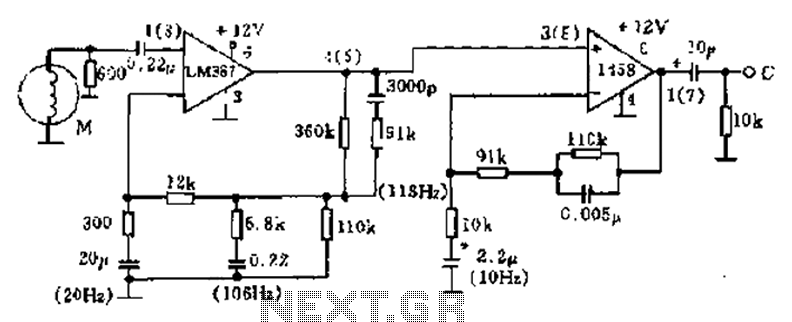
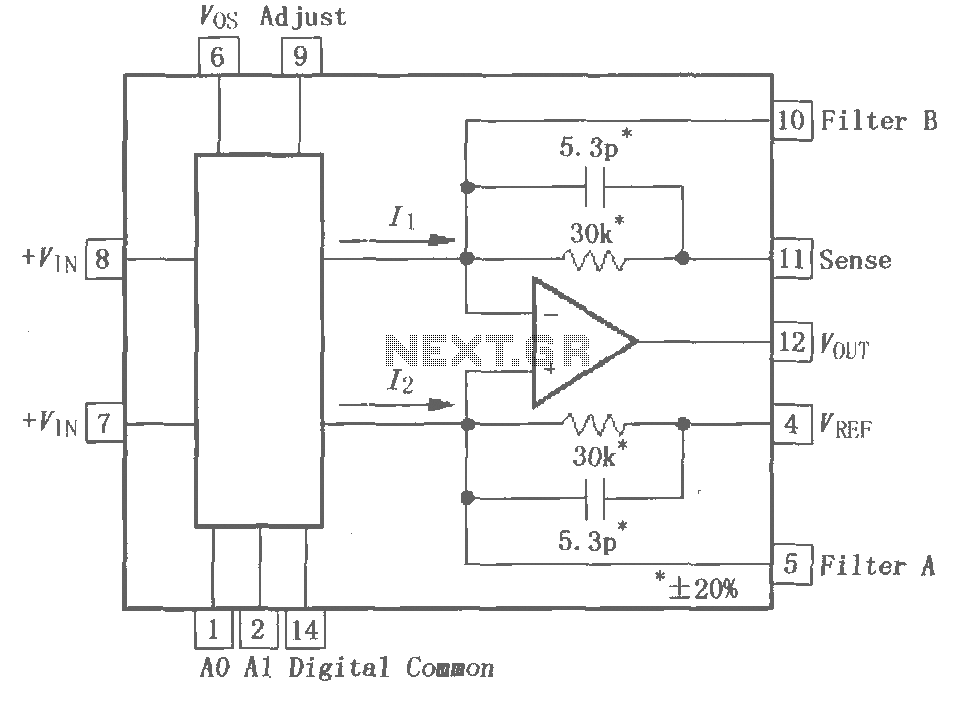
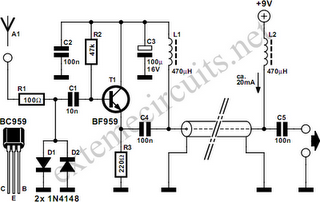
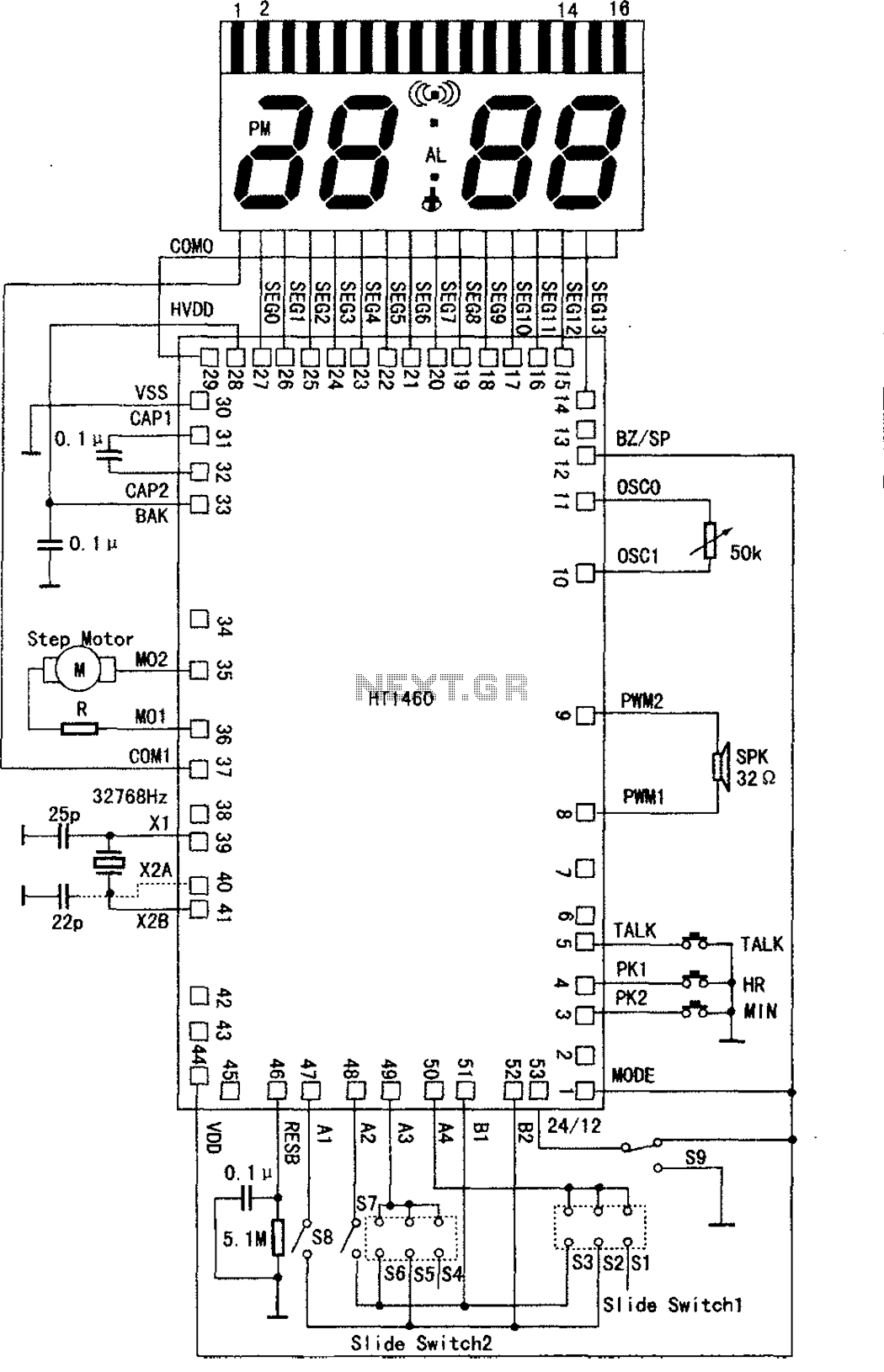
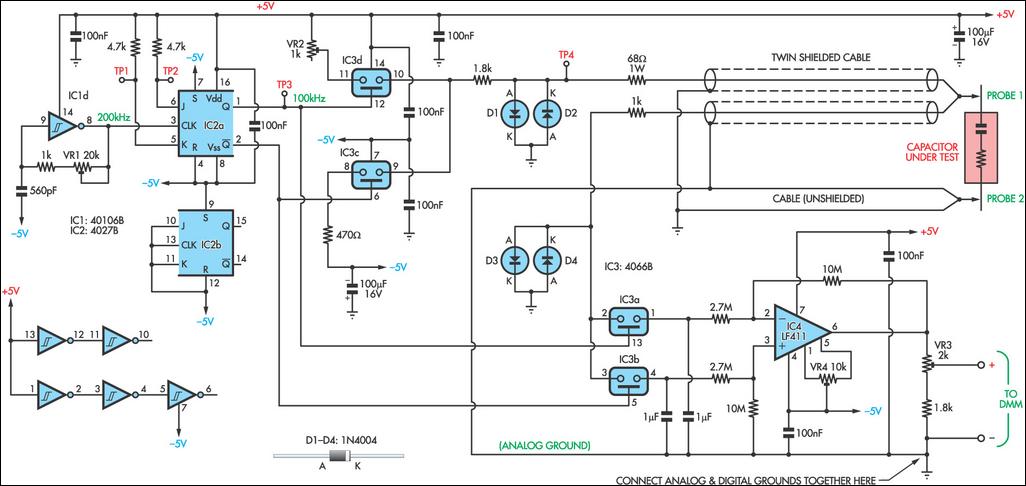
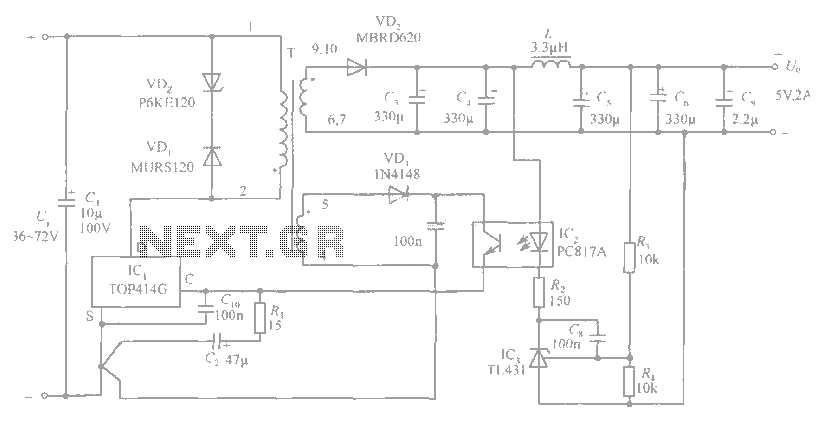
Frequency Meter Circuit
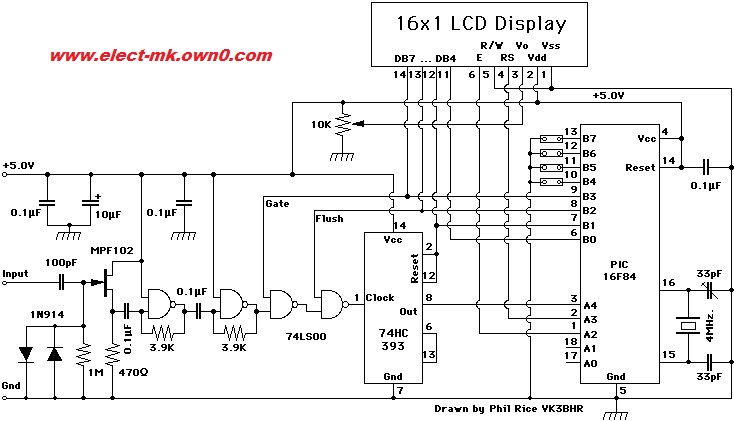
Frequency meter circuit for service applications, including all standard frequency bands: amateur HF, VHF, and UHF, displayed on an LCD screen.
The frequency meter circuit is designed to accurately measure and display frequency across various amateur radio bands, specifically HF (High Frequency), VHF (Very High Frequency), and UHF (Ultra High Frequency). The circuit utilizes a microcontroller or dedicated frequency counter IC to process the incoming signal and convert it into a readable format.
The input stage typically consists of an RF front end, which may include a low-noise amplifier (LNA) to boost weak signals and a bandpass filter to isolate the desired frequency range from unwanted signals. The filtered signal is then fed into the frequency counter, which counts the number of cycles over a defined time period, allowing it to determine the frequency of the incoming signal accurately.
To display the measured frequency, an LCD screen is employed. The microcontroller processes the frequency data and formats it for output to the LCD. The display is designed to show the frequency in a user-friendly manner, often with options for different units (such as MHz or kHz) based on the frequency range being measured.
