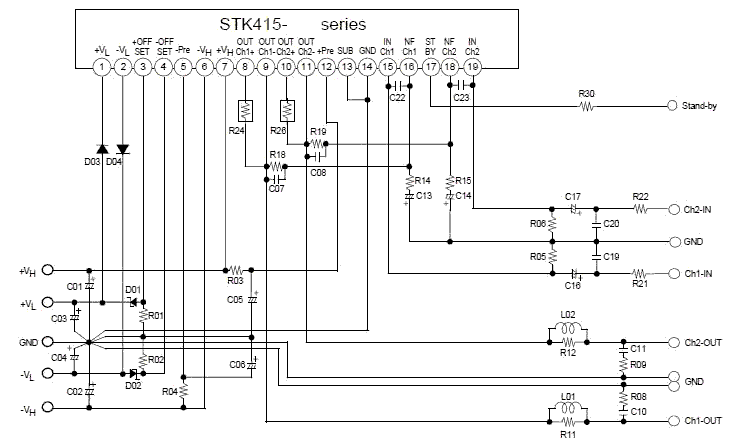
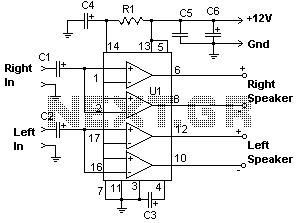
Headphone Amplifier
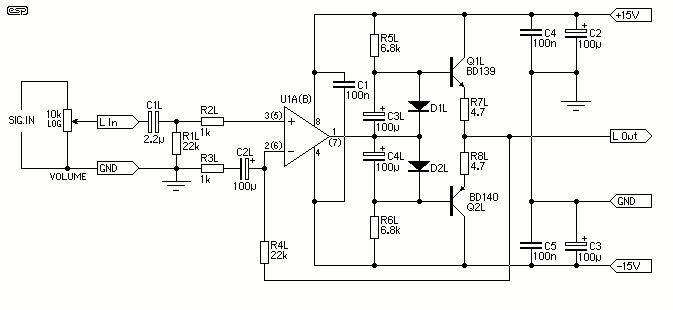
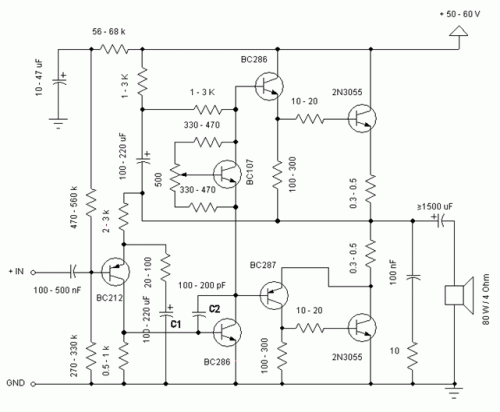
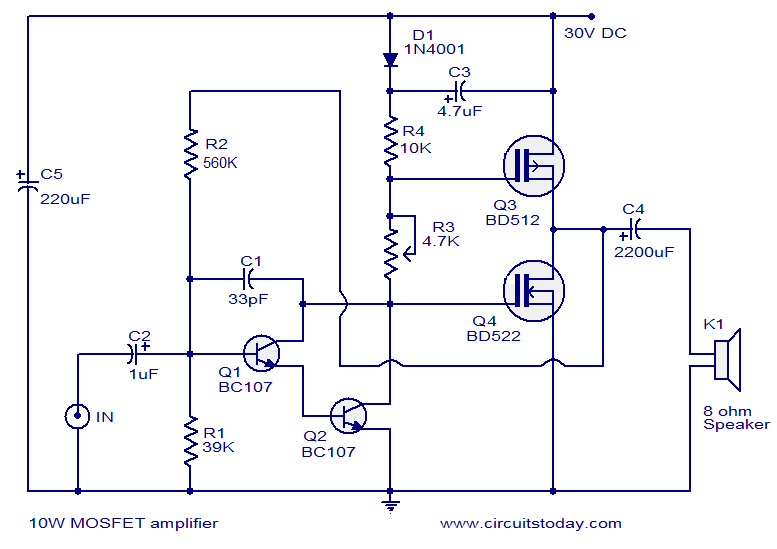
The amplifier is capable of delivering around 1.5W into 8 ohm headphones, and 2.2W into 32 ohms - this is vastly more than will ever be needed in practice. The use of a 120 Ohm output resistor is recommended, as this is supposed to be the standard source impedance for headphones. Unfortunately, many users have found that their phones perform better when driven from a low impedance source. More: The circuit is based on an opamp, with its output current boosted by a pair of transistors. Distortion is well below my measurement threshold at all levels below clipping into any impedance. Noise is virtually non-existent - even with a compression driver.
