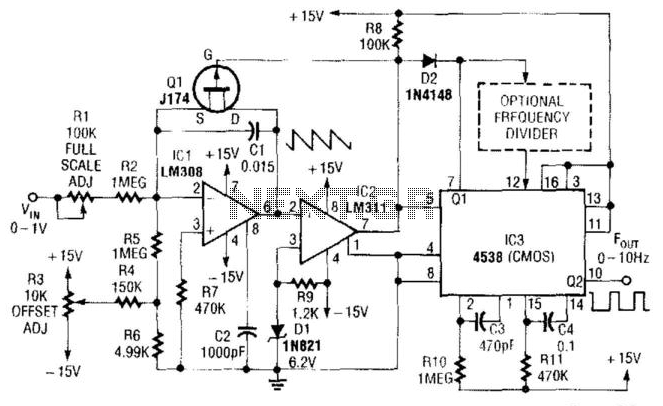
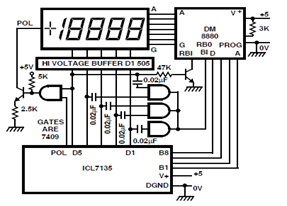
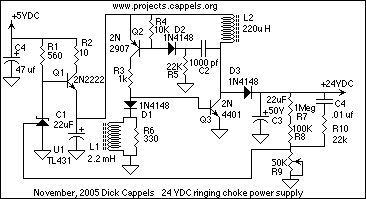
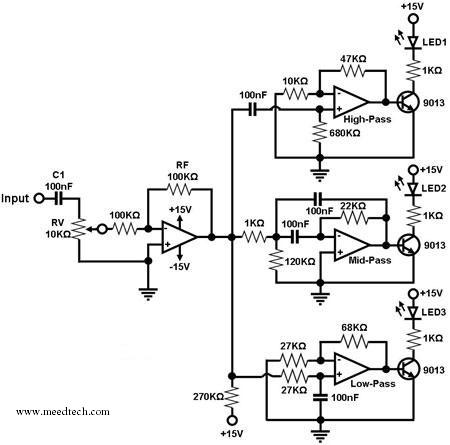
Flyback converter
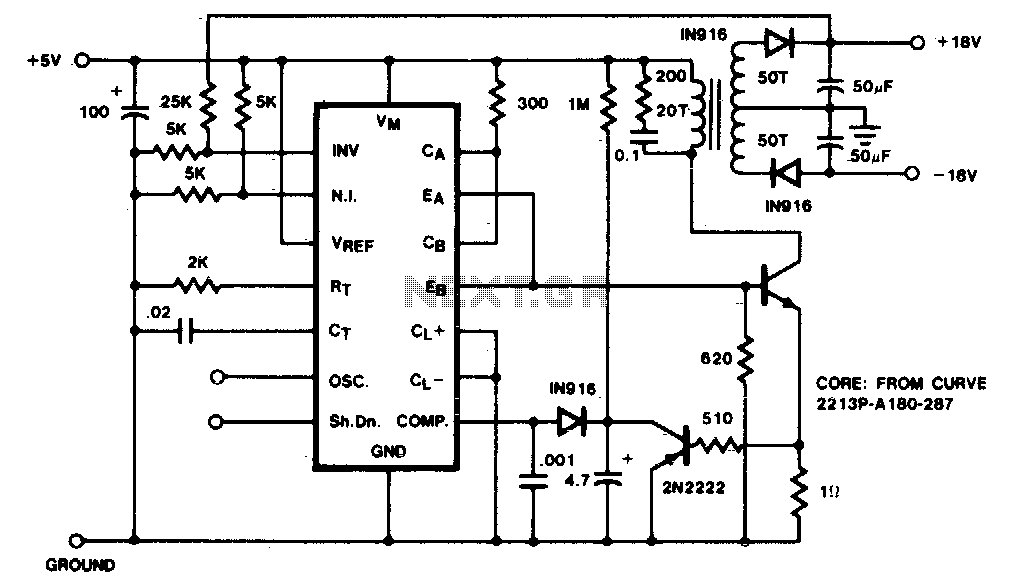
A low-current flyback converter is utilized to generate ±15 volts at 20 mA from a +5 volt regulated line. The reference generator in the SG1524 is not used, with the input voltage serving as the reference. Current limiting in a flyback converter presents challenges, which are addressed here by sensing the current in the primary line and resetting a soft-start circuit.
