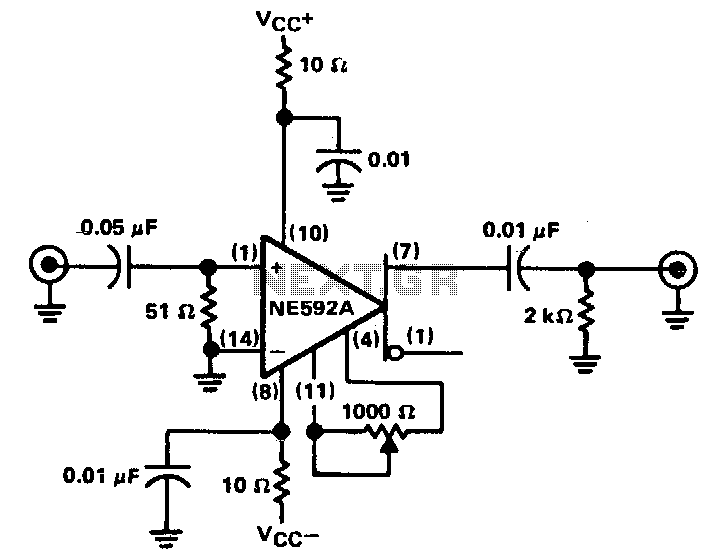
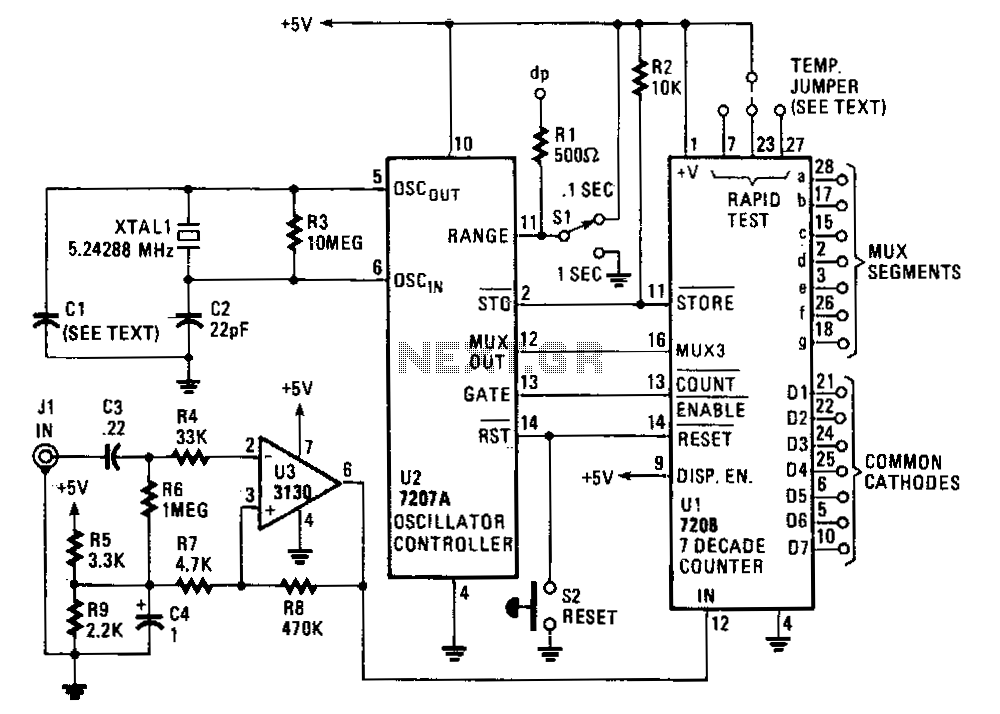
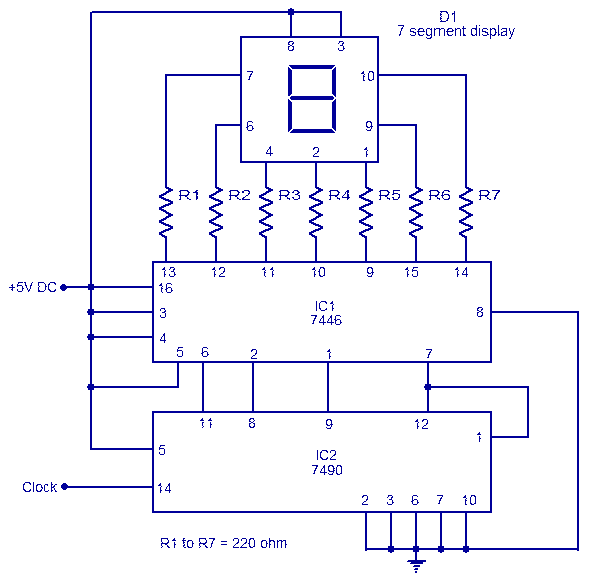
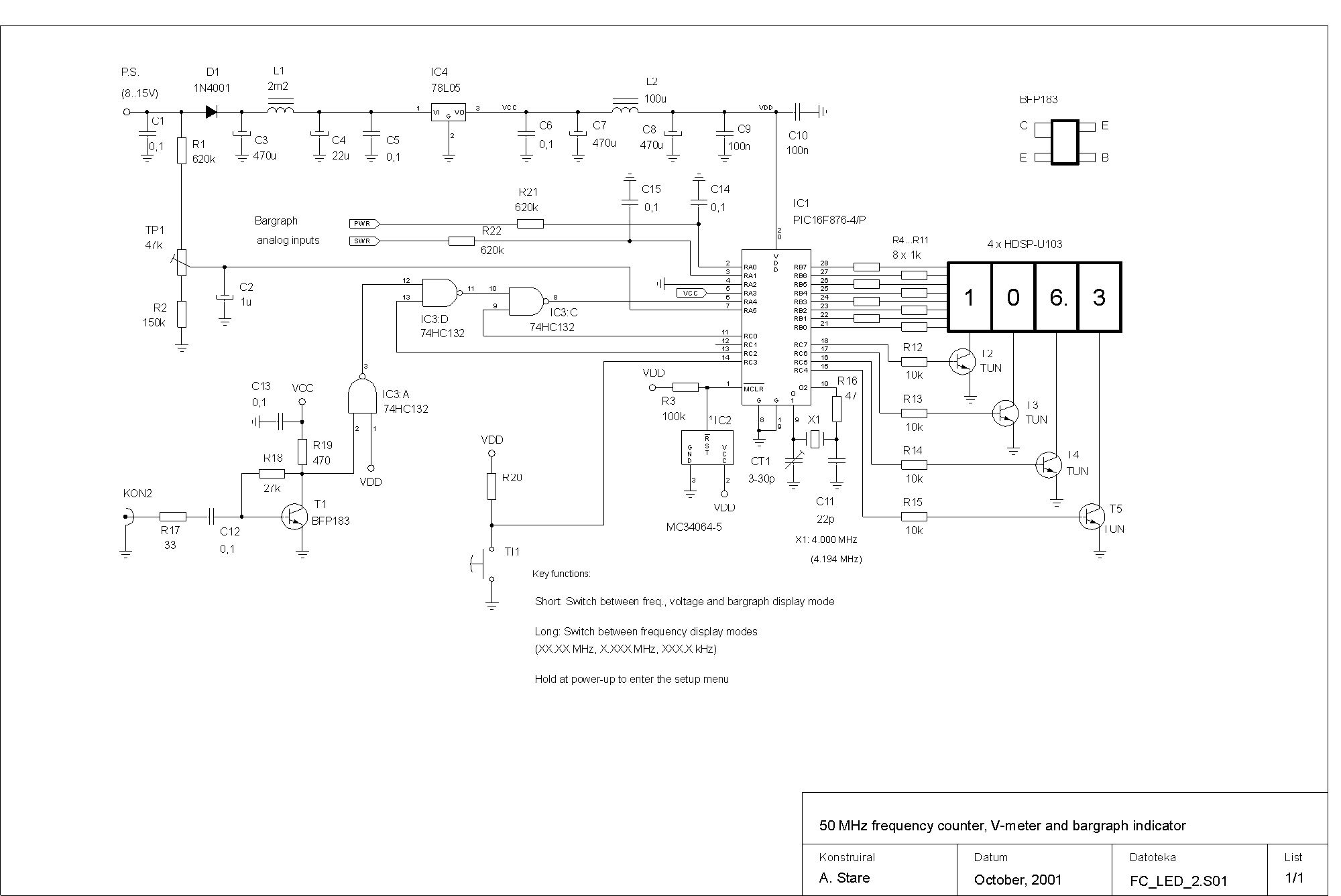
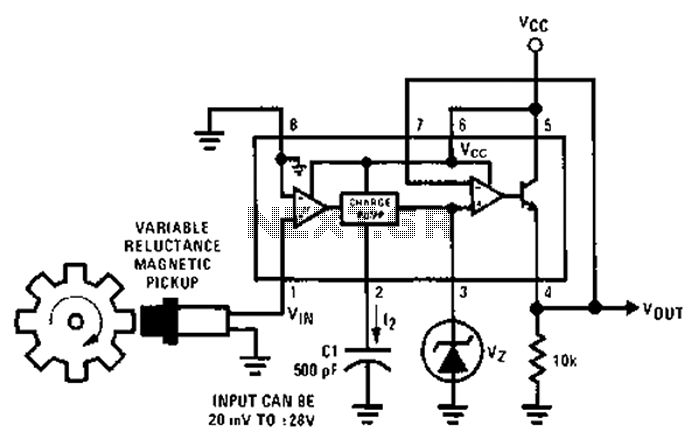
Geiger Counter Uses Cockroft-Walton Multiplier

The recent tsunami in Japan and the ongoing calamity at the Fukushima nuclear power plant has significantly increased sales of radiation meters.
The surge in demand for radiation meters can be attributed to heightened public awareness and concern regarding radiation exposure following the Fukushima incident. These devices are essential for measuring ionizing radiation levels, which can pose serious health risks. Radiation meters, also known as Geiger counters or dosimeters, are designed to detect alpha, beta, and gamma radiation, providing real-time readings that can inform users of their safety in contaminated areas.
Typically, radiation meters consist of a detection component, often a Geiger-Müller tube, which registers ionizing events and produces audible clicks or visual indicators corresponding to radiation levels. The output can be displayed in various units, such as microsieverts per hour (µSv/h) or counts per minute (CPM), allowing users to assess environmental conditions effectively.
