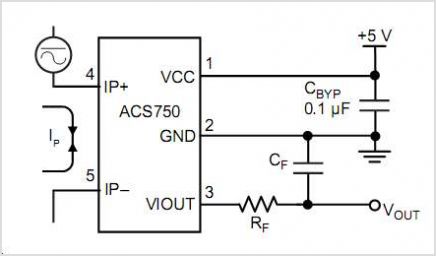
Fully Integrated Hall Effect-Based Linear Current Sensor With High Voltage Isolation And A Low-Resistance Current Conductor
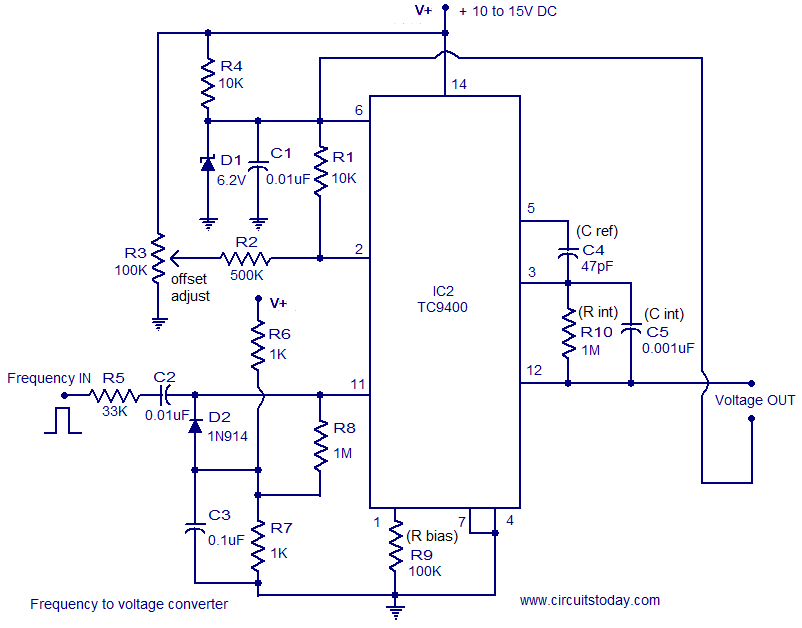
The AD537 is a monolithic voltage-to-frequency (V-F) converter that includes an input amplifier, a precision oscillator system, an accurate internal reference generator, and a high-current output stage. A single external resistor-capacitor (RC) network is sufficient to configure any full-scale (F.S.) frequency up to 100 kHz and any F.S. input voltage up to 30 V. The linearity error is as low as 0.05% for a 10 kHz F.S., and operation is guaranteed over an 80 dB dynamic range. The overall temperature coefficient (excluding the effects of external components) is typically 30 ppm/°C. The AD537 operates from a single supply voltage ranging from 5 V to 36 V and consumes only 1.2 mA of quiescent current. A temperature-proportional output, scaled to 1.00 mV/K, allows the circuit to function as a reliable temperature-to-frequency converter; in conjunction with the fixed reference output of 1.00 V, offset scales such as 0°C or 0°F can be generated. The low drift (1 V/°C typical) input amplifier enables operation directly from small signals (e.g., thermocouples or strain gauges) while providing a high input resistance of 250 MΩ. Unlike most V-F converters, the AD537 delivers a square-wave output and can drive up to 12 TTL loads, LEDs, long cables, etc. The excellent temperature characteristics and long-term stability of the AD537 are ensured by the primary bandgap reference generator and the low temperature coefficient silicon chromium thin film resistors used throughout the device. The AD537 is available in either a TO-116 ceramic dual in-line package (DIP) or a TO-100 metal can, both of which are hermetically sealed. The device comes in three performance/temperature grades: the J and K grades are specified for operation over the 0°C to +70°C range, while the AD537S is specified for operation over the extended temperature range of -55°C to +125°C. This device is protected by Patent Nos. 3,889,963 and RE 20,586.
The AD537 voltage-to-frequency converter is designed for high precision applications where converting voltage signals into frequency signals is essential. The internal architecture includes a high-performance input amplifier that ensures low drift and high input impedance, making it suitable for interfacing with low-level signals from sensors such as thermocouples or strain gauges. The precision oscillator system generates a stable frequency output that is proportional to the input voltage, allowing for accurate signal conversion across a wide frequency range.
The device's ability to operate with a single supply voltage simplifies the design of power supply circuits, and the low quiescent current of 1.2 mA contributes to energy efficiency, making the AD537 ideal for battery-operated devices. The temperature-proportional output enhances its utility in temperature measurement applications, enabling easy integration with temperature control systems.
The output characteristics of the AD537 are particularly advantageous, as the square-wave output can drive multiple TTL loads, making it suitable for interfacing with digital circuits and microcontrollers. The robust construction, featuring hermetically sealed packages, ensures reliability in harsh environments, while the availability of different performance grades allows for flexibility in selecting the appropriate version based on the application's temperature requirements.
