Hartley oscillator
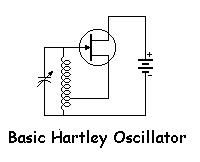
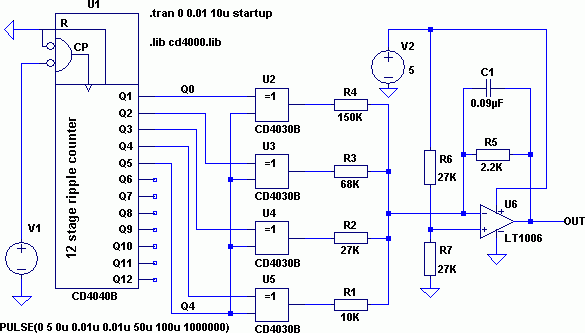
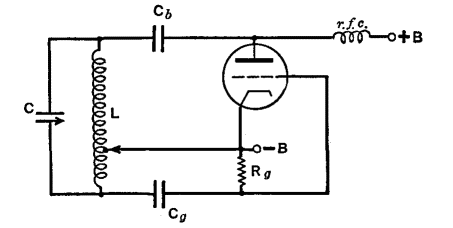
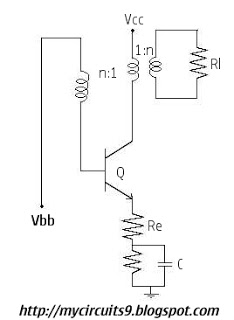
The Hartley Oscillator is an LC oscillator that derives its feedback from magnetically coupled energy in a tapped coil. Hartley oscillators are inductively coupled variable frequency oscillators.
The Hartley Oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that utilizes an inductor-capacitor (LC) circuit to generate oscillations. It is characterized by its use of two inductors and one capacitor, which form a resonant circuit. The feedback mechanism is achieved through a tapped coil, allowing for variable frequency operation.
In a typical Hartley oscillator circuit, the two inductors are often connected in series, and one of them is tapped to provide feedback to the amplifier stage. This feedback is crucial for maintaining oscillations, as it ensures that the output signal is amplified and fed back into the circuit in phase with the input signal. The frequency of oscillation is primarily determined by the values of the inductors and the capacitor, following the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{L_{total}C}} \]
where \( L_{total} \) is the equivalent inductance of the two inductors. The configuration allows for easy tuning of the oscillation frequency by adjusting the tap point or changing the values of the inductors or the capacitor.
The Hartley oscillator is commonly used in radio frequency applications, signal generators, and other electronic devices where stable oscillations are required. Its ability to produce a sine wave output makes it suitable for various applications, including modulation and demodulation in communication systems. The design can be implemented using discrete components or integrated circuits, depending on the required specifications and performance criteria.
Overall, the Hartley oscillator is valued for its simplicity, reliability, and ease of frequency adjustment, making it a popular choice in oscillator design.The Hartley Oscillator is an L C oscillator that derives its feedback from magnetically coupled energy in a tapped coil. Hartley oscillator are inductively coupled variable frequency oscillators. 🔗 External reference
The Hartley Oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that utilizes an inductor-capacitor (LC) circuit to generate oscillations. It is characterized by its use of two inductors and one capacitor, which form a resonant circuit. The feedback mechanism is achieved through a tapped coil, allowing for variable frequency operation.
In a typical Hartley oscillator circuit, the two inductors are often connected in series, and one of them is tapped to provide feedback to the amplifier stage. This feedback is crucial for maintaining oscillations, as it ensures that the output signal is amplified and fed back into the circuit in phase with the input signal. The frequency of oscillation is primarily determined by the values of the inductors and the capacitor, following the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{L_{total}C}} \]
where \( L_{total} \) is the equivalent inductance of the two inductors. The configuration allows for easy tuning of the oscillation frequency by adjusting the tap point or changing the values of the inductors or the capacitor.
The Hartley oscillator is commonly used in radio frequency applications, signal generators, and other electronic devices where stable oscillations are required. Its ability to produce a sine wave output makes it suitable for various applications, including modulation and demodulation in communication systems. The design can be implemented using discrete components or integrated circuits, depending on the required specifications and performance criteria.
Overall, the Hartley oscillator is valued for its simplicity, reliability, and ease of frequency adjustment, making it a popular choice in oscillator design.The Hartley Oscillator is an L C oscillator that derives its feedback from magnetically coupled energy in a tapped coil. Hartley oscillator are inductively coupled variable frequency oscillators. 🔗 External reference