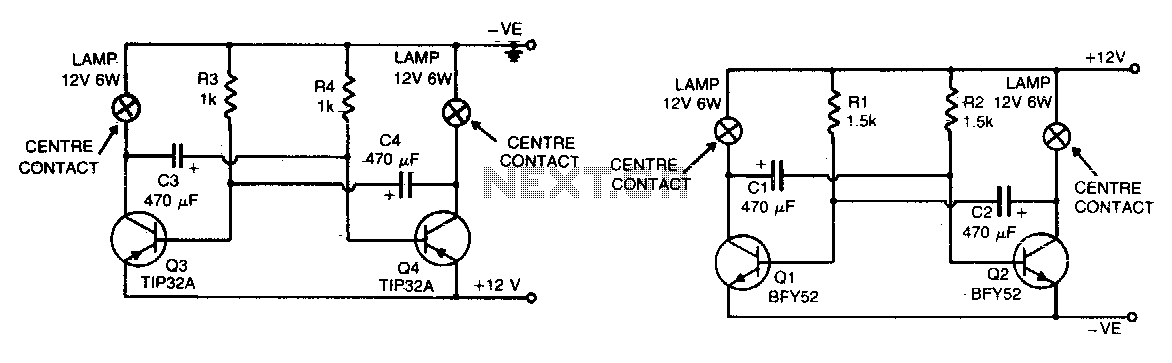
The flashing action is generated by a basic astable multivibrator configured to produce a flashing rate of approximately 60 flashes per minute for each lamp. The circuit designed for positive earth systems employs NPN transistors, while alternative configurations utilize PNP transistors.
The described circuit utilizes an astable multivibrator, which is a type of oscillator that continuously switches between its high and low states without requiring any external triggering. In this configuration, the flashing rate is determined by the time constants of the resistors and capacitors used in the circuit.
For a positive earth system, NPN transistors are employed, which are typically used for their ability to switch on and off quickly, allowing for efficient control of the lamp's flashing. The NPN transistors are connected in such a way that they alternately turn on and off, creating the desired flashing effect. The timing components, usually consisting of resistors and capacitors, set the frequency of the oscillation, effectively controlling the number of flashes per minute.
Conversely, when utilizing PNP transistors, the circuit configuration is modified to accommodate the different characteristics of these transistors. PNP transistors conduct when their base is pulled low relative to their emitter, which is connected to a positive voltage in a positive earth system. The design must ensure that the timing components are appropriately selected to achieve the same flashing rate of approximately 60 flashes per minute.
Overall, the astable multivibrator circuit is a versatile solution for generating flashing lights in various applications, with the choice of transistor type allowing for compatibility with different electrical systems.The flashing action is provided by a simple astable multivibrator timed to give a flashing rate of about 60 flashes for each lamp per minute. Circuit for positive earth systems uses NPN transistors The other uses PNP transistors.
The described circuit utilizes an astable multivibrator, which is a type of oscillator that continuously switches between its high and low states without requiring any external triggering. In this configuration, the flashing rate is determined by the time constants of the resistors and capacitors used in the circuit.
For a positive earth system, NPN transistors are employed, which are typically used for their ability to switch on and off quickly, allowing for efficient control of the lamp's flashing. The NPN transistors are connected in such a way that they alternately turn on and off, creating the desired flashing effect. The timing components, usually consisting of resistors and capacitors, set the frequency of the oscillation, effectively controlling the number of flashes per minute.
Conversely, when utilizing PNP transistors, the circuit configuration is modified to accommodate the different characteristics of these transistors. PNP transistors conduct when their base is pulled low relative to their emitter, which is connected to a positive voltage in a positive earth system. The design must ensure that the timing components are appropriately selected to achieve the same flashing rate of approximately 60 flashes per minute.
Overall, the astable multivibrator circuit is a versatile solution for generating flashing lights in various applications, with the choice of transistor type allowing for compatibility with different electrical systems.The flashing action is provided by a simple astable multivibrator timed to give a flashing rate of about 60 flashes for each lamp per minute. Circuit for positive earth systems uses NPN transistors The other uses PNP transistors.