In summary, the AD537 is a versatile and reliable voltage-to-frequency converter that combines high accuracy, low power consumption, and excellent temperature stability, making it an ideal choice for a wide range of electronic applications.The AD537 is a monolithic V-F converter consisting of an input Amplifier a precision Oscillator system, an accurate internal reference generator and a high current output stage. Only a single external RC network is required to set up any full-scale (F. S. ) frequency up to 100 kHz and any F. S. input voltage up to 30 V. Linearity error is as low as 0 . 05% for 10 kHz F. S. , and operation is guaranteed over an 80 dB dynamic range. The overall temperature coefficient (excluding the effects of external components) is typically 30 ppm/C. The AD537 operates from a single supply of 5 V to 36 V and consumes only 1. 2 mA quiescent current. A temperature-proportional output, scaled to 1. 00 mV/K, enables the circuit to be used as a reliable temperature-to-frequency converter; in combination with the fixed reference output of 1.
00 V, offset scales such as 0C or 0F CAN be generated. The low drift (1V/C typ) input Amplifier allows operation directly from small signals (e. g. , thermocouples or strain gages) while offering a high (250 M(Ohm) input resistance. Unlike most V-F converters, the AD537 provides a square-wave output, and CAN drive up to 12 TTL loads, LEDs very long cables, etc. The excellent temperature characteristics and long-term stability of the AD537 are guaranteed by the primary bandgap reference generator and the low T.
C. silicon chromium thin film resistors used throughout. The device is available in either a TO-116 ceramic DIP or a TO-100 metal can; both are hermetically sealed packages. The AD537 is available in three performance/temperature grades; the J and K grades are specified for operation over the 0C to +70C range while the AD537S is specified for operation over the extended temperature range, -55C to +125C.
*Protected by Patent Nos. 3, 88, 963 and RE 20, 586. 🔗 External reference
The AD537 voltage-to-frequency converter is designed for high precision applications where converting voltage signals into frequency signals is essential. The internal architecture includes a high-performance input amplifier that ensures low drift and high input impedance, making it suitable for interfacing with low-level signals from sensors such as thermocouples or strain gauges. The precision oscillator system generates a stable frequency output that is proportional to the input voltage, allowing for accurate signal conversion across a wide frequency range.
The device's ability to operate with a single supply voltage simplifies the design of power supply circuits, and the low quiescent current of 1.2 mA contributes to energy efficiency, making the AD537 ideal for battery-operated devices. The temperature-proportional output enhances its utility in temperature measurement applications, enabling easy integration with temperature control systems.
The output characteristics of the AD537 are particularly advantageous, as the square-wave output can drive multiple TTL loads, making it suitable for interfacing with digital circuits and microcontrollers. The robust construction, featuring hermetically sealed packages, ensures reliability in harsh environments, while the availability of different performance grades allows for flexibility in selecting the appropriate version based on the application's temperature requirements.
In summary, the AD537 is a versatile and reliable voltage-to-frequency converter that combines high accuracy, low power consumption, and excellent temperature stability, making it an ideal choice for a wide range of electronic applications.The AD537 is a monolithic V-F converter consisting of an input Amplifier a precision Oscillator system, an accurate internal reference generator and a high current output stage. Only a single external RC network is required to set up any full-scale (F. S. ) frequency up to 100 kHz and any F. S. input voltage up to 30 V. Linearity error is as low as 0 . 05% for 10 kHz F. S. , and operation is guaranteed over an 80 dB dynamic range. The overall temperature coefficient (excluding the effects of external components) is typically 30 ppm/C. The AD537 operates from a single supply of 5 V to 36 V and consumes only 1. 2 mA quiescent current. A temperature-proportional output, scaled to 1. 00 mV/K, enables the circuit to be used as a reliable temperature-to-frequency converter; in combination with the fixed reference output of 1.
00 V, offset scales such as 0C or 0F CAN be generated. The low drift (1V/C typ) input Amplifier allows operation directly from small signals (e. g. , thermocouples or strain gages) while offering a high (250 M(Ohm) input resistance. Unlike most V-F converters, the AD537 provides a square-wave output, and CAN drive up to 12 TTL loads, LEDs very long cables, etc. The excellent temperature characteristics and long-term stability of the AD537 are guaranteed by the primary bandgap reference generator and the low T.
C. silicon chromium thin film resistors used throughout. The device is available in either a TO-116 ceramic DIP or a TO-100 metal can; both are hermetically sealed packages. The AD537 is available in three performance/temperature grades; the J and K grades are specified for operation over the 0C to +70C range while the AD537S is specified for operation over the extended temperature range, -55C to +125C.
*Protected by Patent Nos. 3, 88, 963 and RE 20, 586. 🔗 External reference