High Volt LED Flasher
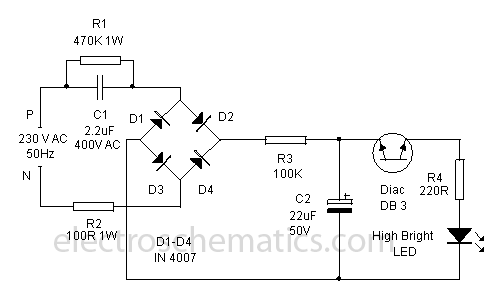
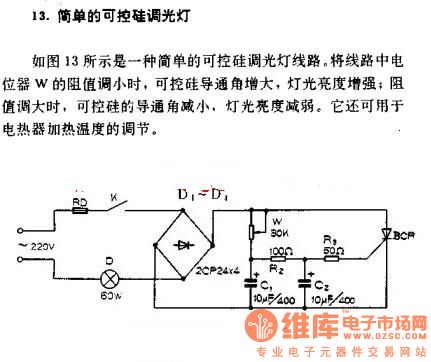
This circuit is a Flasher that directly derives power from AC to produce brilliant flashes at a rate of one flash per second. It utilizes a Diac as the primary element.
The Flasher circuit operates by converting alternating current (AC) into a pulsed output that generates a visual flash effect. The core component of this circuit is the Diac, a semiconductor device that remains off until a certain threshold voltage is reached. When the AC supply voltage exceeds this threshold, the Diac conducts, allowing current to flow through the load, which can be an LED or a bulb, creating a flash.
The circuit typically consists of several key components: an AC power source, a Diac, a resistor, and a capacitive element. The resistor and capacitor form an RC timing network that determines the charging and discharging time, effectively controlling the flash rate. As the capacitor charges through the resistor, it eventually reaches the breakdown voltage of the Diac. At this point, the Diac turns on, discharging the capacitor through the load and producing a flash of light. Once the capacitor discharges, the Diac turns off until the next cycle begins, repeating the process approximately every second.
This circuit is advantageous for applications requiring visual alerts or decorations, as it provides a simple and effective means of creating a flashing light without the need for complex control circuitry. Proper selection of the resistor and capacitor values is crucial for achieving the desired flash rate and intensity. Safety precautions must be observed when working with AC power to prevent electrical hazards.Here is a Flasher circuit that directly derives power from AC to give brilliant flashes at the rate of one flash per second. It uses a Diac as the main ele.. 🔗 External reference
The Flasher circuit operates by converting alternating current (AC) into a pulsed output that generates a visual flash effect. The core component of this circuit is the Diac, a semiconductor device that remains off until a certain threshold voltage is reached. When the AC supply voltage exceeds this threshold, the Diac conducts, allowing current to flow through the load, which can be an LED or a bulb, creating a flash.
The circuit typically consists of several key components: an AC power source, a Diac, a resistor, and a capacitive element. The resistor and capacitor form an RC timing network that determines the charging and discharging time, effectively controlling the flash rate. As the capacitor charges through the resistor, it eventually reaches the breakdown voltage of the Diac. At this point, the Diac turns on, discharging the capacitor through the load and producing a flash of light. Once the capacitor discharges, the Diac turns off until the next cycle begins, repeating the process approximately every second.
This circuit is advantageous for applications requiring visual alerts or decorations, as it provides a simple and effective means of creating a flashing light without the need for complex control circuitry. Proper selection of the resistor and capacitor values is crucial for achieving the desired flash rate and intensity. Safety precautions must be observed when working with AC power to prevent electrical hazards.Here is a Flasher circuit that directly derives power from AC to give brilliant flashes at the rate of one flash per second. It uses a Diac as the main ele.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713