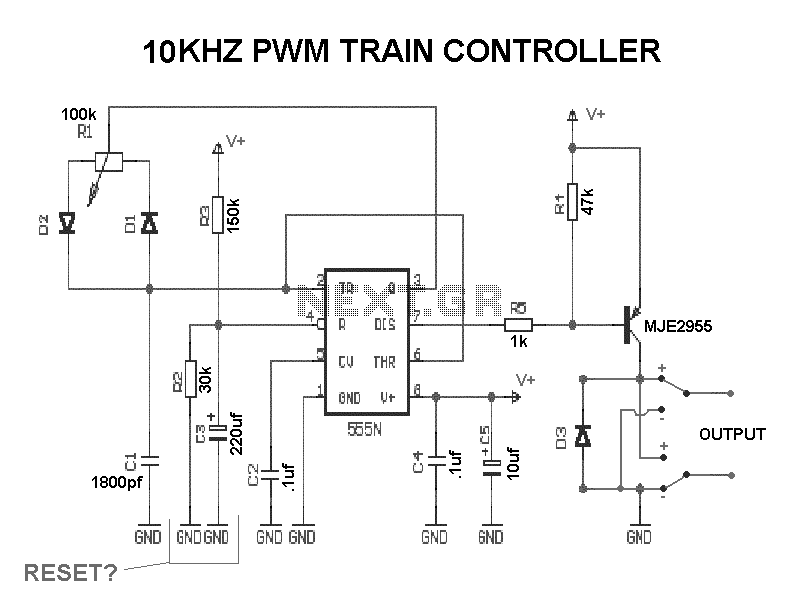
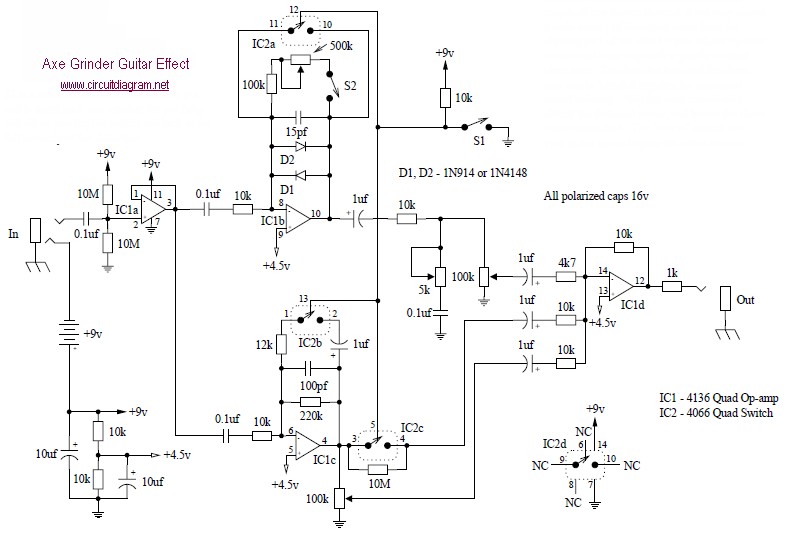
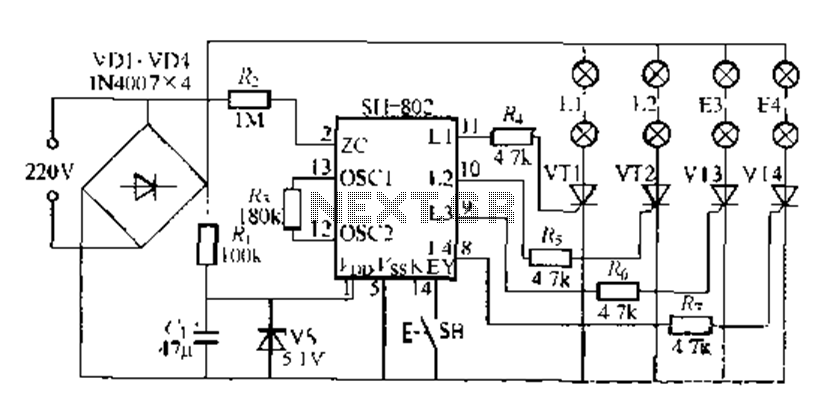
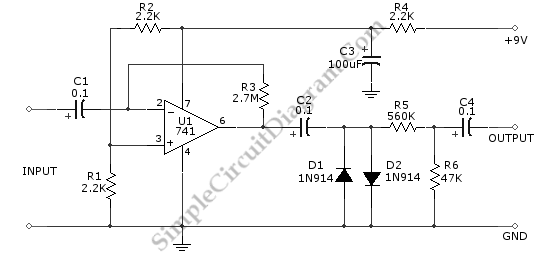
Guitar Circuits Amps and Effects
A collection of guitar fuzz, preamp, and operational amplifier (op-amp) electronic circuits and schematics designed for various guitar effects and distortion effects.
This compilation includes a diverse range of electronic circuits that cater to guitarists seeking to enhance their sound with fuzz, distortion, and preamplification effects. Each circuit is designed to modify the audio signal in unique ways, allowing for a wide array of tonal possibilities.
