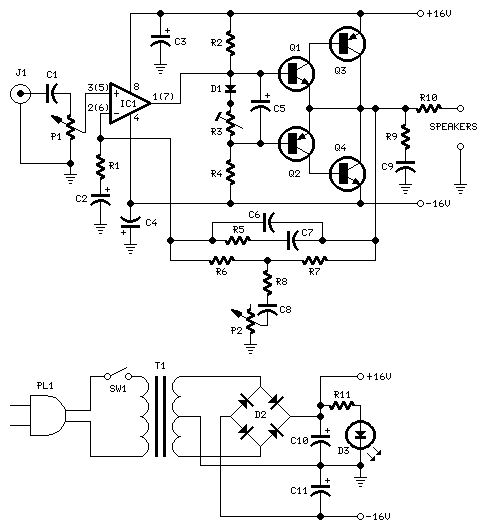
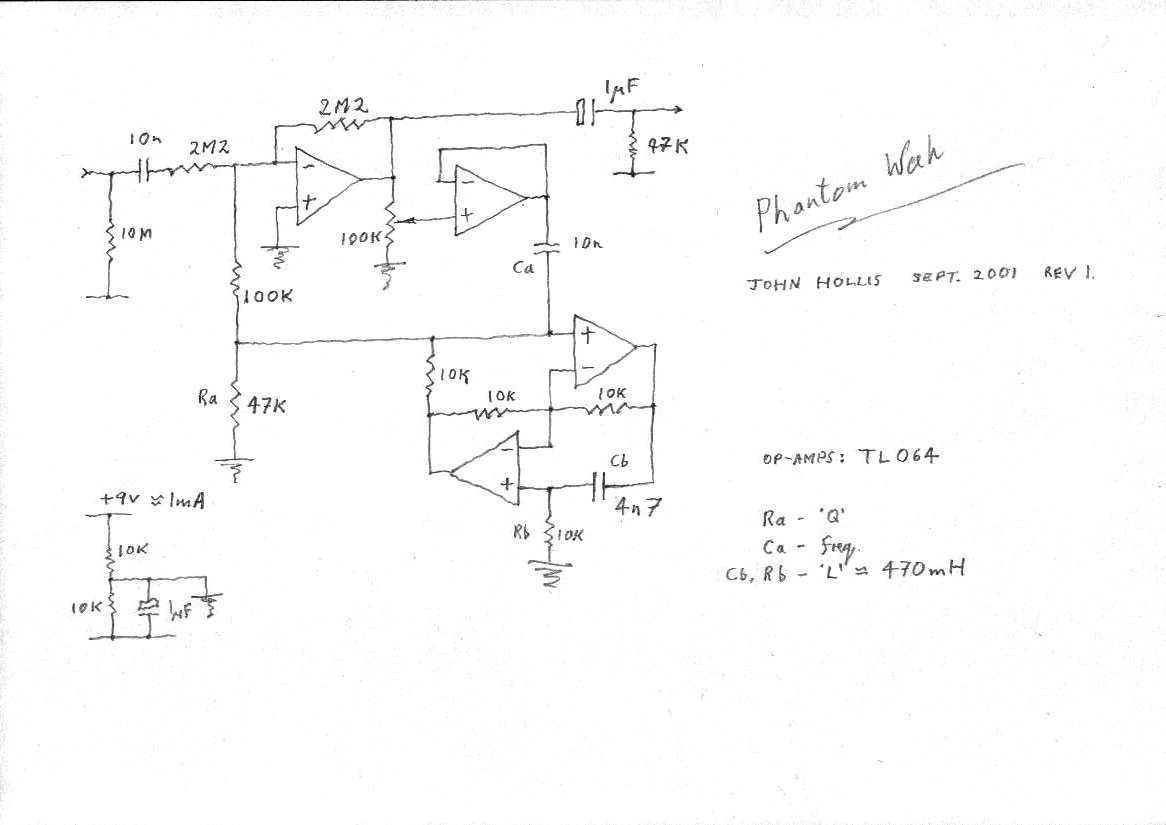
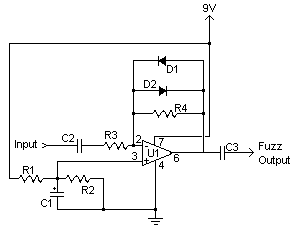
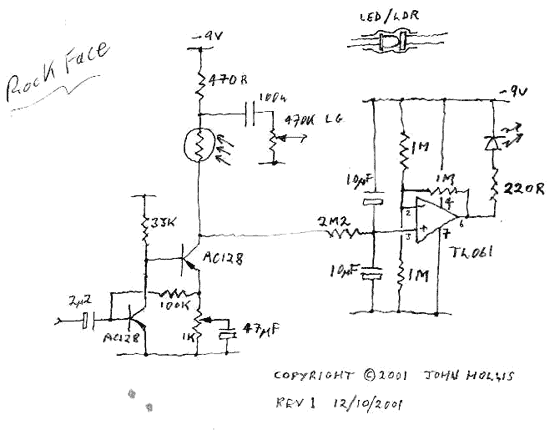
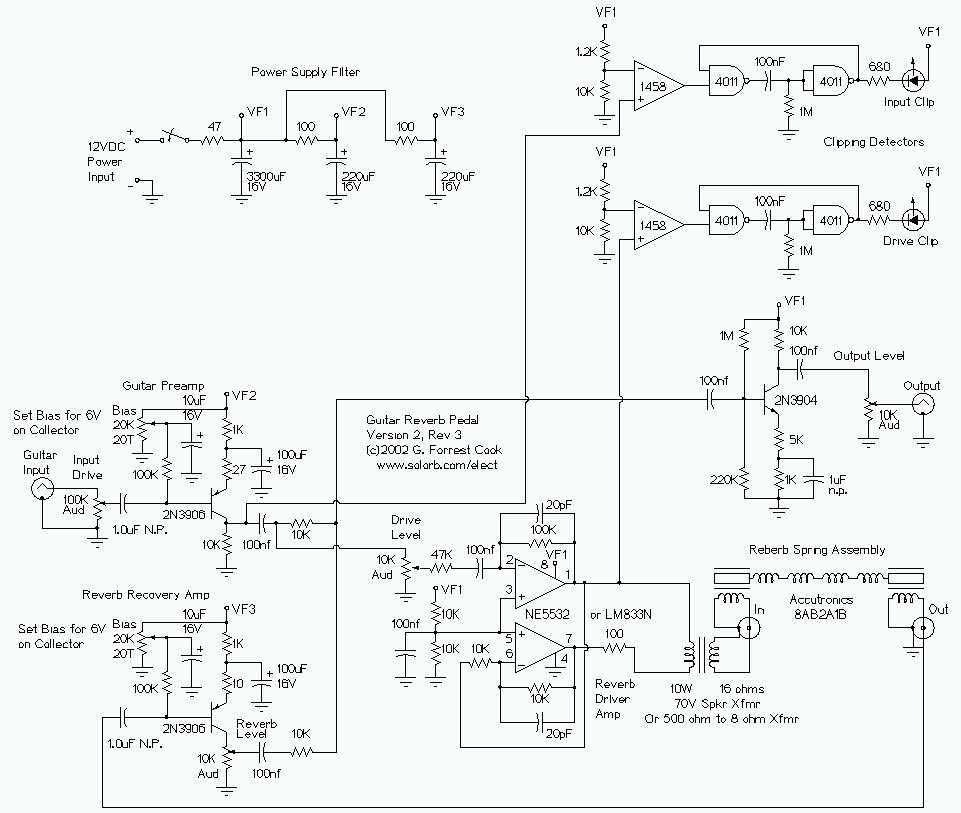
Guitar treble boost
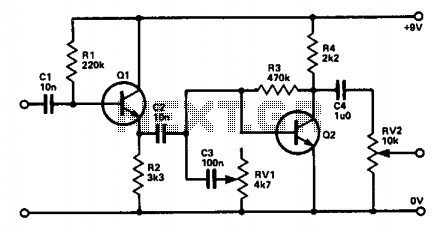
Q1 is connected as an emitter follower to provide a high input impedance for the guitar. Capacitor C2, having a relatively low capacitance, filters out most of the bass frequencies, while C3 in conjunction with variable resistor RV1 functions as a basic tone control to reduce treble frequencies, allowing for adjustable treble boost. Q2 serves as a straightforward preamplifier to compensate for signal losses incurred through C2, C3, and RV1.
