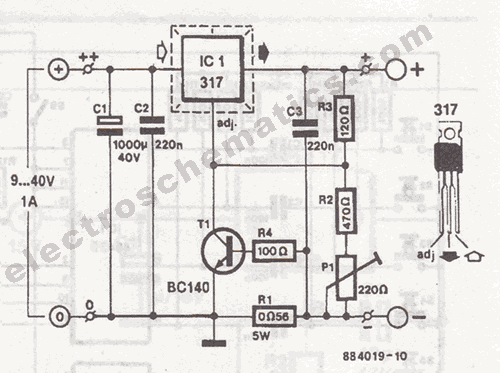
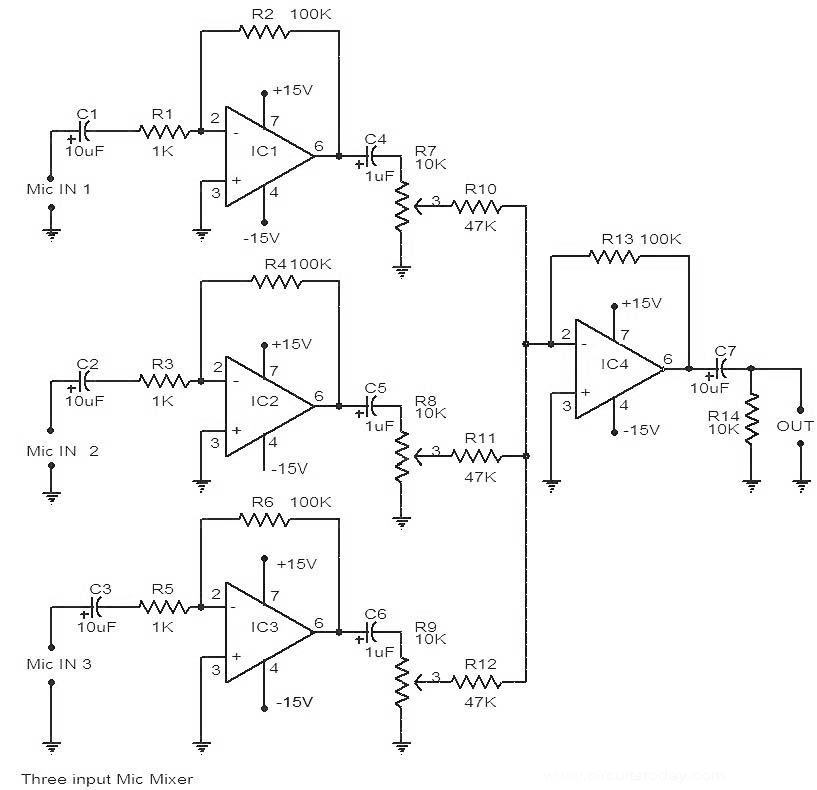
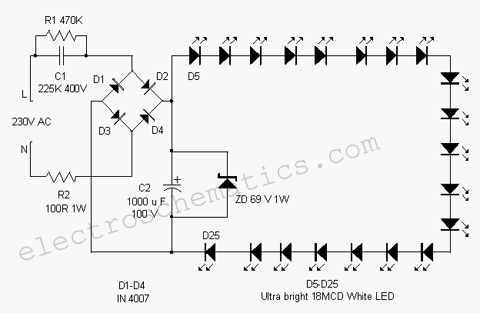
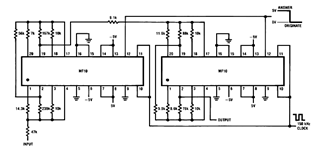
Phonograph amplifier circuit diagram
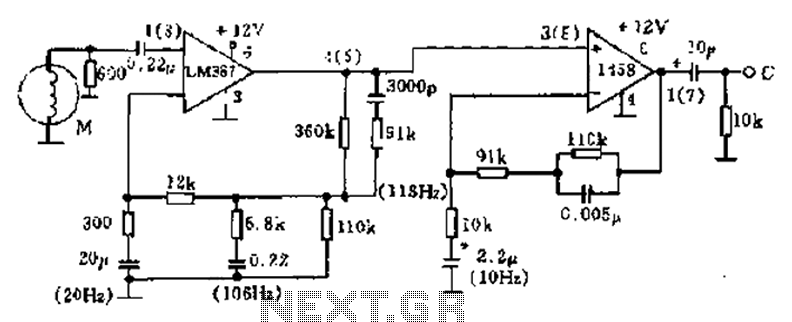
The phonograph pickup head is represented in the schematic as component M, which generates the pick-up signal and is processed through an LM387 amplifier circuit. The LM387 is part of the LM38X series, recognized for its advanced linear amplifier characteristics, including low noise, low distortion, wide bandwidth, and the ability to mitigate beat frequencies. Additionally, it operates on a single power supply and incorporates internal compensation, power supply decoupling, and regulation. The amplifier is capable of significant output voltage variations and provides a broad power bandwidth. The schematic also indicates a 600-ohm resistor connected in parallel with the current flow to serve as a stopping mechanism.
