Heartbeat Monitor Circuit
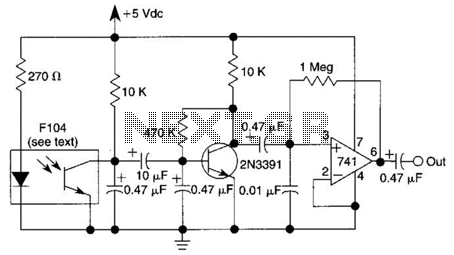
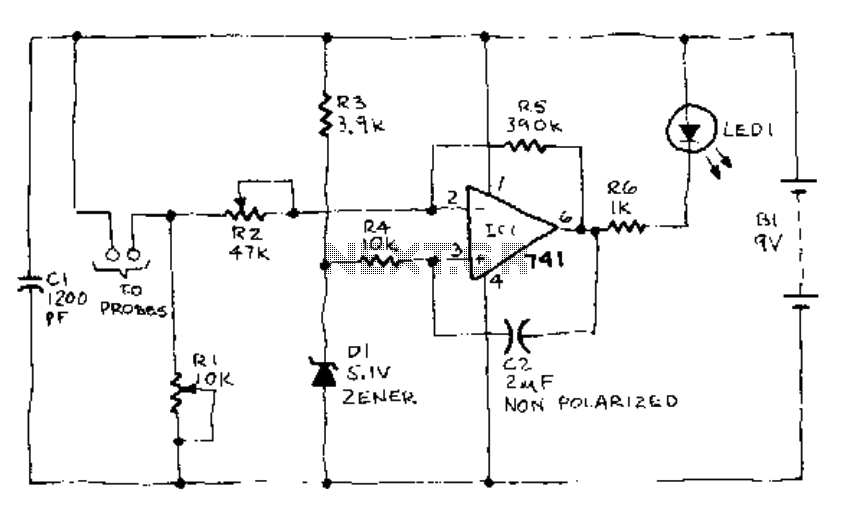
An infrared (IR) photodiode is employed to detect the IR reflectivity of the skin, which changes due to increased blood volume during heart contractions. This device captures a signal that correlates with the heartbeat. A transistor and operational amplifier (op amp) are utilized to amplify this signal to a level that is appropriate for triggering logic circuitry or for visualization on an oscilloscope.
The infrared photodiode operates by converting light into an electrical signal. When the heart contracts, blood volume in the skin increases, leading to variations in IR reflectivity. The photodiode captures these variations, producing a small electrical signal that corresponds to the heartbeat.
To process this weak signal, a transistor is used as a switch or amplifier. The transistor can provide the necessary gain to elevate the signal strength, making it suitable for further processing. The operational amplifier, known for its high input impedance and low output impedance, is configured to amplify the signal from the photodiode. The op amp can be set up in a non-inverting configuration to ensure that the output signal is in phase with the input signal, further enhancing the signal quality.
The amplified signal can then be fed into logic circuitry, allowing for digital processing or triggering of other components in a system. Alternatively, the signal can be connected to an oscilloscope for visualization, enabling real-time monitoring of the heartbeat signal. This configuration is essential for applications in medical devices, fitness monitoring, and other health-related technologies where accurate heart rate detection is necessary. The design should also consider factors such as noise reduction and signal integrity to ensure reliable performance in various environments. An IR photodiode, which senses IR skin reflectivity as a result of increased blood volume during the periods that the heart forcibly contracts, is used to pick up a signal that is correlated with the heartbeat. A transistor and op amp raise this to a level suitable to trigger logic circuitry or to be displayed on a scope.
The infrared photodiode operates by converting light into an electrical signal. When the heart contracts, blood volume in the skin increases, leading to variations in IR reflectivity. The photodiode captures these variations, producing a small electrical signal that corresponds to the heartbeat.
To process this weak signal, a transistor is used as a switch or amplifier. The transistor can provide the necessary gain to elevate the signal strength, making it suitable for further processing. The operational amplifier, known for its high input impedance and low output impedance, is configured to amplify the signal from the photodiode. The op amp can be set up in a non-inverting configuration to ensure that the output signal is in phase with the input signal, further enhancing the signal quality.
The amplified signal can then be fed into logic circuitry, allowing for digital processing or triggering of other components in a system. Alternatively, the signal can be connected to an oscilloscope for visualization, enabling real-time monitoring of the heartbeat signal. This configuration is essential for applications in medical devices, fitness monitoring, and other health-related technologies where accurate heart rate detection is necessary. The design should also consider factors such as noise reduction and signal integrity to ensure reliable performance in various environments. An IR photodiode, which senses IR skin reflectivity as a result of increased blood volume during the periods that the heart forcibly contracts, is used to pick up a signal that is correlated with the heartbeat. A transistor and op amp raise this to a level suitable to trigger logic circuitry or to be displayed on a scope.