fm transmitter circuit with max2606
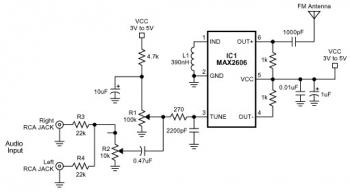
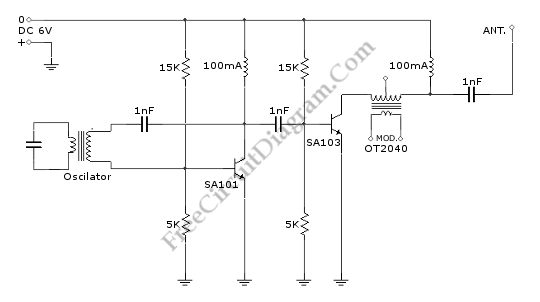
The FM transmitter circuit is built using a single MAX2606 chip. This simple FM transmitter connects a home entertainment system to a portable radio, allowing music to be played in one room and listened to in another, such as during a backyard barbeque. The MAX2606 functions as a voltage-controlled oscillator with an integrated varactor, with its nominal frequency of oscillation set by an inductor (L1). A value of 390nH tunes the frequency to 100MHz. A potentiometer (R1) enables channel selection, tuning within the FM band of 88MHz to 108MHz. The output power is approximately -21dBm into a 50-ohm load, which is within the acceptable emission limits for most nations. The left and right audio signals from the home system are combined using resistors (R3 and R4) and can be attenuated by an optional potentiometer (R2), which modulates the RF frequency for volume adjustment. Signals exceeding 60mV may cause distortion, hence the potentiometer reduces the signal level. In the absence of a common FM radio antenna, a 75cm (30 inches) wire can serve as a transmitting antenna, ideally mounted parallel to the receiving antenna for optimal reception. The IC operates on a power supply voltage ranging from 3V to 5V, with regulated voltage preferred to minimize frequency drift and noise. A PCB can be created by designing the layout using PCB design software like Eagle, printing it on photo or glossy paper with a laser printer, adhering it to the copper side of the PCB, and then using a hot iron to transfer the design for the etching process. If a laser printer is unavailable, designs can be printed on standard paper and copied onto glossy paper at a local copy service.
The FM transmitter circuit utilizing the MAX2606 chip is an efficient solution for wireless audio transmission within a limited range, making it particularly useful for home entertainment systems. The integration of a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) allows for precise frequency tuning, ensuring that the transmitter operates effectively within the FM band. The choice of a 390nH inductor for frequency setting is critical, as it directly influences the oscillator's performance, allowing for clear audio transmission without interference.
The circuit design incorporates a user-friendly interface for tuning and volume control. The potentiometer (R1) provides the flexibility to select different channels, which is essential for avoiding interference from other FM signals. The inclusion of resistors (R3 and R4) for audio signal summation is a standard practice in audio applications, ensuring that both left and right channels are mixed appropriately before transmission. The optional potentiometer (R2) serves a dual purpose: it not only adjusts the volume but also helps to prevent distortion by limiting the audio signal level fed into the transmitter.
For optimal performance, the transmitter should be paired with a suitable antenna. While a simple wire can suffice, the design emphasizes the importance of antenna placement and orientation to enhance reception quality. The operating voltage range of 3V to 5V ensures compatibility with various power sources, but stabilizing the supply voltage is recommended to maintain consistent operation.
The PCB design process outlined provides a straightforward approach for hobbyists and engineers to create their own FM transmitter. The use of readily available software tools and materials makes this project accessible, while the detailed steps for transferring the circuit design to a PCB ensure that even those with limited experience can successfully fabricate the transmitter. Overall, this FM transmitter circuit represents a practical and engaging project for those interested in exploring wireless audio technology.FM transmitter circuit which is build using single chip of MAX2606. A very simple FM transmitter connects your home-entertainment system to a portable radio that will be carried surrounding the house and into the back yard. As an example, it is possible to play music on the CD player in your private room, and listen to it on a portable radio by th
e back-yard barbeque. IC1 is a voltage-controlled oscillator with integrated varactor. Its nominal frequency of oscillation is set by inductor L1, and a 390nH value places that frequency at 100MHz. Potentiometer R1 then allows you to choose a channel by tuning above the FM band of 88MHz to 108MHz. Output power is about -21dBm into 50 (most nations accept emissions below 10dBm in the FM band). The home system`s left and right audio signals are summed by R3 and R4, and attenuated by the (optional) potentiometer R2.
