Frequency Divider circuit
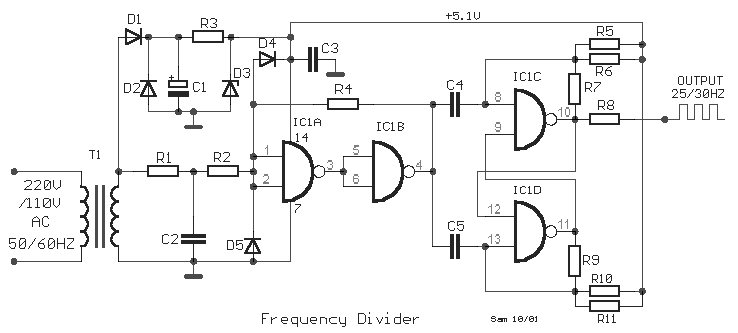
This is a classic frequency divider by two, implemented using a T-flip flop circuit, specifically with IC1 [4011]. In this circuit, the frequency from the network, after limiting the negative half-period of the sine wave and transforming it into a square wave, is divided by two. Consequently, for an input frequency of 50 Hz, the output pulse frequency will be 25 Hz. The circuit operates with a supply voltage of +5V and does not require a high current capacity.
The frequency divider circuit utilizes a T-flip flop, which is a type of bistable multivibrator. The T-flip flop toggles its output state on each clock pulse received at its input. In this implementation, the input clock signal is derived from a sine wave source, which is first conditioned to remove the negative half-cycle. This is typically accomplished using a comparator or Schmitt trigger circuit to ensure that the output is a clean square wave.
The IC used, the 4011, is a quad 2-input NAND gate, which can be configured to perform the necessary logic operations for the T-flip flop. The output frequency is half of the input frequency due to the nature of the T-flip flop operation, where each transition of the input clock results in a state change in the output.
The power supply for this circuit is modest, requiring only +5V, making it suitable for low-power applications. The current draw is minimal, allowing for efficient operation in battery-powered devices or low-energy systems. The design is straightforward and can be easily implemented on a breadboard or a PCB for prototyping purposes.
Overall, this frequency divider circuit serves as an essential building block in digital electronics, enabling the manipulation of signal frequencies for various applications, including clock generation and signal processing.This is a classic divider of frequency via two. It is achieved with a classic circuit T-flipFlop, round IC1 [ 4011 ]. In the circuit, the frequency of network, after are limit the negative half-s period of sine wave and transform in square wave, are divided via two. Thus for frequency50 HZ, we will take in the exit pulse of frequency 25 HZ. The supply of circuit it is + 5V and does not need high benefit in current.. 🔗 External reference
The frequency divider circuit utilizes a T-flip flop, which is a type of bistable multivibrator. The T-flip flop toggles its output state on each clock pulse received at its input. In this implementation, the input clock signal is derived from a sine wave source, which is first conditioned to remove the negative half-cycle. This is typically accomplished using a comparator or Schmitt trigger circuit to ensure that the output is a clean square wave.
The IC used, the 4011, is a quad 2-input NAND gate, which can be configured to perform the necessary logic operations for the T-flip flop. The output frequency is half of the input frequency due to the nature of the T-flip flop operation, where each transition of the input clock results in a state change in the output.
The power supply for this circuit is modest, requiring only +5V, making it suitable for low-power applications. The current draw is minimal, allowing for efficient operation in battery-powered devices or low-energy systems. The design is straightforward and can be easily implemented on a breadboard or a PCB for prototyping purposes.
Overall, this frequency divider circuit serves as an essential building block in digital electronics, enabling the manipulation of signal frequencies for various applications, including clock generation and signal processing.This is a classic divider of frequency via two. It is achieved with a classic circuit T-flipFlop, round IC1 [ 4011 ]. In the circuit, the frequency of network, after are limit the negative half-s period of sine wave and transform in square wave, are divided via two. Thus for frequency50 HZ, we will take in the exit pulse of frequency 25 HZ. The supply of circuit it is + 5V and does not need high benefit in current.. 🔗 External reference