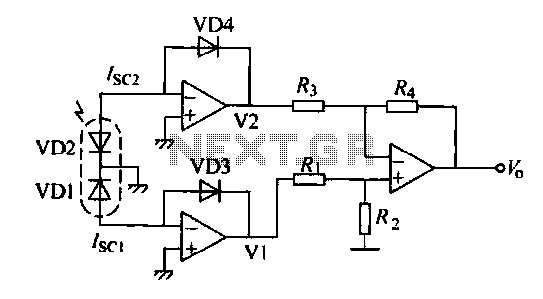
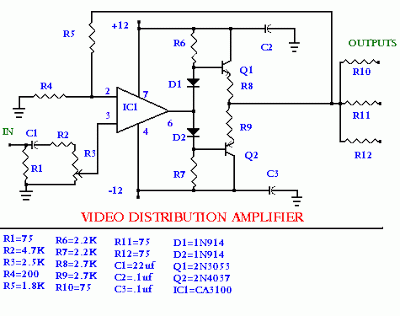
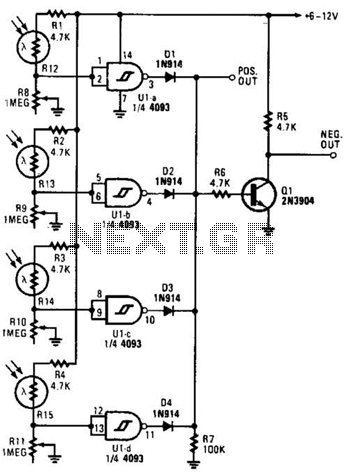
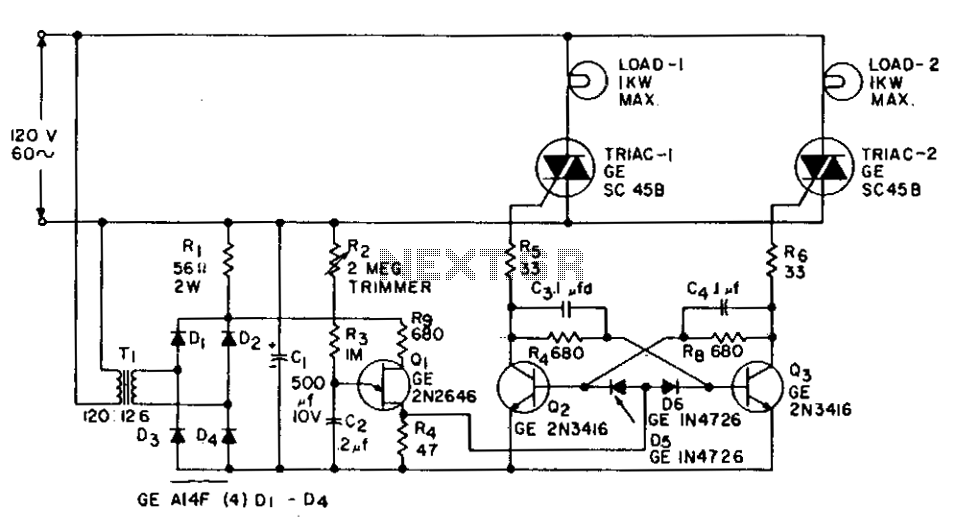
Frequency-Ratio Monitoring Circuit
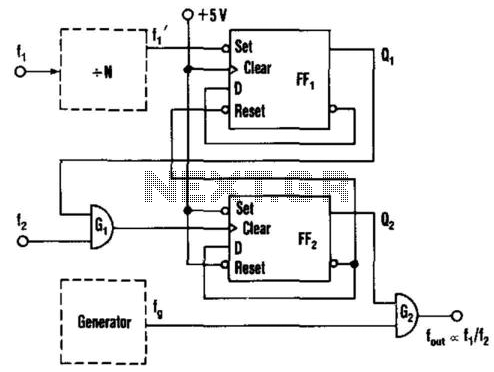
This circuit generates an output frequency that is linearly proportional to the ratio of two input frequencies. Each pulse of the bias frequency will open a switch for a period equal to half of the second input frequency, allowing a specific number of pulses to pass to the output.
The circuit operates by utilizing a frequency divider mechanism, which is essential in applications requiring precise frequency control. The two input frequencies, denoted as f1 and f2, are fed into the circuit, where they are processed to yield an output frequency (fout) that is a function of their ratio (fout = k * (f1/f2), where k is a constant that defines the scaling of the output).
The switch, referred to as G1 in the description, is a crucial component that modulates the flow of pulses based on the input frequencies. Each pulse of the bias frequency activates G1 for a specific duration, T, which is determined to be half of the period of the second input frequency (T = 1/(2*f2)). This timing ensures that the circuit allows a defined number of pulses to pass through, specifically fg/f2 pulses, where fg represents the frequency of the bias signal.
The design may incorporate additional components such as resistors and capacitors to filter the signals, ensuring that the output frequency is stable and free from noise. Furthermore, the circuit can be implemented using various technologies, including discrete components or integrated circuits, depending on the application requirements and desired performance characteristics.
In summary, this circuit provides a method for generating an output frequency that is directly related to the ratio of two input frequencies, utilizing a switch mechanism to control pulse transmission, thereby enabling precise frequency modulation in various electronic applications. This circuit produces an output frequency that is linearly proportional to the ratio of two input freque ncies /i//2. Each pulse of the bias fa (or/) will open G1 for a period T= l//2 so that fg/f2 pulses pass to the output.
The circuit operates by utilizing a frequency divider mechanism, which is essential in applications requiring precise frequency control. The two input frequencies, denoted as f1 and f2, are fed into the circuit, where they are processed to yield an output frequency (fout) that is a function of their ratio (fout = k * (f1/f2), where k is a constant that defines the scaling of the output).
The switch, referred to as G1 in the description, is a crucial component that modulates the flow of pulses based on the input frequencies. Each pulse of the bias frequency activates G1 for a specific duration, T, which is determined to be half of the period of the second input frequency (T = 1/(2*f2)). This timing ensures that the circuit allows a defined number of pulses to pass through, specifically fg/f2 pulses, where fg represents the frequency of the bias signal.
The design may incorporate additional components such as resistors and capacitors to filter the signals, ensuring that the output frequency is stable and free from noise. Furthermore, the circuit can be implemented using various technologies, including discrete components or integrated circuits, depending on the application requirements and desired performance characteristics.
In summary, this circuit provides a method for generating an output frequency that is directly related to the ratio of two input frequencies, utilizing a switch mechanism to control pulse transmission, thereby enabling precise frequency modulation in various electronic applications. This circuit produces an output frequency that is linearly proportional to the ratio of two input freque ncies /i//2. Each pulse of the bias fa (or/) will open G1 for a period T= l//2 so that fg/f2 pulses pass to the output.