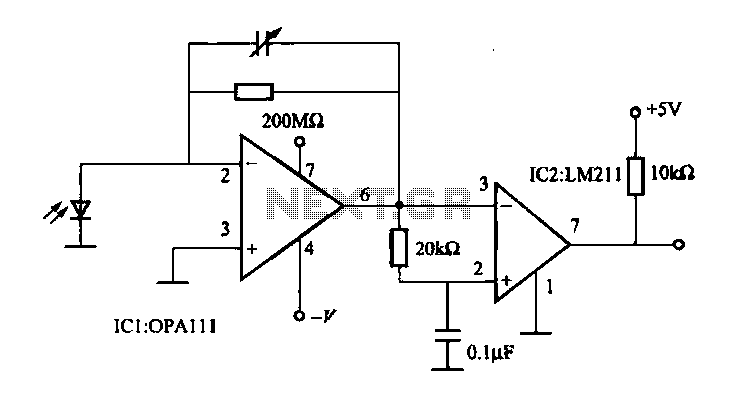
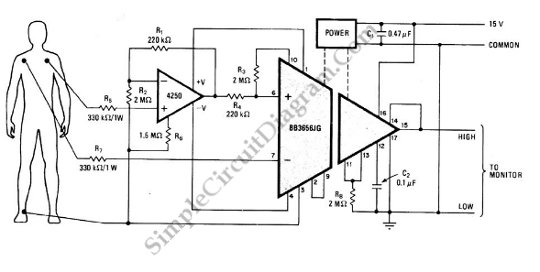
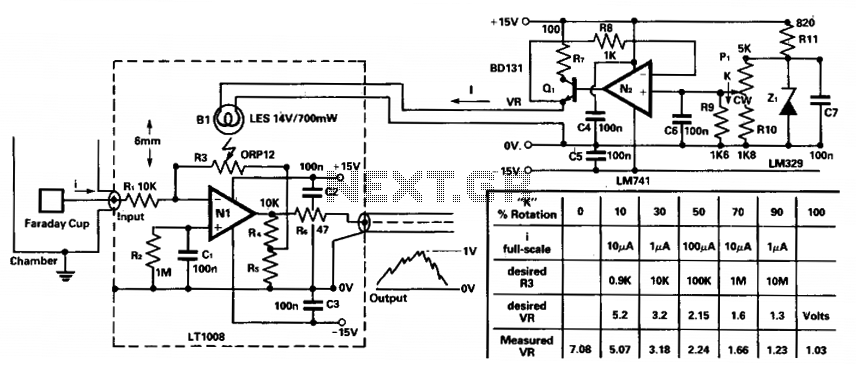
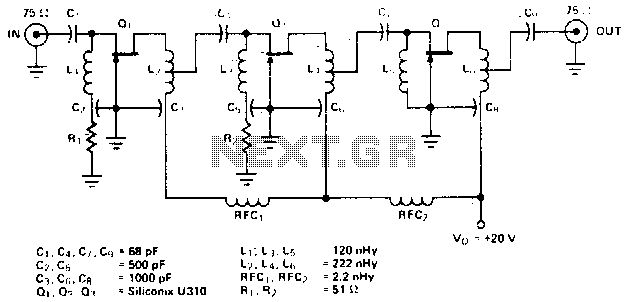
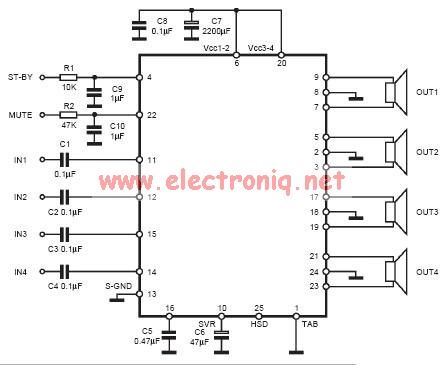
Headphone amplifier with TDA2004
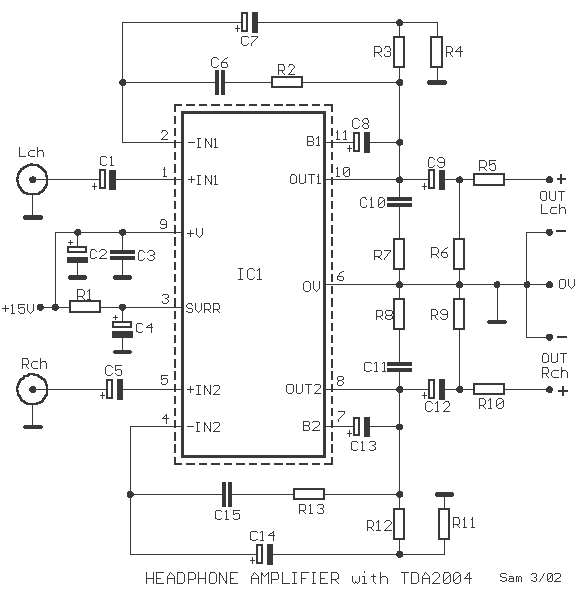
The provided description pertains to an operational amplifier (opamp) of medium power, specifically configured to amplify headphone signals and drive low loads. The opamp essentially comprises two amplifiers. The voltage gain for each amplifier is set at 40dB, determined by resistors R3-4 and R11-12 for each channel, respectively.
The bandwidth restriction for each unit is regulated by the combination of specific components. For instance, the combination of resistor R12 and capacitor C2, as well as resistor R13 and capacitor C15, is responsible for limiting the frequency response to 22KHz. This frequency cap ensures that the amplifier remains stable and does not oscillate at high frequencies, which could potentially damage the connected headphones.
Furthermore, resistors R5 and R10 play a crucial role in impedance matching. These resistors help adapt the impedance of the earphones, ensuring optimal power transfer from the amplifier to the earphones. Impedance matching is particularly important in this context as it prevents signal loss and distortion, thereby improving the overall sound quality.
In summary, this medium-power operational amplifier has been designed with a focus on headphone amplification, featuring a dual-amplifier setup, a voltage gain of 40dB per channel, a bandwidth limit of 22KHz, and dedicated components for impedance matching.A opamp. medium power, here its used as amplifier of headphones with possibility drive low loads. It contains in a nutshell two amplifiers. The voltage gain, has been determined in 40dB, from the R3-4 and R11-12, for each channel, respectively. The restriction of bandwidth for each unit is regulated by the combination of R12, C2 and R13, C15, in 22KHZ.
