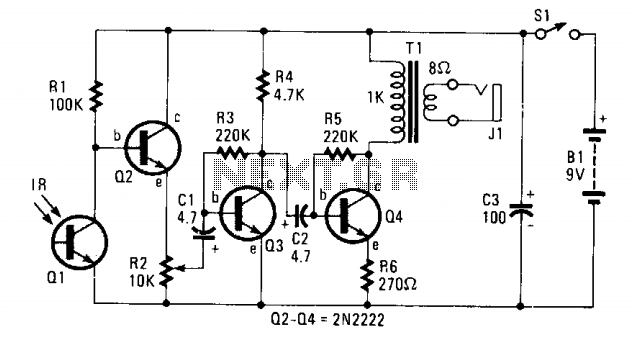
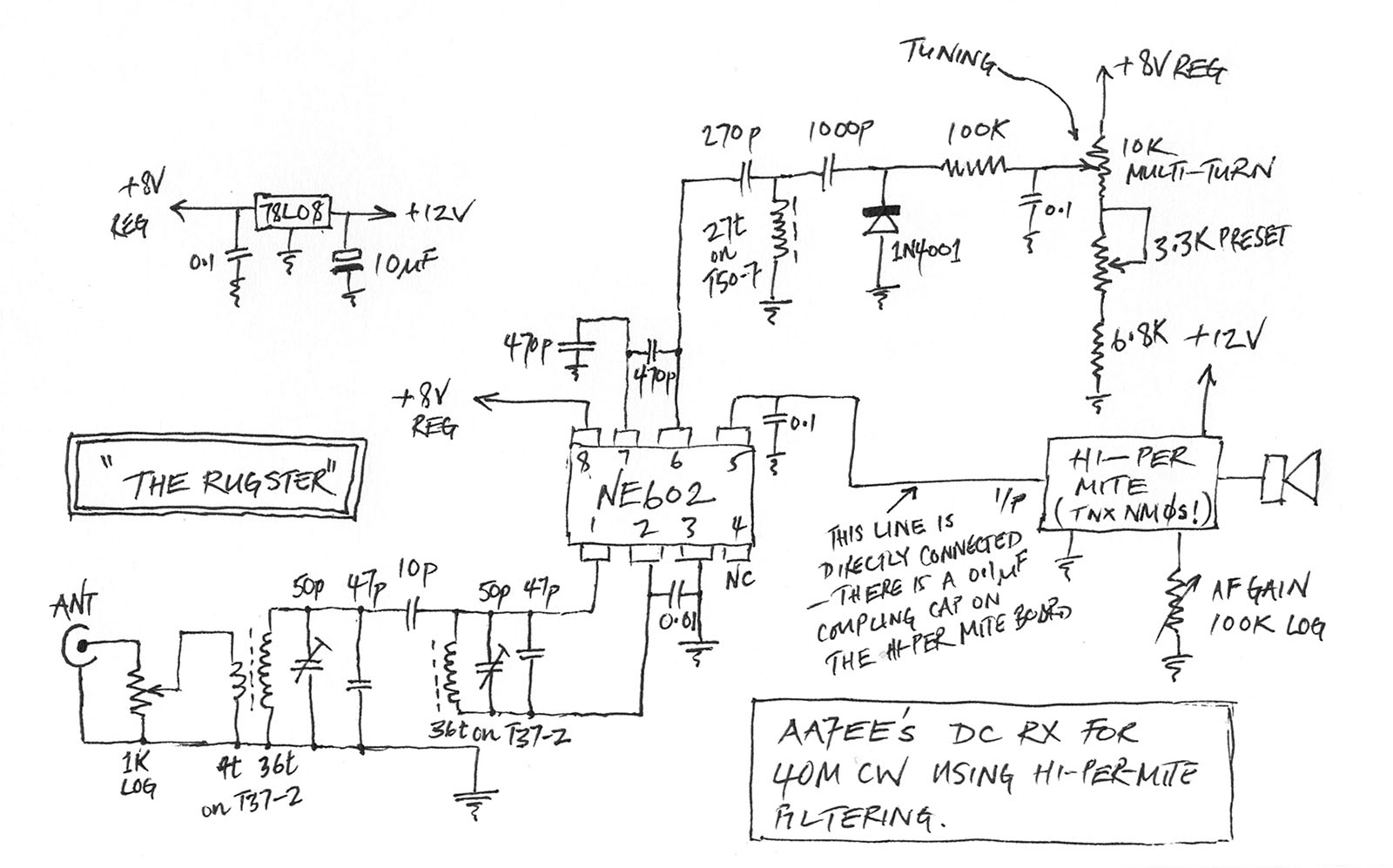
GPS receiver
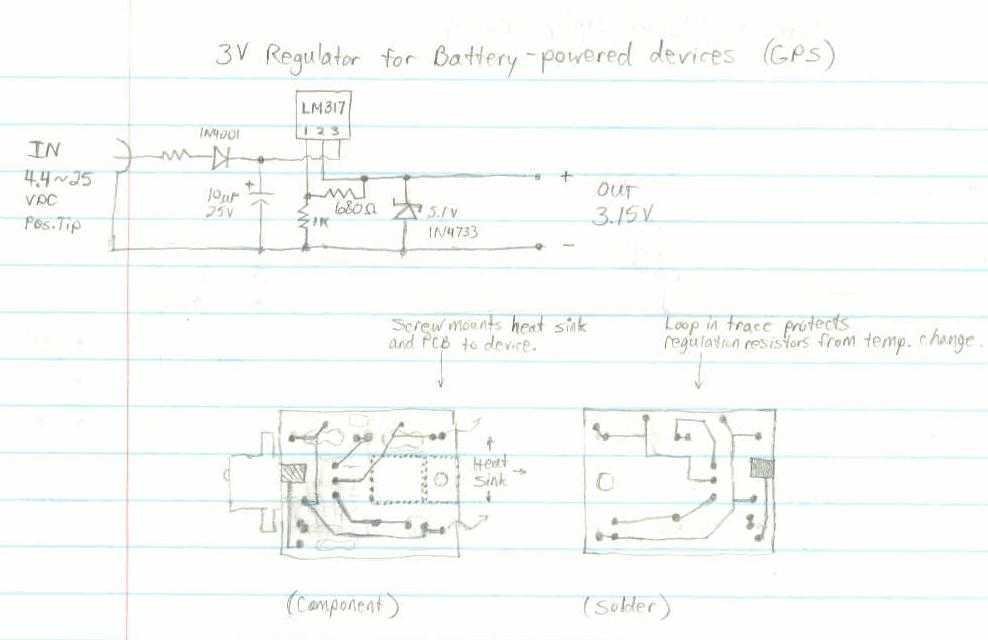
This GPS receiver is powered by 2 AA batteries. They are only strong enough for the GPS to stay on for about two hours, and this seems like quite a waste. I would like to be able to use a larger battery, and sometimes even an AC adapter.
