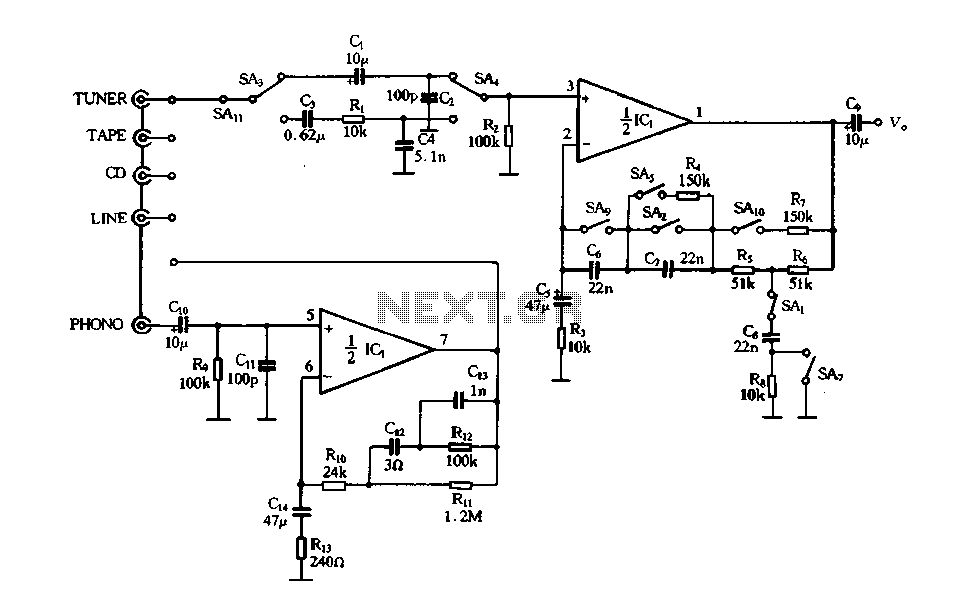
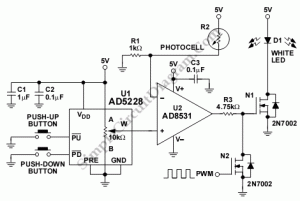
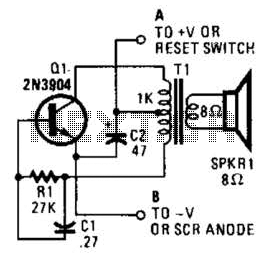
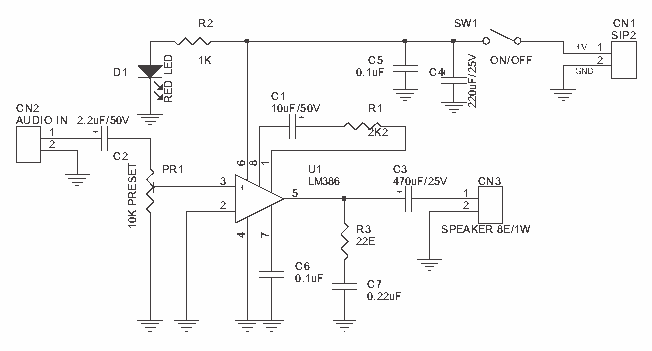
GaAsFET amplifier circuit

The control circuit is designed to operate by doubling a positive supply, which activates the first door when powered on and deactivates when the first drain is engaged, as illustrated in the accompanying figure. This circuit incorporates the LM123, a three-terminal positive voltage regulator, alongside a DC-DC converter. The output from this configuration supplies the drains and gates of a GaAsFET power relay used in a power amplifier. The controller output drives a three-terminal DC-DC converter, which exits through an N-channel MOSFET, effectively pulling the base of the series pass transistor (2N6107) to a level that turns it on. Additionally, the circuit is designed to supply Tum leak whenever the negative potential on the gate fails.
The circuit described is a sophisticated control mechanism that utilizes an LM123 voltage regulator to maintain stable output voltage levels while interfacing with a DC-DC converter. The integration of the LM123 allows for efficient voltage regulation, ensuring that the power supply remains consistent even under varying load conditions. The choice of a GaAsFET power relay enhances the performance of the power amplifier, providing high efficiency and fast switching capabilities.
The N-channel MOSFET serves as a critical component in the control circuit, enabling precise control over the base of the 2N6107 pass transistor. By pulling the base to an appropriate level, the MOSFET ensures that the transistor operates in the saturation region, allowing for maximum current flow and minimal heat dissipation. This configuration is essential for maintaining the reliability and longevity of the circuit.
Moreover, the circuit's ability to supply Tum leak during negative potential failures on the gate indicates a protective feature that enhances operational safety. This characteristic ensures that the circuit can handle unexpected conditions without compromising overall functionality.
In summary, this control circuit exemplifies a well-designed integration of components that work together to provide efficient power management and reliable operation in electronic applications, particularly in power amplification scenarios.The control circuit operates to double from a positive supply, which, when turned on the power of the first door. and goes off when the first drain as shown in FIG. This circuit integrates the LM123, a three-terminal positive regulator and a dc dc + converter, whose output power drains and gates of GaAsFET-power relay in a power amplifier.
The controller output drives a three-terminal DC + DC converter - which exit through an N-channel lFET properly so as to pull the base of the series pass transistor 2N6107 at a level to turn it on. The circuit will supply Tum leak every time the negative potential on the gate fails.
The circuit described is a sophisticated control mechanism that utilizes an LM123 voltage regulator to maintain stable output voltage levels while interfacing with a DC-DC converter. The integration of the LM123 allows for efficient voltage regulation, ensuring that the power supply remains consistent even under varying load conditions. The choice of a GaAsFET power relay enhances the performance of the power amplifier, providing high efficiency and fast switching capabilities.
The N-channel MOSFET serves as a critical component in the control circuit, enabling precise control over the base of the 2N6107 pass transistor. By pulling the base to an appropriate level, the MOSFET ensures that the transistor operates in the saturation region, allowing for maximum current flow and minimal heat dissipation. This configuration is essential for maintaining the reliability and longevity of the circuit.
Moreover, the circuit's ability to supply Tum leak during negative potential failures on the gate indicates a protective feature that enhances operational safety. This characteristic ensures that the circuit can handle unexpected conditions without compromising overall functionality.
In summary, this control circuit exemplifies a well-designed integration of components that work together to provide efficient power management and reliable operation in electronic applications, particularly in power amplification scenarios.The control circuit operates to double from a positive supply, which, when turned on the power of the first door. and goes off when the first drain as shown in FIG. This circuit integrates the LM123, a three-terminal positive regulator and a dc dc + converter, whose output power drains and gates of GaAsFET-power relay in a power amplifier.
The controller output drives a three-terminal DC + DC converter - which exit through an N-channel lFET properly so as to pull the base of the series pass transistor 2N6107 at a level to turn it on. The circuit will supply Tum leak every time the negative potential on the gate fails.