R2`s wiper signal serves as a volume adjustment by modulating the RF frequency. Signals above 60mV introduce distortion, so the pot attenuates down from that level. In the absence of a common FM radio antenna, 75cm (30 inches) of wire will suffice as a transmitting antenna. For most effective reception, it need to be mounted parallel with the receiving antenna. The IC operates on a single power supply voltage inside the range 3V to 5V, but it is best to regulate the applied voltage to reduce frequency drift and noise.
Make a PCB in very easy steps. ! Create your PCB design using PCB designer software like Eagle, print out your design on photo paper or glossy paper with laserjet printer. Stick the printed design on the PCB (copper side) and then heat it using hot iron plate. The ink will stick on the PCB and it will be ready for etching process. Note: If you don`t have laserjet printer, then you can print the design on standard paper. Copy the printed design at Copy Service around your location (with glossy paper). 🔗 External reference
The FM transmitter circuit utilizing the MAX2606 chip is an efficient solution for wireless audio transmission within a limited range, making it particularly useful for home entertainment systems. The integration of a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) allows for precise frequency tuning, ensuring that the transmitter operates effectively within the FM band. The choice of a 390nH inductor for frequency setting is critical, as it directly influences the oscillator's performance, allowing for clear audio transmission without interference.
The circuit design incorporates a user-friendly interface for tuning and volume control. The potentiometer (R1) provides the flexibility to select different channels, which is essential for avoiding interference from other FM signals. The inclusion of resistors (R3 and R4) for audio signal summation is a standard practice in audio applications, ensuring that both left and right channels are mixed appropriately before transmission. The optional potentiometer (R2) serves a dual purpose: it not only adjusts the volume but also helps to prevent distortion by limiting the audio signal level fed into the transmitter.
For optimal performance, the transmitter should be paired with a suitable antenna. While a simple wire can suffice, the design emphasizes the importance of antenna placement and orientation to enhance reception quality. The operating voltage range of 3V to 5V ensures compatibility with various power sources, but stabilizing the supply voltage is recommended to maintain consistent operation.
The PCB design process outlined provides a straightforward approach for hobbyists and engineers to create their own FM transmitter. The use of readily available software tools and materials makes this project accessible, while the detailed steps for transferring the circuit design to a PCB ensure that even those with limited experience can successfully fabricate the transmitter. Overall, this FM transmitter circuit represents a practical and engaging project for those interested in exploring wireless audio technology.FM transmitter circuit which is build using single chip of MAX2606. A very simple FM transmitter connects your home-entertainment system to a portable radio that will be carried surrounding the house and into the back yard. As an example, it is possible to play music on the CD player in your private room, and listen to it on a portable radio by th
e back-yard barbeque. IC1 is a voltage-controlled oscillator with integrated varactor. Its nominal frequency of oscillation is set by inductor L1, and a 390nH value places that frequency at 100MHz. Potentiometer R1 then allows you to choose a channel by tuning above the FM band of 88MHz to 108MHz. Output power is about -21dBm into 50 (most nations accept emissions below 10dBm in the FM band). The home system`s left and right audio signals are summed by R3 and R4, and attenuated by the (optional) potentiometer R2.
R2`s wiper signal serves as a volume adjustment by modulating the RF frequency. Signals above 60mV introduce distortion, so the pot attenuates down from that level. In the absence of a common FM radio antenna, 75cm (30 inches) of wire will suffice as a transmitting antenna. For most effective reception, it need to be mounted parallel with the receiving antenna. The IC operates on a single power supply voltage inside the range 3V to 5V, but it is best to regulate the applied voltage to reduce frequency drift and noise.
Make a PCB in very easy steps. ! Create your PCB design using PCB designer software like Eagle, print out your design on photo paper or glossy paper with laserjet printer. Stick the printed design on the PCB (copper side) and then heat it using hot iron plate. The ink will stick on the PCB and it will be ready for etching process. Note: If you don`t have laserjet printer, then you can print the design on standard paper. Copy the printed design at Copy Service around your location (with glossy paper). 🔗 External reference