How to Apply Additional PWM Intensity Control to LED Drivers
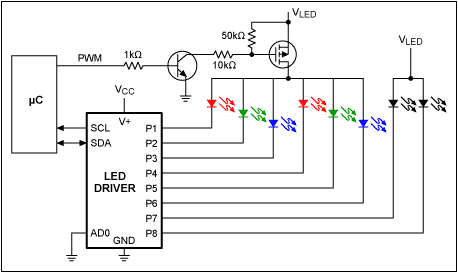
Various techniques demonstrate how enhanced PWM (pulse-width modulation) intensity control can be utilized in LED (light-emitting diode) drivers.
PWM intensity control is a widely adopted method in LED driver circuits to regulate brightness levels. This technique involves modulating the width of the pulses in a periodic signal, which effectively adjusts the average power delivered to the LED. By varying the duty cycle of the PWM signal, the perceived brightness of the LED can be finely tuned without impacting the color quality or efficiency of the light output.
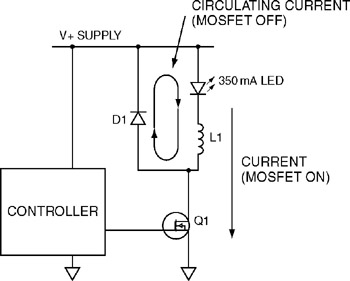
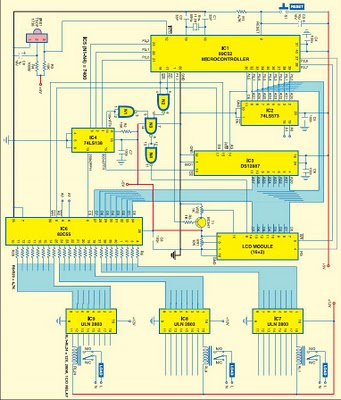
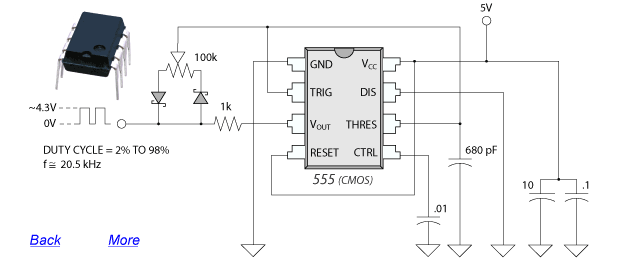
In an LED driver circuit employing PWM, the control signal is typically generated by a microcontroller or dedicated PWM controller. The output from this controller drives a switching device, such as a MOSFET or a transistor, which regulates the current flowing through the LED. The switching device rapidly turns on and off, creating a series of pulses that correspond to the desired brightness level.
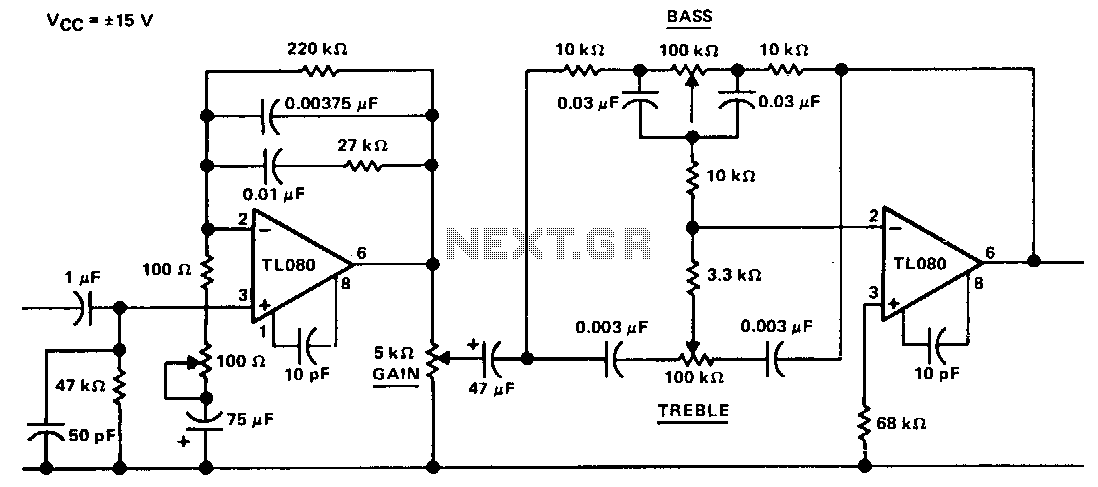
Several techniques can enhance PWM control in LED drivers. One approach is the use of frequency modulation, where the frequency of the PWM signal is adjusted based on the ambient light conditions or user preferences. This can help reduce flicker and improve visual comfort. Another technique involves the implementation of adaptive PWM, which adjusts the duty cycle dynamically in response to changes in input voltage or temperature, ensuring stable operation and prolonging LED lifespan.
Furthermore, advanced control algorithms can be integrated into the LED driver circuit to optimize performance. For instance, closed-loop control systems can be employed to maintain consistent brightness levels by continuously monitoring the output and adjusting the PWM signal accordingly. This method enhances the reliability and efficiency of the LED driver, particularly in applications requiring precise lighting control.
In summary, the application of PWM intensity control in LED drivers is a critical aspect of modern lighting systems. By utilizing various techniques to optimize PWM performance, designers can achieve greater flexibility, efficiency, and user satisfaction in LED lighting solutions.Different techniques show how additional PWM (pulse-width modulation) intensity control can be applied to LED (light-emitting diode) drivers.. 🔗 External reference
PWM intensity control is a widely adopted method in LED driver circuits to regulate brightness levels. This technique involves modulating the width of the pulses in a periodic signal, which effectively adjusts the average power delivered to the LED. By varying the duty cycle of the PWM signal, the perceived brightness of the LED can be finely tuned without impacting the color quality or efficiency of the light output.
In an LED driver circuit employing PWM, the control signal is typically generated by a microcontroller or dedicated PWM controller. The output from this controller drives a switching device, such as a MOSFET or a transistor, which regulates the current flowing through the LED. The switching device rapidly turns on and off, creating a series of pulses that correspond to the desired brightness level.
Several techniques can enhance PWM control in LED drivers. One approach is the use of frequency modulation, where the frequency of the PWM signal is adjusted based on the ambient light conditions or user preferences. This can help reduce flicker and improve visual comfort. Another technique involves the implementation of adaptive PWM, which adjusts the duty cycle dynamically in response to changes in input voltage or temperature, ensuring stable operation and prolonging LED lifespan.
Furthermore, advanced control algorithms can be integrated into the LED driver circuit to optimize performance. For instance, closed-loop control systems can be employed to maintain consistent brightness levels by continuously monitoring the output and adjusting the PWM signal accordingly. This method enhances the reliability and efficiency of the LED driver, particularly in applications requiring precise lighting control.
In summary, the application of PWM intensity control in LED drivers is a critical aspect of modern lighting systems. By utilizing various techniques to optimize PWM performance, designers can achieve greater flexibility, efficiency, and user satisfaction in LED lighting solutions.Different techniques show how additional PWM (pulse-width modulation) intensity control can be applied to LED (light-emitting diode) drivers.. 🔗 External reference