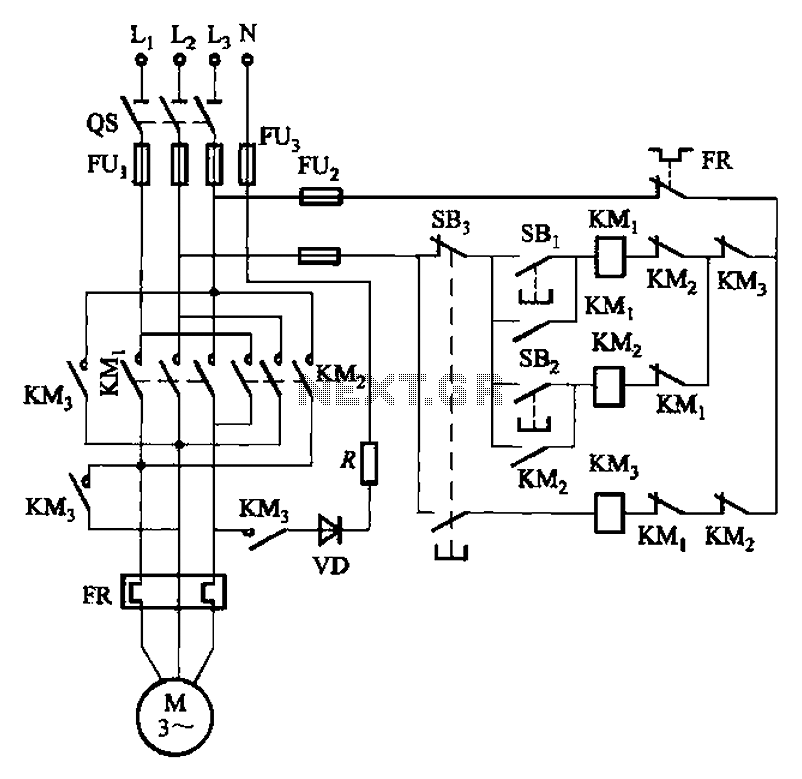
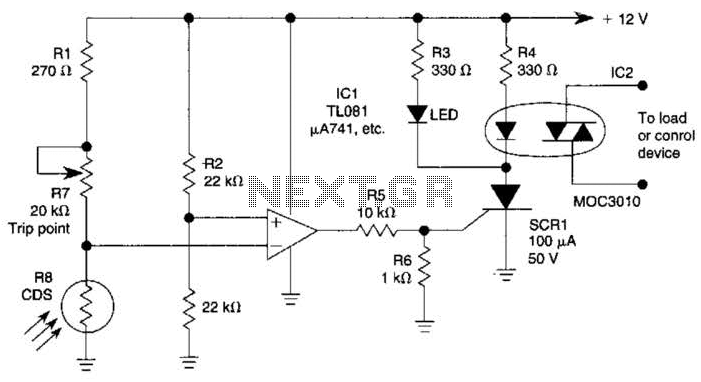
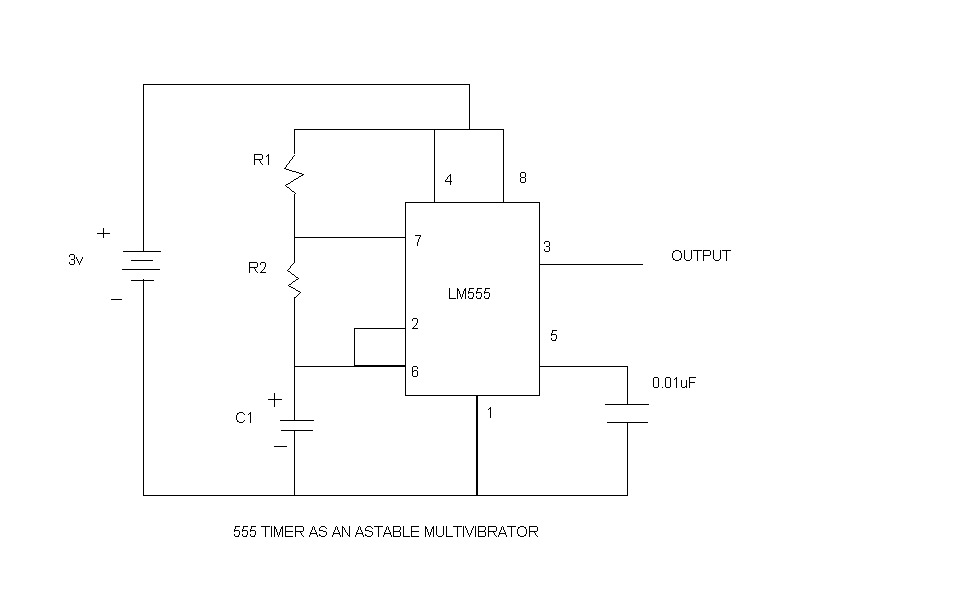
Four reversing operation of the reverse brake circuit
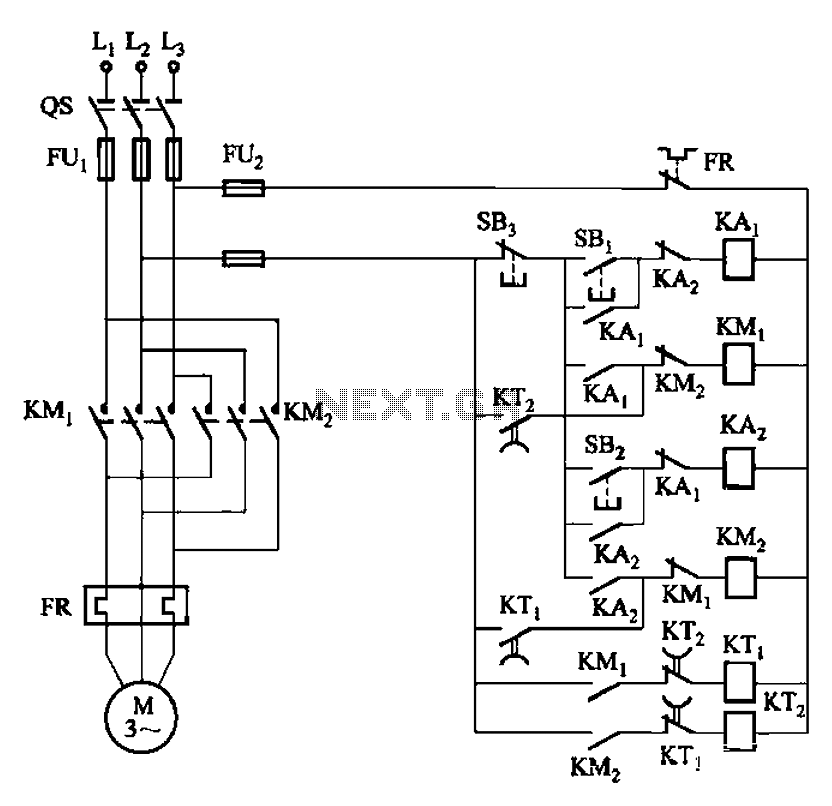
The circuit depicted in Figure 3-131 utilizes a relay instead of a speed control relay. It is designed to operate effectively in dusty environments and other challenging conditions.
The circuit operates by employing a relay as a primary switching mechanism, which enhances its reliability in adverse environmental conditions such as dust and moisture. The relay is activated by a control signal that dictates the operational state of the connected load, which can include motors or other devices requiring speed regulation.
Key components of the circuit include the relay itself, which is rated for the specific voltage and current required by the load. The relay contacts are designed to handle the electrical load while minimizing wear and tear, thus extending the operational life of the circuit. The circuit may also incorporate protective devices such as fuses or circuit breakers to prevent damage from overload conditions.
In addition to the relay, the circuit may feature capacitors and resistors to filter noise and stabilize the control signal, ensuring smooth operation under varying load conditions. The design may also include indicators such as LEDs to provide visual feedback on the operational status of the relay.
Overall, this circuit is optimized for durability and reliability, making it suitable for applications in industries where equipment is exposed to harsh environmental factors. Proper installation and maintenance are essential to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of the circuit in real-world applications. Circuit shown in Figure 3-131. It uses a relay in place of the speed control relay. The circuit is suitable for dusty rings and other poor environmental situation.
The circuit operates by employing a relay as a primary switching mechanism, which enhances its reliability in adverse environmental conditions such as dust and moisture. The relay is activated by a control signal that dictates the operational state of the connected load, which can include motors or other devices requiring speed regulation.
Key components of the circuit include the relay itself, which is rated for the specific voltage and current required by the load. The relay contacts are designed to handle the electrical load while minimizing wear and tear, thus extending the operational life of the circuit. The circuit may also incorporate protective devices such as fuses or circuit breakers to prevent damage from overload conditions.
In addition to the relay, the circuit may feature capacitors and resistors to filter noise and stabilize the control signal, ensuring smooth operation under varying load conditions. The design may also include indicators such as LEDs to provide visual feedback on the operational status of the relay.
Overall, this circuit is optimized for durability and reliability, making it suitable for applications in industries where equipment is exposed to harsh environmental factors. Proper installation and maintenance are essential to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of the circuit in real-world applications. Circuit shown in Figure 3-131. It uses a relay in place of the speed control relay. The circuit is suitable for dusty rings and other poor environmental situation.