The R5, R10 attend to the adaptation of impedance earphones. 🔗 External reference
The bandwidth restriction for each unit is regulated by the combination of specific components. For instance, the combination of resistor R12 and capacitor C2, as well as resistor R13 and capacitor C15, is responsible for limiting the frequency response to 22KHz. This frequency cap ensures that the amplifier remains stable and does not oscillate at high frequencies, which could potentially damage the connected headphones.
Furthermore, resistors R5 and R10 play a crucial role in impedance matching. These resistors help adapt the impedance of the earphones, ensuring optimal power transfer from the amplifier to the earphones. Impedance matching is particularly important in this context as it prevents signal loss and distortion, thereby improving the overall sound quality.
In summary, this medium-power operational amplifier has been designed with a focus on headphone amplification, featuring a dual-amplifier setup, a voltage gain of 40dB per channel, a bandwidth limit of 22KHz, and dedicated components for impedance matching.A opamp. medium power, here its used as amplifier of headphones with possibility drive low loads. It contains in a nutshell two amplifiers. The voltage gain, has been determined in 40dB, from the R3-4 and R11-12, for each channel, respectively. The restriction of bandwidth for each unit is regulated by the combination of R12, C2 and R13, C15, in 22KHZ.
The R5, R10 attend to the adaptation of impedance earphones. 🔗 External reference