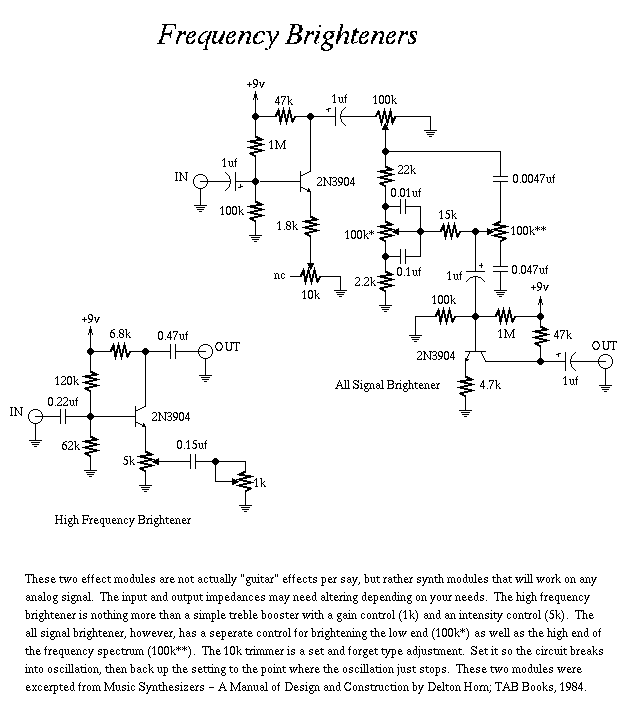
1. **Guitar Fuzz Circuits**: Fuzz circuits are known for their ability to create a rich, saturated sound that adds warmth and character to guitar tones. Common designs include the classic Fuzz Face, which utilizes transistors to achieve its signature sound, and the Big Muff, known for its sustain and harmonically rich distortion. These circuits typically consist of a gain stage, followed by clipping diodes that produce the desired fuzz effect.
2. **Preamp Circuits**: Preamp circuits serve to boost the guitar signal to line level, making them essential for driving amplifiers or effects pedals. They can be designed using op-amps or discrete transistor configurations. A common approach is to use an op-amp in a non-inverting configuration, providing high input impedance and low output impedance, which preserves the tone of the guitar while amplifying the signal.
3. **Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) Circuits**: Op-amps are versatile components that can be used in various configurations to achieve different effects. They can be employed in filters, mixers, and gain stages. For example, an op-amp can be configured as a low-pass filter to remove high-frequency noise, or as a summing amplifier to combine multiple signals. Utilizing feedback and gain control, op-amps can shape the audio signal in numerous ways, making them invaluable in the design of guitar effects.
4. **Distortion Effects**: Distortion circuits generally combine elements of fuzz and overdrive to create a more aggressive sound. They often incorporate both clipping diodes and gain stages to achieve a range of distortion characteristics, from subtle warmth to heavy saturation. Popular designs include the Tube Screamer, which utilizes op-amps to emulate the warmth of a tube amplifier.
These circuits can be implemented on printed circuit boards (PCBs) or breadboards for prototyping. Each schematic typically includes component values, pin configurations, and layout guidelines to assist in the construction process. Comprehensive knowledge of electronic components, soldering techniques, and circuit analysis is essential for successful implementation and troubleshooting of these guitar effects circuits.List of Guitar Fuzz, PreAmp, OpAmp electronic circuits and electronic schematics for a variety of Guitar effects and distortion fx.. 🔗 External reference
This compilation includes a diverse range of electronic circuits that cater to guitarists seeking to enhance their sound with fuzz, distortion, and preamplification effects. Each circuit is designed to modify the audio signal in unique ways, allowing for a wide array of tonal possibilities.
1. **Guitar Fuzz Circuits**: Fuzz circuits are known for their ability to create a rich, saturated sound that adds warmth and character to guitar tones. Common designs include the classic Fuzz Face, which utilizes transistors to achieve its signature sound, and the Big Muff, known for its sustain and harmonically rich distortion. These circuits typically consist of a gain stage, followed by clipping diodes that produce the desired fuzz effect.
2. **Preamp Circuits**: Preamp circuits serve to boost the guitar signal to line level, making them essential for driving amplifiers or effects pedals. They can be designed using op-amps or discrete transistor configurations. A common approach is to use an op-amp in a non-inverting configuration, providing high input impedance and low output impedance, which preserves the tone of the guitar while amplifying the signal.
3. **Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) Circuits**: Op-amps are versatile components that can be used in various configurations to achieve different effects. They can be employed in filters, mixers, and gain stages. For example, an op-amp can be configured as a low-pass filter to remove high-frequency noise, or as a summing amplifier to combine multiple signals. Utilizing feedback and gain control, op-amps can shape the audio signal in numerous ways, making them invaluable in the design of guitar effects.
4. **Distortion Effects**: Distortion circuits generally combine elements of fuzz and overdrive to create a more aggressive sound. They often incorporate both clipping diodes and gain stages to achieve a range of distortion characteristics, from subtle warmth to heavy saturation. Popular designs include the Tube Screamer, which utilizes op-amps to emulate the warmth of a tube amplifier.
These circuits can be implemented on printed circuit boards (PCBs) or breadboards for prototyping. Each schematic typically includes component values, pin configurations, and layout guidelines to assist in the construction process. Comprehensive knowledge of electronic components, soldering techniques, and circuit analysis is essential for successful implementation and troubleshooting of these guitar effects circuits.List of Guitar Fuzz, PreAmp, OpAmp electronic circuits and electronic schematics for a variety of Guitar effects and distortion fx.. 🔗 External reference