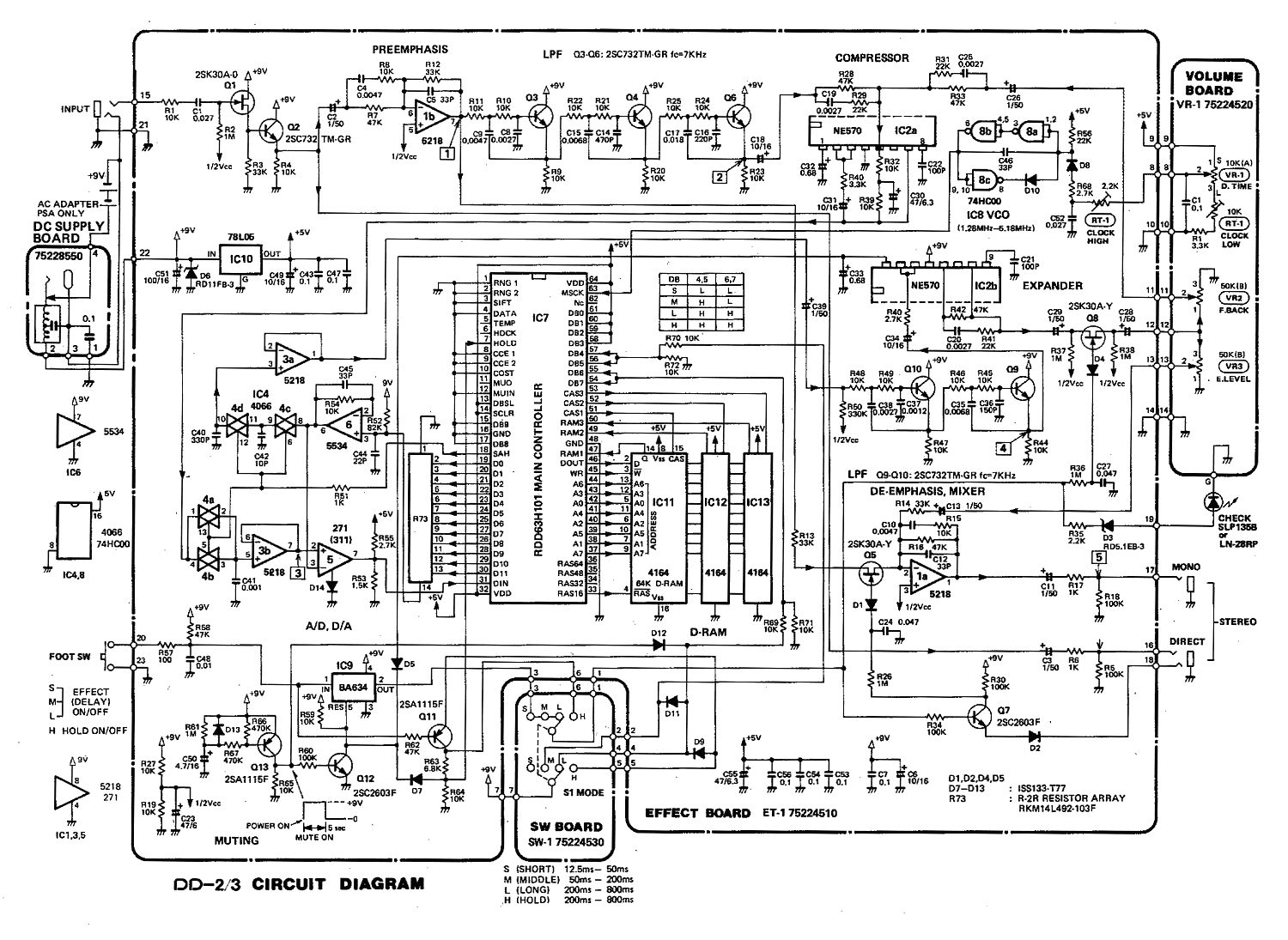
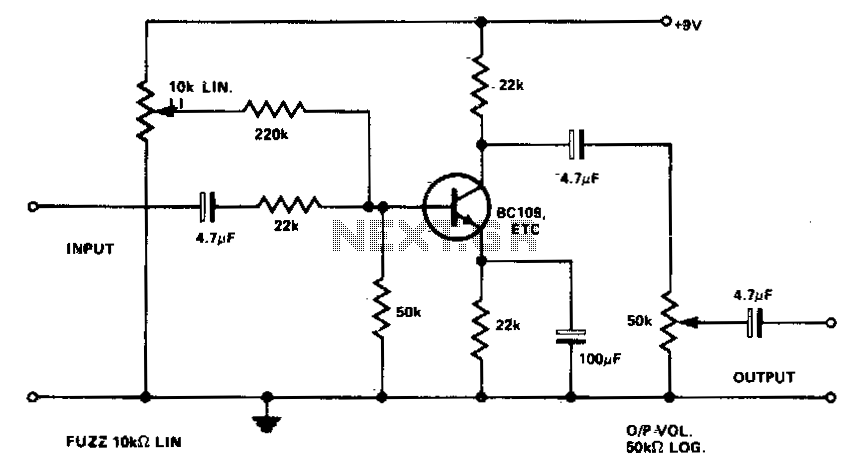
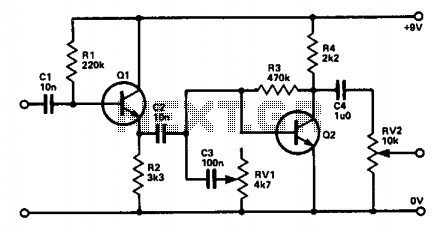
Guitar fuzz
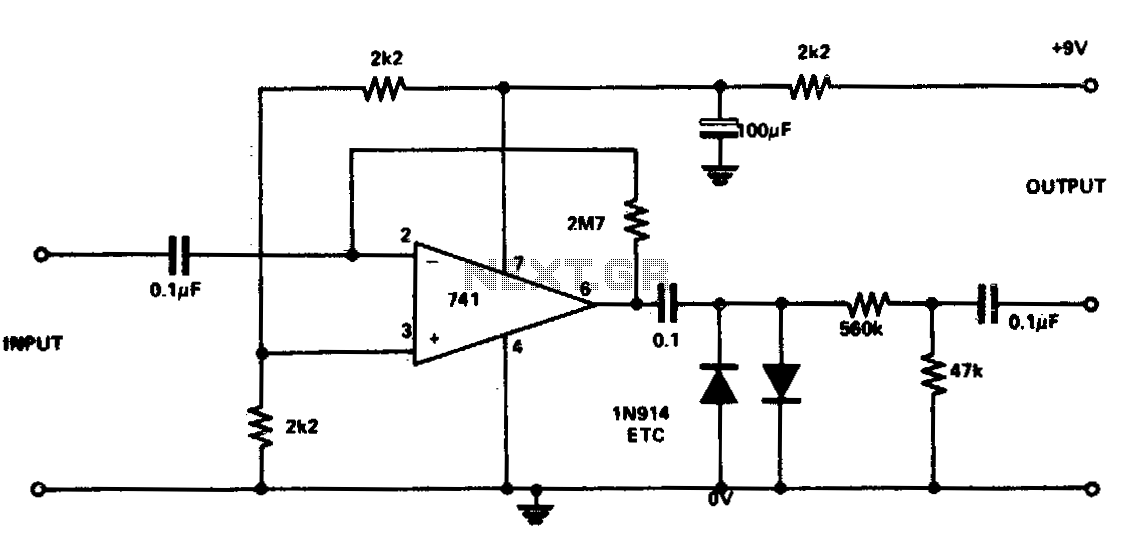
The 741 operational amplifier has a maximum gain of 20,000. However, the circuit is designed to amplify the gain to 2,700,000, resulting in output distortion. This distortion creates a fuzz effect. The two diodes in the circuit clip the output to reduce the level, which is further lowered by a potential divider. Additionally, this circuit sustains the notes through clipping, producing a completely new sound.
The circuit utilizes a 741 operational amplifier, known for its versatility in various applications, including audio processing. By configuring the amplifier to achieve a gain of 2,700,000, the circuit intentionally pushes the operational limits of the IC, resulting in significant distortion. This distortion is a desirable characteristic in certain audio effects, particularly in electric guitar applications, where it contributes to the iconic fuzz sound.
The inclusion of two diodes serves a critical function in the circuit. They are placed in such a manner that they clip the output signal when it exceeds a certain threshold, effectively limiting the amplitude. This clipping action not only reduces the overall output level but also introduces harmonic distortion, which enriches the sound and adds texture. The potential divider further attenuates the signal, allowing for greater control over the output level and ensuring that the distortion remains within a manageable range.
Moreover, the circuit's ability to sustain notes through clipping is noteworthy. When the output signal is clipped, it creates a sustain effect, allowing notes to linger longer than they would in a standard amplifier configuration. This characteristic is particularly appealing in musical contexts, where prolonged notes can enhance the overall musical expression. The combination of high gain, diode clipping, and potential division results in a unique sound profile that distinguishes this circuit from traditional amplifier designs.