The described amplifier circuit utilizes an operational amplifier (op-amp) configuration to achieve significant power output suitable for driving headphones. The output power ratings indicate that the amplifier can deliver approximately 1.5W into an 8-ohm load and 2.2W into a 32-ohm load, which are substantial figures for headphone applications. This high output capability suggests the design is robust, allowing for dynamic audio performance without distortion, which is critical for high-fidelity sound reproduction.
A 120-ohm output resistor is recommended for the circuit, aligning with standard practices for headphone impedance matching. This resistor serves to stabilize the output and ensure that the amplifier operates within the desired parameters. However, it is noted that many headphones perform better when connected to a low impedance source, indicating that users may need to consider their specific headphone characteristics when integrating this amplifier.
The core of the amplifier is based on an op-amp, which is known for its high gain and low distortion properties. The op-amp's output is further enhanced by a pair of transistors that serve to boost the current output. This configuration allows the circuit to handle varying loads effectively while maintaining audio quality. The low distortion levels reported suggest that the amplifier can operate cleanly across its output range, with distortion levels remaining below the measurement threshold, even as the output approaches clipping.
Additionally, the noise performance of the amplifier is highlighted as virtually non-existent, indicating a well-designed circuit that minimizes unwanted audio artifacts. This is particularly important when driving sensitive components like compression drivers, where noise can significantly impact audio clarity and overall performance.
In summary, the amplifier circuit is designed to deliver high power output with low distortion and noise, making it suitable for a range of headphone applications while considering impedance matching for optimal performance.The amplifier is capable of delivering around 1.5W into 8 ohm headphones, and 2.2W into 32 ohms - this is vastly more than will ever be needed in practice. The use of a 120 Ohm output resistor is recommended, as this is supposed to be the standard source impedance for headphones.
Unfortunately, many users have found that their `phones perform better when driven from a low impedance source. The circuit is based on an opamp, with its output current boosted by a pair of transistors. Distortion is well below my measurement threshold at all levels below clipping into any impedance. Noise is virtually non-existent - even with a compression driver 🔗 External reference
The described amplifier circuit utilizes an operational amplifier (op-amp) configuration to achieve significant power output suitable for driving headphones. The output power ratings indicate that the amplifier can deliver approximately 1.5W into an 8-ohm load and 2.2W into a 32-ohm load, which are substantial figures for headphone applications. This high output capability suggests the design is robust, allowing for dynamic audio performance without distortion, which is critical for high-fidelity sound reproduction.
A 120-ohm output resistor is recommended for the circuit, aligning with standard practices for headphone impedance matching. This resistor serves to stabilize the output and ensure that the amplifier operates within the desired parameters. However, it is noted that many headphones perform better when connected to a low impedance source, indicating that users may need to consider their specific headphone characteristics when integrating this amplifier.
The core of the amplifier is based on an op-amp, which is known for its high gain and low distortion properties. The op-amp's output is further enhanced by a pair of transistors that serve to boost the current output. This configuration allows the circuit to handle varying loads effectively while maintaining audio quality. The low distortion levels reported suggest that the amplifier can operate cleanly across its output range, with distortion levels remaining below the measurement threshold, even as the output approaches clipping.
Additionally, the noise performance of the amplifier is highlighted as virtually non-existent, indicating a well-designed circuit that minimizes unwanted audio artifacts. This is particularly important when driving sensitive components like compression drivers, where noise can significantly impact audio clarity and overall performance.
In summary, the amplifier circuit is designed to deliver high power output with low distortion and noise, making it suitable for a range of headphone applications while considering impedance matching for optimal performance.The amplifier is capable of delivering around 1.5W into 8 ohm headphones, and 2.2W into 32 ohms - this is vastly more than will ever be needed in practice. The use of a 120 Ohm output resistor is recommended, as this is supposed to be the standard source impedance for headphones.
Unfortunately, many users have found that their `phones perform better when driven from a low impedance source. The circuit is based on an opamp, with its output current boosted by a pair of transistors. Distortion is well below my measurement threshold at all levels below clipping into any impedance. Noise is virtually non-existent - even with a compression driver 🔗 External reference