Power supply considerations are also important in this circuit design. A stable voltage source is required to ensure accurate measurements and reliable operation. It is common to use a regulated power supply or battery to provide the necessary voltage levels for the circuit components.
Additional features may include a calibration function to ensure accuracy, a backlight for the LCD for use in low-light conditions, and possibly a user interface with buttons or a rotary encoder for selecting frequency ranges or modes of operation.
Overall, this frequency meter circuit serves as a valuable tool for amateur radio operators and service technicians, allowing them to monitor and troubleshoot communication equipment effectively across multiple frequency bands.Frequency Meter Circuit of Service Include all the standard frequency bands amateur hf and vhf and uhf And displayed on the LCD screen This is to e. 🔗 External reference
The frequency meter circuit is designed to accurately measure and display frequency across various amateur radio bands, specifically HF (High Frequency), VHF (Very High Frequency), and UHF (Ultra High Frequency). The circuit utilizes a microcontroller or dedicated frequency counter IC to process the incoming signal and convert it into a readable format.
The input stage typically consists of an RF front end, which may include a low-noise amplifier (LNA) to boost weak signals and a bandpass filter to isolate the desired frequency range from unwanted signals. The filtered signal is then fed into the frequency counter, which counts the number of cycles over a defined time period, allowing it to determine the frequency of the incoming signal accurately.
To display the measured frequency, an LCD screen is employed. The microcontroller processes the frequency data and formats it for output to the LCD. The display is designed to show the frequency in a user-friendly manner, often with options for different units (such as MHz or kHz) based on the frequency range being measured.
Power supply considerations are also important in this circuit design. A stable voltage source is required to ensure accurate measurements and reliable operation. It is common to use a regulated power supply or battery to provide the necessary voltage levels for the circuit components.
Additional features may include a calibration function to ensure accuracy, a backlight for the LCD for use in low-light conditions, and possibly a user interface with buttons or a rotary encoder for selecting frequency ranges or modes of operation.
Overall, this frequency meter circuit serves as a valuable tool for amateur radio operators and service technicians, allowing them to monitor and troubleshoot communication equipment effectively across multiple frequency bands.Frequency Meter Circuit of Service Include all the standard frequency bands amateur hf and vhf and uhf And displayed on the LCD screen This is to e. 🔗 External reference