Overall, the design of this circuit exemplifies how operational amplifiers can be creatively employed to generate distinctive audio effects, demonstrating the intersection of electronics and music production.The 741 has a maximum gain of 20,000, but the circuit is so designed that the IC"s gain is 2,700,000 which then distorts the output. This distortion gives the fuzz effect. The two diodes clip the output to drop the level, also lowered by the potential divider This circuit also sustains the notes, due to clipping, giving a totally new sound.
The circuit utilizes a 741 operational amplifier, known for its versatility in various applications, including audio processing. By configuring the amplifier to achieve a gain of 2,700,000, the circuit intentionally pushes the operational limits of the IC, resulting in significant distortion. This distortion is a desirable characteristic in certain audio effects, particularly in electric guitar applications, where it contributes to the iconic fuzz sound.
The inclusion of two diodes serves a critical function in the circuit. They are placed in such a manner that they clip the output signal when it exceeds a certain threshold, effectively limiting the amplitude. This clipping action not only reduces the overall output level but also introduces harmonic distortion, which enriches the sound and adds texture. The potential divider further attenuates the signal, allowing for greater control over the output level and ensuring that the distortion remains within a manageable range.
Moreover, the circuit's ability to sustain notes through clipping is noteworthy. When the output signal is clipped, it creates a sustain effect, allowing notes to linger longer than they would in a standard amplifier configuration. This characteristic is particularly appealing in musical contexts, where prolonged notes can enhance the overall musical expression. The combination of high gain, diode clipping, and potential division results in a unique sound profile that distinguishes this circuit from traditional amplifier designs.
Overall, the design of this circuit exemplifies how operational amplifiers can be creatively employed to generate distinctive audio effects, demonstrating the intersection of electronics and music production.The 741 has a maximum gain of 20,000, but the circuit is so designed that the IC"s gain is 2,700,000 which then distorts the output. This distortion gives the fuzz effect. The two diodes clip the output to drop the level, also lowered by the potential divider This circuit also sustains the notes, due to clipping, giving a totally new sound.