The phonograph pickup head serves as the initial transducer in the audio signal chain, converting mechanical vibrations from the vinyl record into an electrical signal. This signal is typically weak and requires amplification to be usable for further processing. The LM387 amplifier circuit is specifically designed to enhance the quality of this signal while minimizing noise and distortion, which is critical for high-fidelity audio reproduction.
The LM387 amplifier is notable for its low noise operation, which is essential in audio applications to prevent unwanted hiss or background noise from interfering with the desired sound. Its low distortion characteristics ensure that the output signal closely resembles the original input, preserving the integrity of the audio signal. The wide bandwidth capability allows the amplifier to handle a broad range of audio frequencies, making it suitable for various audio applications, including high-fidelity sound systems.
The use of a single power supply simplifies the design and reduces the complexity of the circuit, making it easier to implement in various audio devices. Internal compensation helps to stabilize the amplifier's performance over a range of operating conditions, while power supply decoupling reduces the impact of power supply variations on the amplifier's output.
The 600-ohm resistor connected in parallel with the current flow serves a dual purpose. It helps to limit the current to a safe level, protecting the amplifier from potential damage due to excessive current, while also acting as a load that optimizes the performance of the pickup head. This configuration ensures that the system operates efficiently, providing high-quality audio output while maintaining reliability and longevity.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies the integration of advanced amplifier technology with traditional audio components, resulting in a high-performance solution for vinyl playback systems. As shown in FIG phonograph pickup head M from the pick-up signal and l458 through LM387 amplifier circuit. LM387 is LM38X series one. LM38X series are highly advanced linear am plifier IC, with low noise, low distortion, wide-band and curb the beat and so on. In addition, a single power supply, internal compensation, power supply decoupling and regulation, large output voltage change and larger power broadband, but also its features. Figure and pickup head 600 ohm resistor in parallel with the current F to stopping.
The phonograph pickup head serves as the initial transducer in the audio signal chain, converting mechanical vibrations from the vinyl record into an electrical signal. This signal is typically weak and requires amplification to be usable for further processing. The LM387 amplifier circuit is specifically designed to enhance the quality of this signal while minimizing noise and distortion, which is critical for high-fidelity audio reproduction.
The LM387 amplifier is notable for its low noise operation, which is essential in audio applications to prevent unwanted hiss or background noise from interfering with the desired sound. Its low distortion characteristics ensure that the output signal closely resembles the original input, preserving the integrity of the audio signal. The wide bandwidth capability allows the amplifier to handle a broad range of audio frequencies, making it suitable for various audio applications, including high-fidelity sound systems.
The use of a single power supply simplifies the design and reduces the complexity of the circuit, making it easier to implement in various audio devices. Internal compensation helps to stabilize the amplifier's performance over a range of operating conditions, while power supply decoupling reduces the impact of power supply variations on the amplifier's output.
The 600-ohm resistor connected in parallel with the current flow serves a dual purpose. It helps to limit the current to a safe level, protecting the amplifier from potential damage due to excessive current, while also acting as a load that optimizes the performance of the pickup head. This configuration ensures that the system operates efficiently, providing high-quality audio output while maintaining reliability and longevity.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies the integration of advanced amplifier technology with traditional audio components, resulting in a high-performance solution for vinyl playback systems. As shown in FIG phonograph pickup head M from the pick-up signal and l458 through LM387 amplifier circuit. LM387 is LM38X series one. LM38X series are highly advanced linear am plifier IC, with low noise, low distortion, wide-band and curb the beat and so on. In addition, a single power supply, internal compensation, power supply decoupling and regulation, large output voltage change and larger power broadband, but also its features. Figure and pickup head 600 ohm resistor in parallel with the current F to stopping.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713