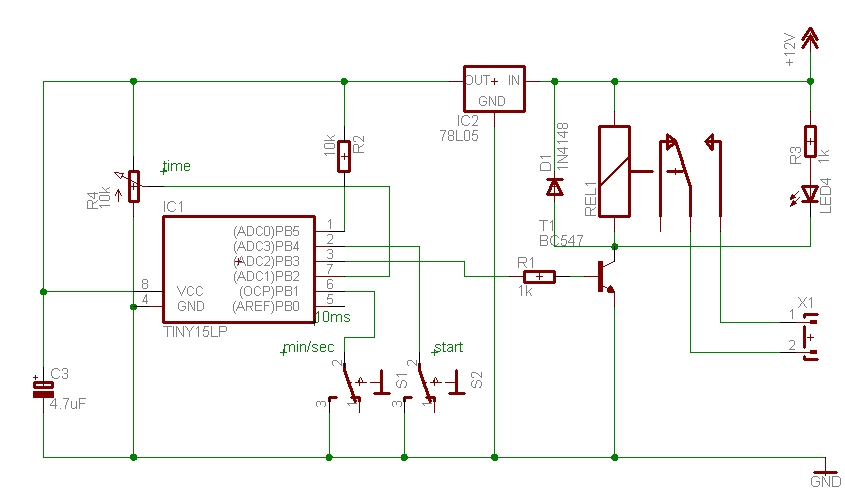
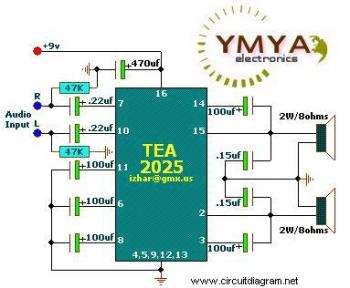
Simple silicon-controlled dimmer circuit diagram
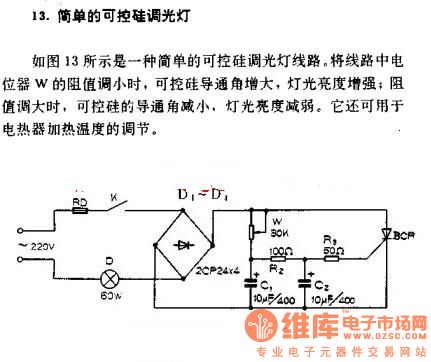
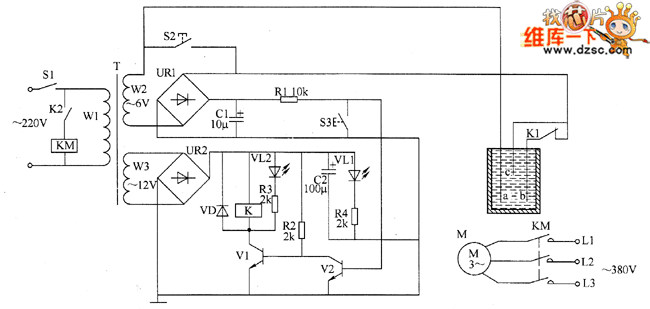
A simple silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) dimmer circuit is depicted in Figure 13. This circuit is designed to control the brightness of lights. As the resistance in the potentiometer decreases, the conduction angle of the SCR increases, resulting in an increase in light intensity. Conversely, when the resistance increases, the SCR conduction angle decreases, leading to a reduction in light intensity. This circuit can also be utilized for adjusting heating temperatures.
The SCR dimmer circuit operates by manipulating the phase angle of the AC waveform supplied to the load, which is typically an incandescent light bulb or a resistive heating element. The key components of the circuit include a silicon-controlled rectifier, a potentiometer, and a resistor-capacitor (RC) timing network.
In this configuration, the potentiometer serves as a variable resistor, allowing for the adjustment of the gate trigger voltage applied to the SCR. When the SCR is triggered, it begins conducting current, allowing power to flow to the load. The timing network, composed of a resistor and capacitor, determines the delay before the SCR is triggered during each half-cycle of the AC waveform. By adjusting the potentiometer, the user can change the timing of this trigger, effectively controlling how much of the AC waveform is applied to the load.
The relationship between the resistance of the potentiometer and the SCR conduction angle is critical. A lower resistance results in a shorter delay, allowing the SCR to conduct for a larger portion of the AC cycle, which increases the average voltage and, consequently, the brightness of the light. Conversely, increasing the resistance delays the triggering of the SCR, reducing the conduction angle and dimming the light.
This SCR dimmer circuit can also be adapted for use in heating applications. By controlling the power delivered to a heating element, the circuit can maintain a desired temperature by adjusting the average power delivered to the load. Overall, this simple yet effective circuit provides a versatile solution for dimming lights and controlling heating elements in various applications.Simple silicon-controlled dimmer As shown in Figure 13, it is a simple circuit of SCR dimming lights. The w resistance in the potentiometer decreases, SCR conduction angle increases, the light`s intensity increases, the resistance enlarges, the SCR conduction angle decreases, the light`s intensity decreased.
It can also be used as adjusting the heating tem.. 🔗 External reference
The SCR dimmer circuit operates by manipulating the phase angle of the AC waveform supplied to the load, which is typically an incandescent light bulb or a resistive heating element. The key components of the circuit include a silicon-controlled rectifier, a potentiometer, and a resistor-capacitor (RC) timing network.
In this configuration, the potentiometer serves as a variable resistor, allowing for the adjustment of the gate trigger voltage applied to the SCR. When the SCR is triggered, it begins conducting current, allowing power to flow to the load. The timing network, composed of a resistor and capacitor, determines the delay before the SCR is triggered during each half-cycle of the AC waveform. By adjusting the potentiometer, the user can change the timing of this trigger, effectively controlling how much of the AC waveform is applied to the load.
The relationship between the resistance of the potentiometer and the SCR conduction angle is critical. A lower resistance results in a shorter delay, allowing the SCR to conduct for a larger portion of the AC cycle, which increases the average voltage and, consequently, the brightness of the light. Conversely, increasing the resistance delays the triggering of the SCR, reducing the conduction angle and dimming the light.
This SCR dimmer circuit can also be adapted for use in heating applications. By controlling the power delivered to a heating element, the circuit can maintain a desired temperature by adjusting the average power delivered to the load. Overall, this simple yet effective circuit provides a versatile solution for dimming lights and controlling heating elements in various applications.Simple silicon-controlled dimmer As shown in Figure 13, it is a simple circuit of SCR dimming lights. The w resistance in the potentiometer decreases, SCR conduction angle increases, the light`s intensity increases, the resistance enlarges, the SCR conduction angle decreases, the light`s intensity decreased.
It can also be used as adjusting the heating tem.. 🔗 External reference