The low-current flyback converter design is an efficient solution for generating dual output voltages of ±15 volts from a single +5 volt input. This configuration typically involves the SG1524 integrated circuit, which is a versatile PWM controller capable of managing various power supply applications. In this particular setup, the reference generator feature of the SG1524 is bypassed, indicating that the input voltage itself is applied as a reference signal for the control loop.
The converter operates by storing energy in the magnetic field of a transformer during the on-time of the switch (usually a transistor). When the switch is turned off, the energy is released to the output, providing the required voltage levels. The flyback topology is particularly advantageous for applications requiring isolation between input and output, as well as for generating multiple output voltages from a single input source.
Current limiting is a critical aspect of flyback converter design to prevent damage due to overcurrent conditions. In this circuit, current sensing is implemented in the primary side of the transformer. This is typically achieved using a shunt resistor or a current transformer, which detects the current flowing through the primary winding. When the sensed current reaches a predetermined threshold, the control circuit can take action to limit the output current, such as by adjusting the duty cycle of the PWM signal.
Additionally, a soft-start circuit is integrated to prevent inrush current during startup. This circuit gradually increases the duty cycle of the PWM signal, allowing the converter to ramp up to its operating conditions smoothly. The combination of current sensing and soft-start functionality enhances the reliability and performance of the flyback converter, ensuring stable operation under varying load conditions.
Overall, the design of this low-current flyback converter effectively meets the requirements for generating regulated ±15 volts from a +5 volt input while addressing key challenges related to current limiting and startup behavior.A low-current flyback converter is used here to generate ±15 volts at 20 mA from a +5 volt regulated line. The reference generator in the SG1524 is unused with the input voltage providing the reference Current limiting in a flyback converter is difficult and is accomplished here by sensing current in the primary line and resetting a soft-start circuit.
The low-current flyback converter design is an efficient solution for generating dual output voltages of ±15 volts from a single +5 volt input. This configuration typically involves the SG1524 integrated circuit, which is a versatile PWM controller capable of managing various power supply applications. In this particular setup, the reference generator feature of the SG1524 is bypassed, indicating that the input voltage itself is applied as a reference signal for the control loop.
The converter operates by storing energy in the magnetic field of a transformer during the on-time of the switch (usually a transistor). When the switch is turned off, the energy is released to the output, providing the required voltage levels. The flyback topology is particularly advantageous for applications requiring isolation between input and output, as well as for generating multiple output voltages from a single input source.
Current limiting is a critical aspect of flyback converter design to prevent damage due to overcurrent conditions. In this circuit, current sensing is implemented in the primary side of the transformer. This is typically achieved using a shunt resistor or a current transformer, which detects the current flowing through the primary winding. When the sensed current reaches a predetermined threshold, the control circuit can take action to limit the output current, such as by adjusting the duty cycle of the PWM signal.
Additionally, a soft-start circuit is integrated to prevent inrush current during startup. This circuit gradually increases the duty cycle of the PWM signal, allowing the converter to ramp up to its operating conditions smoothly. The combination of current sensing and soft-start functionality enhances the reliability and performance of the flyback converter, ensuring stable operation under varying load conditions.
Overall, the design of this low-current flyback converter effectively meets the requirements for generating regulated ±15 volts from a +5 volt input while addressing key challenges related to current limiting and startup behavior.A low-current flyback converter is used here to generate ±15 volts at 20 mA from a +5 volt regulated line. The reference generator in the SG1524 is unused with the input voltage providing the reference Current limiting in a flyback converter is difficult and is accomplished here by sensing current in the primary line and resetting a soft-start circuit.