ghz oscillator
A low-noise block downconverter (LNB) is a crucial component in a satellite receiver system, tasked with converting the relatively high frequency of the received signal into the more manageable L-Band. An examination of its internal workings reveals its design and functionality.
The low-noise block downconverter (LNB) is an essential device in satellite communication systems, primarily used to receive signals from satellites and convert them into a lower frequency range for further processing. The operation of an LNB involves several key stages, including signal amplification, frequency conversion, and filtering.
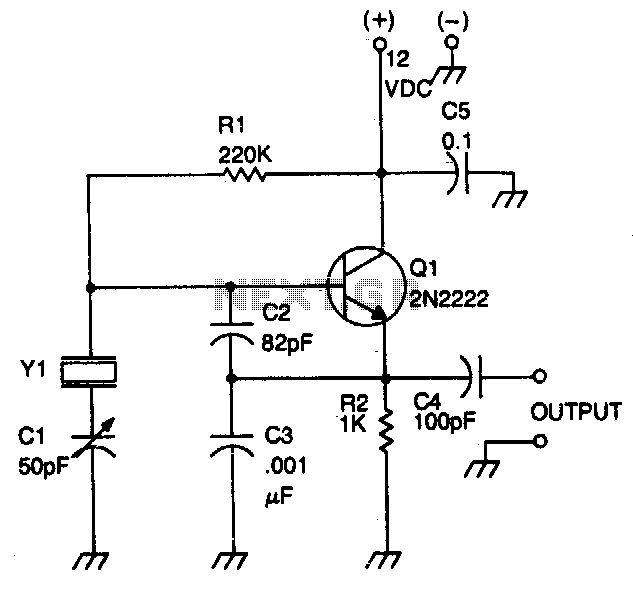
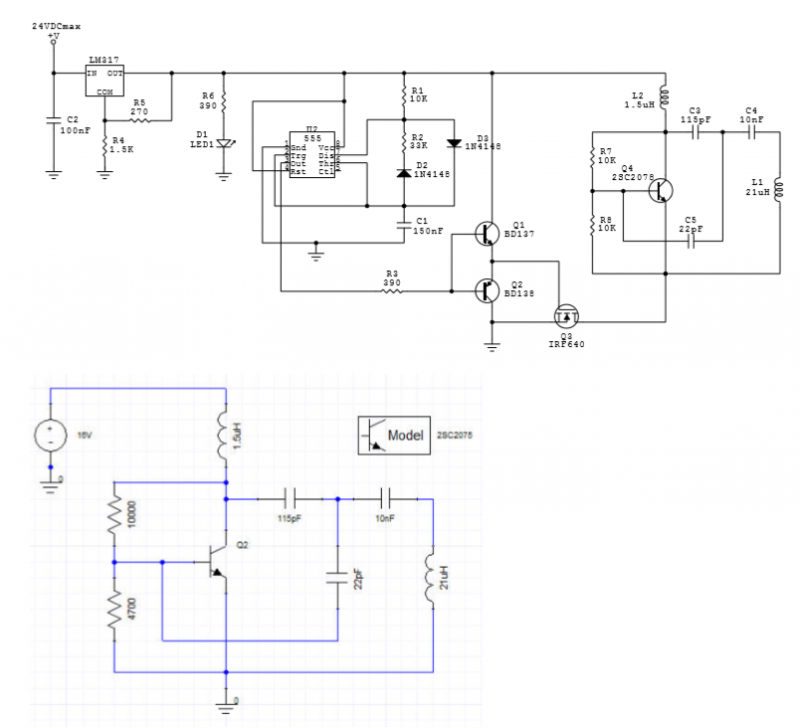
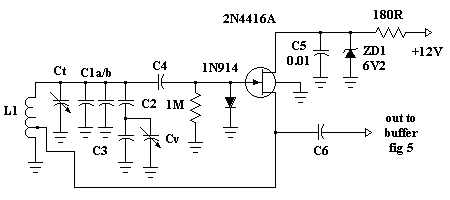
At the core of the LNB is a low-noise amplifier (LNA), which amplifies the weak signals received from the satellite dish. The LNA is designed to minimize the addition of noise to the signal, ensuring that the integrity of the received data is preserved. The amplified signal is then fed into a mixer, where it is combined with a local oscillator (LO) signal. This mixing process generates an intermediate frequency (IF) that falls within the L-Band range, typically between 950 MHz and 2150 MHz.
