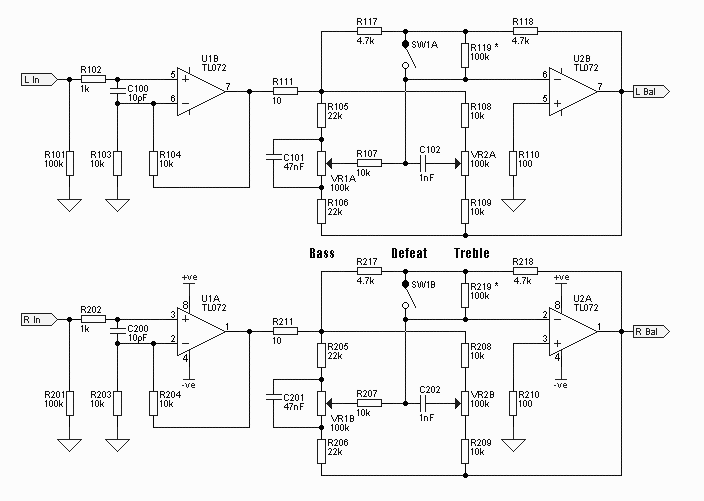
General-Purpose AF Power Amplifier
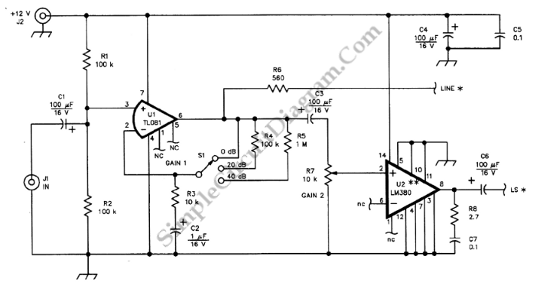
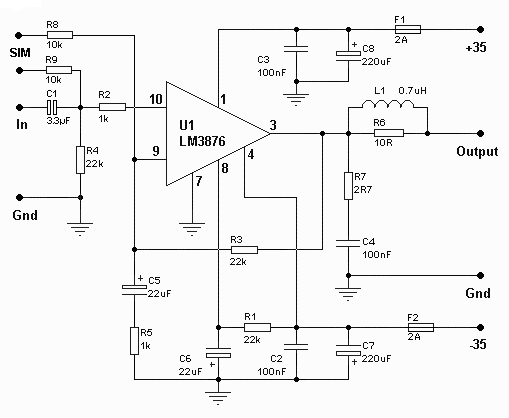
This is a schematic diagram of a general-purpose audio frequency (AF) amplifier circuit. The circuit employs inexpensive 1/4-W resistors, as high precision is not required.
The general-purpose audio frequency (AF) amplifier circuit is designed to amplify audio signals for various applications, such as audio processing, sound reinforcement, and signal conditioning. The schematic typically includes several key components: resistors, capacitors, transistors or operational amplifiers, and possibly diodes for signal clipping or protection.
The use of 1/4-W resistors indicates a focus on cost-effectiveness while maintaining adequate performance for audio applications. These resistors are suitable for handling the power levels typically encountered in audio circuits without the need for high precision components.
The circuit may consist of a multi-stage amplification configuration, where each stage contributes to the overall gain. The input stage usually employs a transistor or an operational amplifier configured as a non-inverting amplifier to provide initial gain and impedance matching. Following this, additional stages may include further amplification and tone control elements, allowing for adjustments to the frequency response of the audio signal.
Capacitors in the circuit serve various purposes, such as coupling and decoupling signals between stages, filtering out unwanted noise, and stabilizing the power supply. The choice of capacitor types, such as electrolytic or ceramic, can influence the performance characteristics of the amplifier, particularly in terms of frequency response and transient response.
Overall, this schematic serves as a fundamental design for audio amplification, suitable for hobbyist projects or educational purposes, where the emphasis is on simplicity and functionality rather than precision and high-end performance.This is a schematic diagram of general-purpose audio frequency (AF) amplifier circuit. This circuit uses cheap 1/4-W resistors, no high precision needed so.. 🔗 External reference
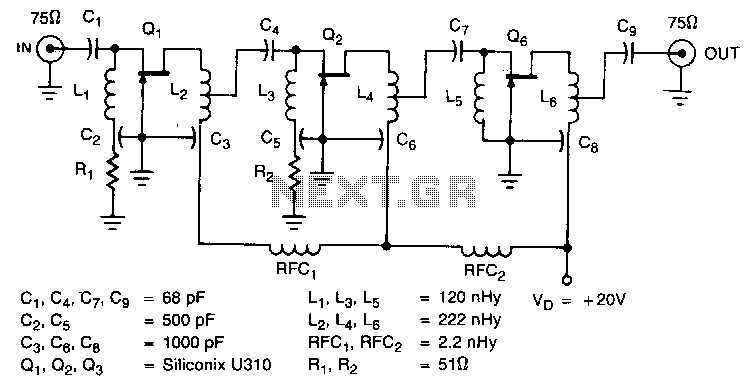
The general-purpose audio frequency (AF) amplifier circuit is designed to amplify audio signals for various applications, such as audio processing, sound reinforcement, and signal conditioning. The schematic typically includes several key components: resistors, capacitors, transistors or operational amplifiers, and possibly diodes for signal clipping or protection.
The use of 1/4-W resistors indicates a focus on cost-effectiveness while maintaining adequate performance for audio applications. These resistors are suitable for handling the power levels typically encountered in audio circuits without the need for high precision components.
The circuit may consist of a multi-stage amplification configuration, where each stage contributes to the overall gain. The input stage usually employs a transistor or an operational amplifier configured as a non-inverting amplifier to provide initial gain and impedance matching. Following this, additional stages may include further amplification and tone control elements, allowing for adjustments to the frequency response of the audio signal.
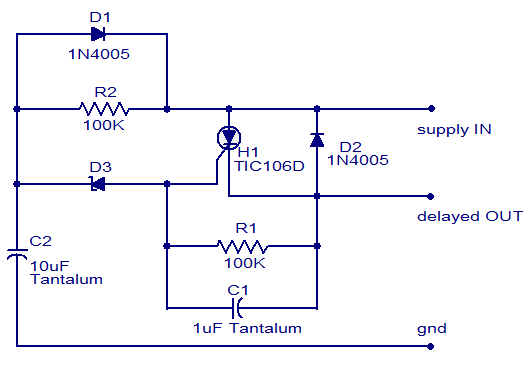
Capacitors in the circuit serve various purposes, such as coupling and decoupling signals between stages, filtering out unwanted noise, and stabilizing the power supply. The choice of capacitor types, such as electrolytic or ceramic, can influence the performance characteristics of the amplifier, particularly in terms of frequency response and transient response.
Overall, this schematic serves as a fundamental design for audio amplification, suitable for hobbyist projects or educational purposes, where the emphasis is on simplicity and functionality rather than precision and high-end performance.This is a schematic diagram of general-purpose audio frequency (AF) amplifier circuit. This circuit uses cheap 1/4-W resistors, no high precision needed so.. 🔗 External reference