In response to the increased demand, manufacturers may focus on enhancing the sensitivity and accuracy of these devices, integrating features such as data logging, Bluetooth connectivity for mobile device integration, and improved user interfaces. This evolution in design aims to cater to a broader audience, including emergency responders, environmental scientists, and concerned citizens, thus ensuring that individuals have the necessary tools to monitor radiation levels in their surroundings.The recent tsunami in Japan and the on-going calamity with the Fukushima nuclear power plant has apparently greatly increased sales of radiation meters, n.. 🔗 External reference
The surge in demand for radiation meters can be attributed to heightened public awareness and concern regarding radiation exposure following the Fukushima incident. These devices are essential for measuring ionizing radiation levels, which can pose serious health risks. Radiation meters, also known as Geiger counters or dosimeters, are designed to detect alpha, beta, and gamma radiation, providing real-time readings that can inform users of their safety in contaminated areas.
Typically, radiation meters consist of a detection component, often a Geiger-Müller tube, which registers ionizing events and produces audible clicks or visual indicators corresponding to radiation levels. The output can be displayed in various units, such as microsieverts per hour (µSv/h) or counts per minute (CPM), allowing users to assess environmental conditions effectively.
In response to the increased demand, manufacturers may focus on enhancing the sensitivity and accuracy of these devices, integrating features such as data logging, Bluetooth connectivity for mobile device integration, and improved user interfaces. This evolution in design aims to cater to a broader audience, including emergency responders, environmental scientists, and concerned citizens, thus ensuring that individuals have the necessary tools to monitor radiation levels in their surroundings.The recent tsunami in Japan and the on-going calamity with the Fukushima nuclear power plant has apparently greatly increased sales of radiation meters, n.. 🔗 External reference