The choice of the local oscillator frequency is critical, as it determines the specific frequency conversion that takes place. The output from the mixer is then passed through a bandpass filter, which selectively allows the desired frequency range to pass while attenuating any unwanted signals and noise. This filtering process is vital for maintaining signal quality and ensuring that only the relevant information is transmitted to the satellite receiver.
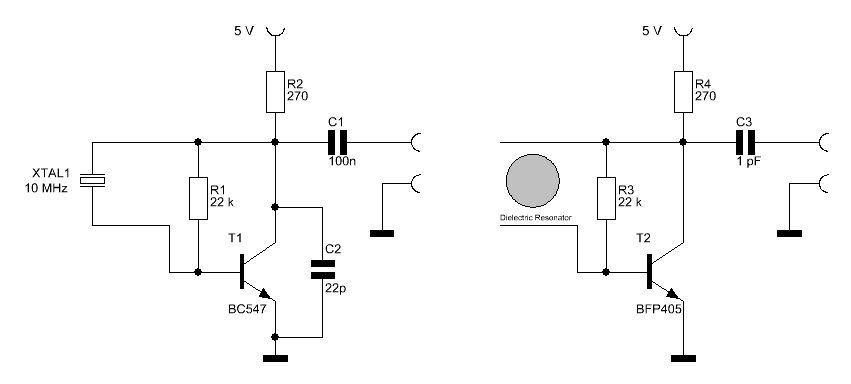
The design of an LNB also includes components such as a dielectric resonator, which helps stabilize the local oscillator frequency, and a phase-locked loop (PLL) circuit that provides frequency control. The overall compact design of the LNB allows it to be mounted directly on the satellite dish, minimizing signal loss and improving performance.
In summary, the low-noise block downconverter plays a fundamental role in satellite communication by effectively converting high-frequency signals to a lower frequency range, thereby facilitating the transmission of data to satellite receivers. Its design incorporates advanced technologies to ensure low noise levels, high gain, and efficient frequency conversion, making it a critical component in modern satellite systems.A low-noise block downconverter (LNB) is a key element in a satellite receiver system and is responsible for converting the relatively high frequency of the received signal into the more convenient L-Band. But how do they work and what do they look like on the inside Let`s have a look! From a theoretical standpoint, a [ ] 🔗 External reference
The low-noise block downconverter (LNB) is an essential device in satellite communication systems, primarily used to receive signals from satellites and convert them into a lower frequency range for further processing. The operation of an LNB involves several key stages, including signal amplification, frequency conversion, and filtering.
At the core of the LNB is a low-noise amplifier (LNA), which amplifies the weak signals received from the satellite dish. The LNA is designed to minimize the addition of noise to the signal, ensuring that the integrity of the received data is preserved. The amplified signal is then fed into a mixer, where it is combined with a local oscillator (LO) signal. This mixing process generates an intermediate frequency (IF) that falls within the L-Band range, typically between 950 MHz and 2150 MHz.
The choice of the local oscillator frequency is critical, as it determines the specific frequency conversion that takes place. The output from the mixer is then passed through a bandpass filter, which selectively allows the desired frequency range to pass while attenuating any unwanted signals and noise. This filtering process is vital for maintaining signal quality and ensuring that only the relevant information is transmitted to the satellite receiver.
The design of an LNB also includes components such as a dielectric resonator, which helps stabilize the local oscillator frequency, and a phase-locked loop (PLL) circuit that provides frequency control. The overall compact design of the LNB allows it to be mounted directly on the satellite dish, minimizing signal loss and improving performance.
In summary, the low-noise block downconverter plays a fundamental role in satellite communication by effectively converting high-frequency signals to a lower frequency range, thereby facilitating the transmission of data to satellite receivers. Its design incorporates advanced technologies to ensure low noise levels, high gain, and efficient frequency conversion, making it a critical component in modern satellite systems.A low-noise block downconverter (LNB) is a key element in a satellite receiver system and is responsible for converting the relatively high frequency of the received signal into the more convenient L-Band. But how do they work and what do they look like on the inside Let`s have a look! From a theoretical standpoint, a [ ] 🔗 External reference