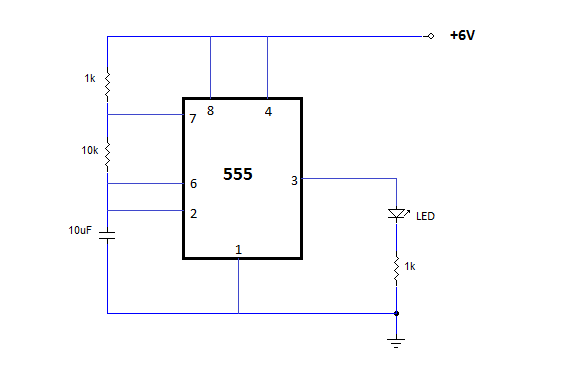
FM wireless transmitter circuit
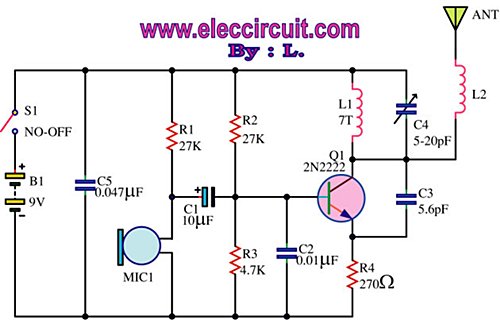
This is an FM wireless transmitter circuit designed to operate a microphone without the need for a cable connecting the microphone to the amplifier.
The FM wireless transmitter circuit typically consists of several key components: a microphone, an oscillator, a modulator, and an antenna. The microphone captures sound waves and converts them into electrical signals. These electrical signals are then fed into the oscillator, which generates a carrier frequency. The modulator combines the audio signal from the microphone with the carrier frequency produced by the oscillator, effectively encoding the audio information onto the carrier wave.
The output of the modulator is then transmitted through an antenna, which radiates the modulated signal as electromagnetic waves. The design of the antenna is crucial for ensuring efficient transmission and reception of the signal. The circuit may also include additional elements such as filters to remove unwanted frequencies, amplifiers to boost the signal strength, and power supply components to ensure stable operation.
In practical applications, the FM wireless transmitter circuit is widely used in various audio transmission scenarios, including public speaking, musical performances, and broadcasting. The absence of a physical connection between the microphone and the amplifier provides greater freedom of movement for the user while maintaining high audio quality. Proper tuning of the circuit is essential to achieve optimal performance, with considerations for frequency stability, range, and audio fidelity.This the fm wireless transmitter circuit, the truth is one kind microphone that developed to be used without a cable from the microphone to the amplifier. Makes.. 🔗 External reference
The FM wireless transmitter circuit typically consists of several key components: a microphone, an oscillator, a modulator, and an antenna. The microphone captures sound waves and converts them into electrical signals. These electrical signals are then fed into the oscillator, which generates a carrier frequency. The modulator combines the audio signal from the microphone with the carrier frequency produced by the oscillator, effectively encoding the audio information onto the carrier wave.
The output of the modulator is then transmitted through an antenna, which radiates the modulated signal as electromagnetic waves. The design of the antenna is crucial for ensuring efficient transmission and reception of the signal. The circuit may also include additional elements such as filters to remove unwanted frequencies, amplifiers to boost the signal strength, and power supply components to ensure stable operation.
In practical applications, the FM wireless transmitter circuit is widely used in various audio transmission scenarios, including public speaking, musical performances, and broadcasting. The absence of a physical connection between the microphone and the amplifier provides greater freedom of movement for the user while maintaining high audio quality. Proper tuning of the circuit is essential to achieve optimal performance, with considerations for frequency stability, range, and audio fidelity.This the fm wireless transmitter circuit, the truth is one kind microphone that developed to be used without a cable from the microphone to the amplifier. Makes.. 🔗 External reference