FM Transmitter (2N2222)
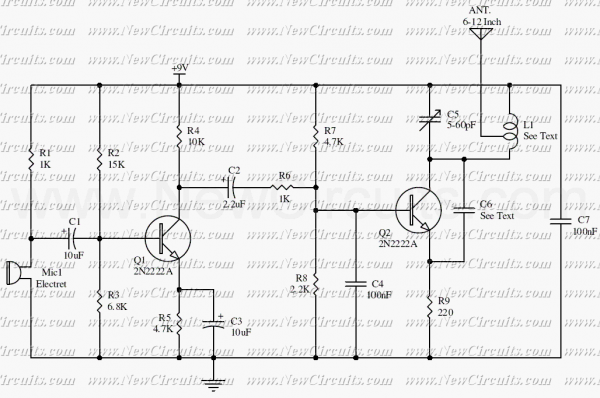
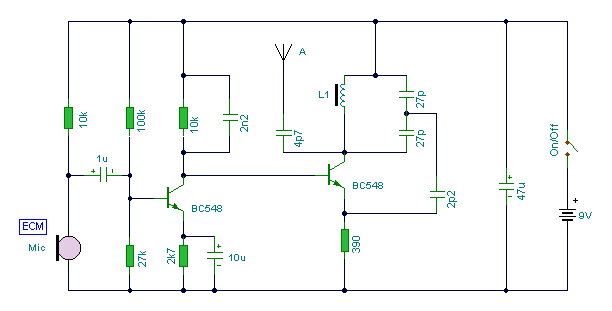
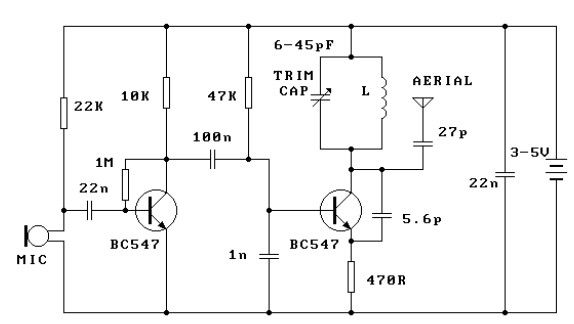
This circuit is a simple two transistor (2N2222) FM transmitter. No license is required for this transmitter according to FCC regulations regarding wireless microphones. If powered by a 9-volt battery and used with an antenna no longer than 12 inches, the transmitter will be within the FCC limits. The microphone is amplified by Q1. Q2, C5, and L1 form an oscillator that operates in the 80 to 130 MHz range. The oscillator is voltage controlled, so it is modulated by the audio signal that is applied to the base of Q2. R6 limits the input to the RF section, and its value can be adjusted as necessary to limit the volume of the input. L1 and C6 can be made with
This circuit design employs two 2N2222 transistors, which serve as the core components for amplification and oscillation. The first transistor, Q1, is configured as a common emitter amplifier, receiving audio input from a microphone. The amplified audio signal is then fed into the base of the second transistor, Q2, which is part of the oscillator circuit.
The oscillator circuit, comprising Q2, capacitor C5, and inductor L1, is designed to operate within the frequency range of 80 to 130 MHz. This range is suitable for FM transmission and complies with FCC regulations for unlicensed devices. The oscillator is voltage-controlled; thus, the frequency can be modulated by varying the amplitude of the audio signal applied to Q2's base. This modulation allows for the transmission of audio signals over radio frequencies.
Resistor R6 plays a crucial role in this circuit by limiting the input to the RF section. The value of R6 can be adjusted to control the volume of the audio input, ensuring that the transmitter operates effectively without distortion. The tuning elements, L1 (inductor) and C6 (capacitor), can be custom-made to achieve the desired resonant frequency and stability of the oscillator. The design allows for flexibility in tuning, which is essential for optimizing performance based on the specific application and environment.
Overall, this simple FM transmitter circuit provides an effective means of wireless audio transmission while adhering to regulatory standards. The use of commonly available components like the 2N2222 transistors makes it accessible for hobbyists and engineers alike.This circuit is a simple two transistor (2N2222) FM transmitter. No license is required for this transmitter according to FCC regulations regarding wireless microphones. If powered by a 9 volt battery and used with an antenna no longer than 12 inches, the transmitter will be within the FCC limits.
The microphone is amplified by Q1. Q2, C5, and L1 form an oscillator that operates in the 80 to 130 MHz range. The oscillator is voltage controlled, so it is modulated by the audio signal that is applied to the base of Q2. R6 limits the input to the RF section, and it's value can be adjusted as necessary to limit the volume of the input.
L1 and C6 can be made with 🔗 External reference
This circuit design employs two 2N2222 transistors, which serve as the core components for amplification and oscillation. The first transistor, Q1, is configured as a common emitter amplifier, receiving audio input from a microphone. The amplified audio signal is then fed into the base of the second transistor, Q2, which is part of the oscillator circuit.
The oscillator circuit, comprising Q2, capacitor C5, and inductor L1, is designed to operate within the frequency range of 80 to 130 MHz. This range is suitable for FM transmission and complies with FCC regulations for unlicensed devices. The oscillator is voltage-controlled; thus, the frequency can be modulated by varying the amplitude of the audio signal applied to Q2's base. This modulation allows for the transmission of audio signals over radio frequencies.
Resistor R6 plays a crucial role in this circuit by limiting the input to the RF section. The value of R6 can be adjusted to control the volume of the audio input, ensuring that the transmitter operates effectively without distortion. The tuning elements, L1 (inductor) and C6 (capacitor), can be custom-made to achieve the desired resonant frequency and stability of the oscillator. The design allows for flexibility in tuning, which is essential for optimizing performance based on the specific application and environment.
Overall, this simple FM transmitter circuit provides an effective means of wireless audio transmission while adhering to regulatory standards. The use of commonly available components like the 2N2222 transistors makes it accessible for hobbyists and engineers alike.This circuit is a simple two transistor (2N2222) FM transmitter. No license is required for this transmitter according to FCC regulations regarding wireless microphones. If powered by a 9 volt battery and used with an antenna no longer than 12 inches, the transmitter will be within the FCC limits.
The microphone is amplified by Q1. Q2, C5, and L1 form an oscillator that operates in the 80 to 130 MHz range. The oscillator is voltage controlled, so it is modulated by the audio signal that is applied to the base of Q2. R6 limits the input to the RF section, and it's value can be adjusted as necessary to limit the volume of the input.
L1 and C6 can be made with 🔗 External reference