In this circuit, Q1 is utilized as an emitter follower configuration, which is characterized by its ability to maintain a high input impedance while providing a low output impedance. This feature is particularly advantageous in guitar applications, where it ensures that the guitar's signal is not significantly loaded down, preserving the integrity of the sound.
Capacitor C2 plays a critical role in shaping the frequency response of the circuit. Its low capacitance value is strategically chosen to attenuate the lower frequency bass signals, thereby allowing the circuit to focus on higher frequencies that are more relevant for guitar tones. This filtering helps to create a cleaner and more defined sound, especially in scenarios where bass frequencies may muddy the overall tone.
C3, in conjunction with RV1, acts as a tone control mechanism. RV1 is a variable resistor (potentiometer) that adjusts the resistance in the circuit, thereby controlling the amount of treble that is allowed to pass through. By altering the resistance, the user can effectively boost or cut treble frequencies, enabling customization of the tonal characteristics to suit personal preferences or specific musical contexts.
Q2 is introduced as a preamplifier stage, which is essential for recovering any signal losses that may occur due to the filtering effects of C2 and C3, as well as the resistive load introduced by RV1. This preamp ensures that the signal remains strong and clear, providing the necessary gain to drive subsequent stages of the audio signal chain. The design emphasizes the importance of maintaining signal integrity throughout the circuit, allowing for a high-quality audio output that is critical in performance settings.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a thoughtful approach to guitar signal processing, combining impedance buffering, frequency filtering, and amplification to achieve a versatile and responsive tone control system.Ql is connected as an emitter follower in order to present a high input impedance to the guitar. C2, being a relatively low capacitance, cuts out most of the bass, and C3 with RV1 acts as a simple tone control to cut the treble, and hence the amount of treble boost can be altered. Q2 is a simple preamp to recover signal losses in C2, C3, and RV1.
In this circuit, Q1 is utilized as an emitter follower configuration, which is characterized by its ability to maintain a high input impedance while providing a low output impedance. This feature is particularly advantageous in guitar applications, where it ensures that the guitar's signal is not significantly loaded down, preserving the integrity of the sound.
Capacitor C2 plays a critical role in shaping the frequency response of the circuit. Its low capacitance value is strategically chosen to attenuate the lower frequency bass signals, thereby allowing the circuit to focus on higher frequencies that are more relevant for guitar tones. This filtering helps to create a cleaner and more defined sound, especially in scenarios where bass frequencies may muddy the overall tone.
C3, in conjunction with RV1, acts as a tone control mechanism. RV1 is a variable resistor (potentiometer) that adjusts the resistance in the circuit, thereby controlling the amount of treble that is allowed to pass through. By altering the resistance, the user can effectively boost or cut treble frequencies, enabling customization of the tonal characteristics to suit personal preferences or specific musical contexts.
Q2 is introduced as a preamplifier stage, which is essential for recovering any signal losses that may occur due to the filtering effects of C2 and C3, as well as the resistive load introduced by RV1. This preamp ensures that the signal remains strong and clear, providing the necessary gain to drive subsequent stages of the audio signal chain. The design emphasizes the importance of maintaining signal integrity throughout the circuit, allowing for a high-quality audio output that is critical in performance settings.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a thoughtful approach to guitar signal processing, combining impedance buffering, frequency filtering, and amplification to achieve a versatile and responsive tone control system.Ql is connected as an emitter follower in order to present a high input impedance to the guitar. C2, being a relatively low capacitance, cuts out most of the bass, and C3 with RV1 acts as a simple tone control to cut the treble, and hence the amount of treble boost can be altered. Q2 is a simple preamp to recover signal losses in C2, C3, and RV1.