The described GPS receiver circuit utilizes two AA batteries as its primary power source. The nominal voltage of two AA batteries in series is approximately 3V, which is typically sufficient for low-power GPS modules. However, the limited capacity of AA batteries results in a relatively short operational time of about two hours, indicating that the current draw of the GPS receiver is significant compared to the battery's energy storage.
To enhance the operational time and versatility of the GPS receiver, it is advisable to design a power management circuit that accommodates a larger battery or an AC adapter. This can be achieved by integrating a DC-DC boost converter that can step up the voltage from a larger battery pack (for instance, a lithium-ion battery) or directly from an AC adapter to the required operating voltage of the GPS module.
The power management circuit should include the following components:
1. **Battery Management System (BMS)**: If a lithium-ion battery pack is utilized, a BMS is essential for monitoring battery health, balancing the cells, and providing overcharge and over-discharge protection.
2. **DC-DC Boost Converter**: This component will convert the higher voltage from the battery or AC adapter to the appropriate voltage level required by the GPS receiver. The boost converter should be selected based on the current requirements of the GPS module to ensure efficient operation.
3. **Power Supply Input**: For the AC adapter, a rectifier circuit will be necessary to convert AC voltage to DC. This can include a transformer if the input AC voltage is higher than the desired output voltage.
4. **Capacitors and Inductors**: These passive components will be used in the boost converter circuit for smoothing and filtering purposes, ensuring stable voltage output to the GPS module.
5. **Protection Diodes**: To prevent reverse polarity connections and protect the circuit from potential damage, diodes should be included in the design.
By implementing this revised power supply system, the GPS receiver can achieve extended operational time and flexibility, allowing for both portable use with larger batteries and stationary use with an AC adapter. The overall efficiency of the circuit will improve, reducing energy waste and enhancing the user experience.This GPS receiver is powered by 2 AA batteries. They are only strong enough for the GPS to stay on for about two hours, and this seems like quite a waste. I would like to be able to use a larger battery, and sometimes even an AC adapter. 🔗 External reference
The described GPS receiver circuit utilizes two AA batteries as its primary power source. The nominal voltage of two AA batteries in series is approximately 3V, which is typically sufficient for low-power GPS modules. However, the limited capacity of AA batteries results in a relatively short operational time of about two hours, indicating that the current draw of the GPS receiver is significant compared to the battery's energy storage.
To enhance the operational time and versatility of the GPS receiver, it is advisable to design a power management circuit that accommodates a larger battery or an AC adapter. This can be achieved by integrating a DC-DC boost converter that can step up the voltage from a larger battery pack (for instance, a lithium-ion battery) or directly from an AC adapter to the required operating voltage of the GPS module.
The power management circuit should include the following components:
1. **Battery Management System (BMS)**: If a lithium-ion battery pack is utilized, a BMS is essential for monitoring battery health, balancing the cells, and providing overcharge and over-discharge protection.
2. **DC-DC Boost Converter**: This component will convert the higher voltage from the battery or AC adapter to the appropriate voltage level required by the GPS receiver. The boost converter should be selected based on the current requirements of the GPS module to ensure efficient operation.
3. **Power Supply Input**: For the AC adapter, a rectifier circuit will be necessary to convert AC voltage to DC. This can include a transformer if the input AC voltage is higher than the desired output voltage.
4. **Capacitors and Inductors**: These passive components will be used in the boost converter circuit for smoothing and filtering purposes, ensuring stable voltage output to the GPS module.
5. **Protection Diodes**: To prevent reverse polarity connections and protect the circuit from potential damage, diodes should be included in the design.
By implementing this revised power supply system, the GPS receiver can achieve extended operational time and flexibility, allowing for both portable use with larger batteries and stationary use with an AC adapter. The overall efficiency of the circuit will improve, reducing energy waste and enhancing the user experience.This GPS receiver is powered by 2 AA batteries. They are only strong enough for the GPS to stay on for about two hours, and this seems like quite a waste. I would like to be able to use a larger battery, and sometimes even an AC adapter. 🔗 External reference