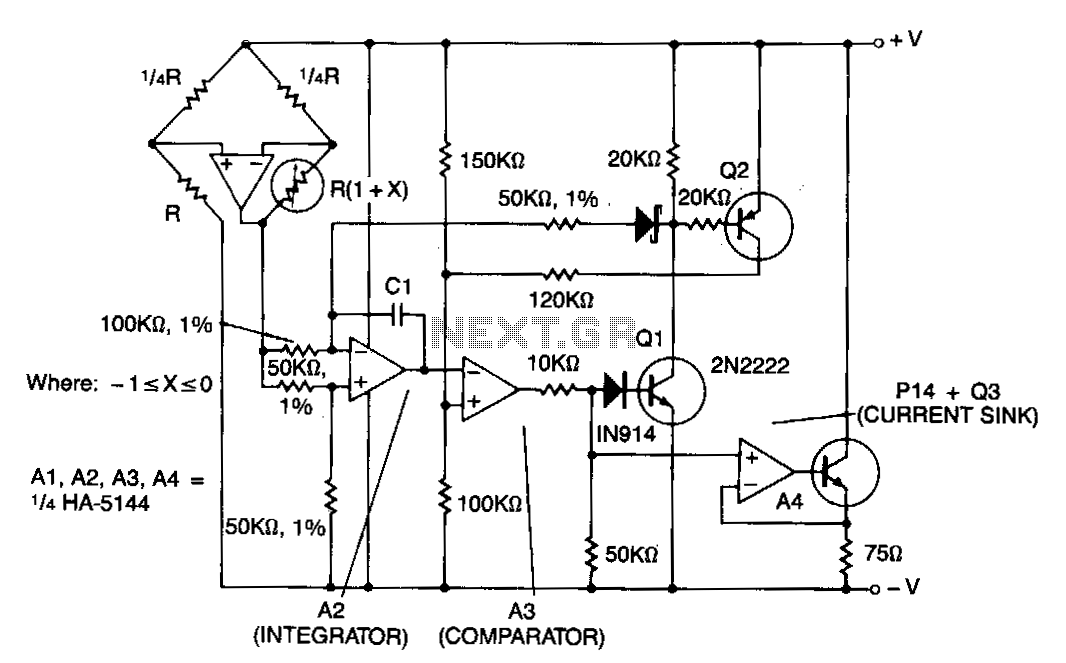
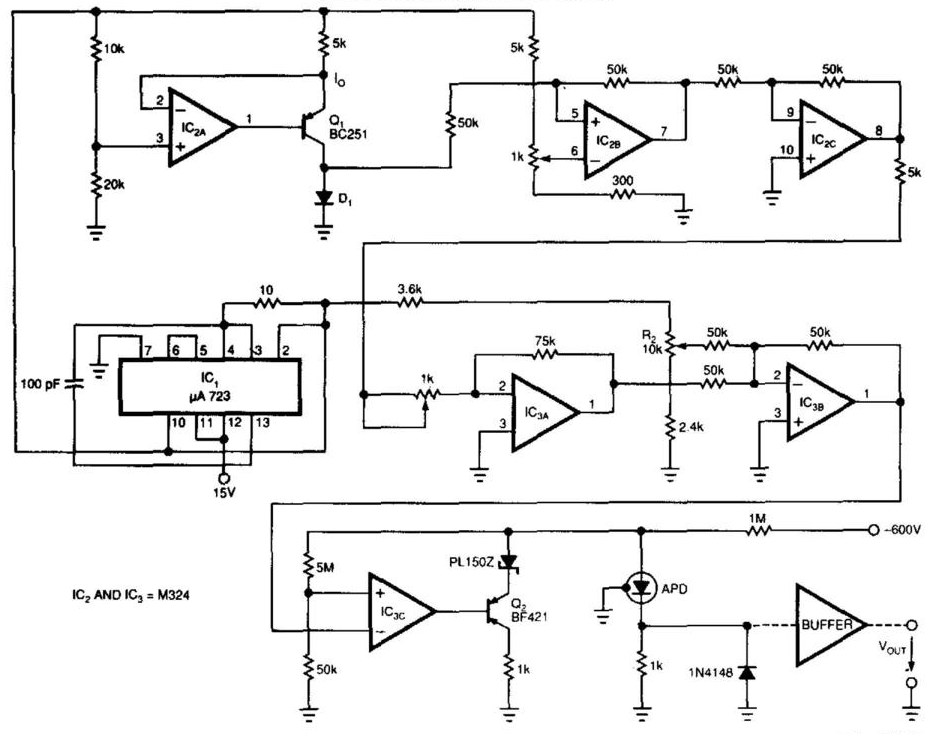
Humidity Sensor with the H14DL
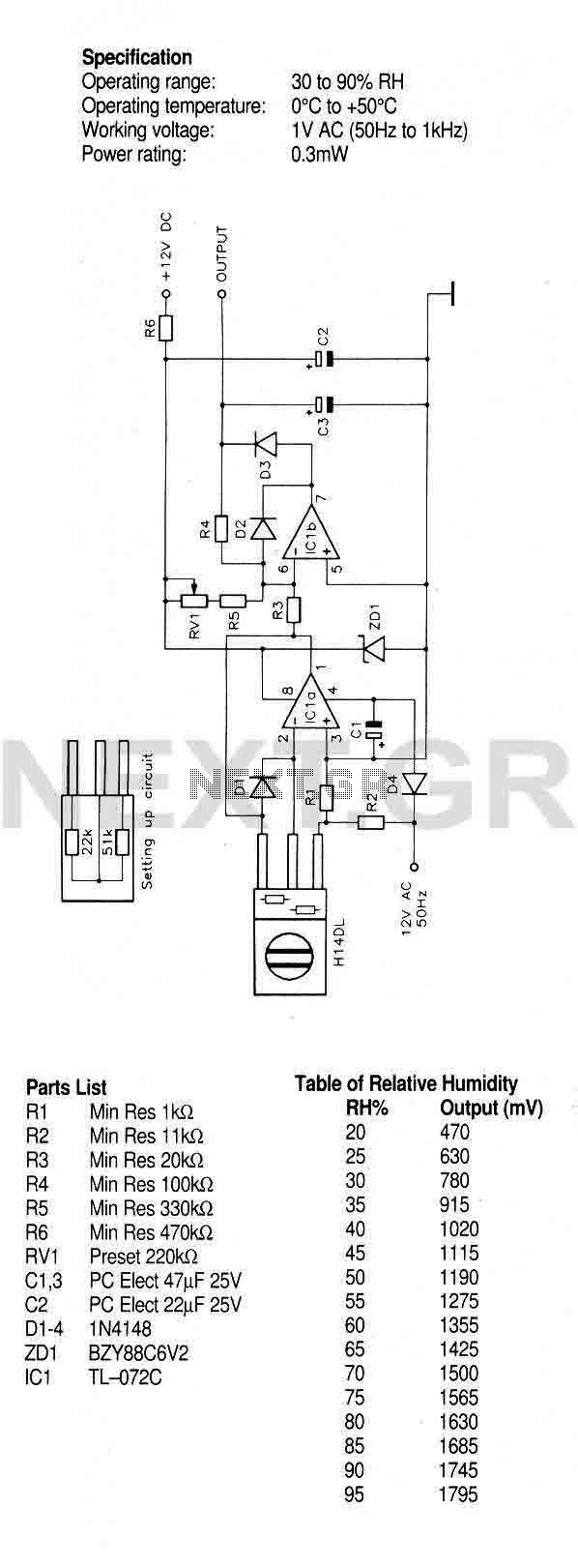
A humidity sensor with temperature compensation built-in. Never apply a DC voltage to the sensor, even measuring the sensor with an ohmmeter will damage the device, always ensure that an AC voltage is applied. Avoid condensation, freezing, dust, mist, oil, alcohol, etc. To set up this circuit replace the H14DL with Min Res 22Kohm and Min Res 51Kohm as shown, Adjust RV1 until a voltmeter between output and ground reads 1.40V. The output will then be as shown in the table to an accuracy of about ~5%.
The humidity sensor described is designed to provide accurate humidity readings while incorporating temperature compensation to enhance measurement precision. The sensor operates optimally when AC voltage is applied, as DC voltage can lead to irreversible damage. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that the circuit is configured to supply AC voltage only, avoiding any direct current conditions.
Environmental conditions must be controlled to maintain sensor accuracy and longevity. Factors such as condensation, freezing temperatures, dust, mist, oil, and alcohol can adversely affect sensor performance. Proper housing or environmental shielding may be necessary to prevent exposure to these elements.
In the circuit setup, the H14DL component should be replaced with two minimum resistors: one with a value of 22 kΩ and another with a value of 51 kΩ. This modification is essential to calibrate the sensor properly. Adjusting the variable resistor (RV1) is a critical step in the setup process. By tuning RV1, the output voltage between the sensor's output and ground should be calibrated to read 1.40V on a voltmeter. This voltage level serves as a baseline for subsequent humidity measurements.
The sensor's output will correlate with humidity levels according to a predefined table, which specifies the output voltage for various humidity percentages. The accuracy of these readings is approximately ±5%, indicating that while the sensor provides reliable data, some variability may occur. Regular calibration and adherence to environmental guidelines will enhance the performance and reliability of the humidity sensor in practical applications.A humidity sensor with temperature compensation built-in. Never apply a DC voltage to the sensor, even measuring the sensor with an ohmmeter will damage the device, always ensure that an AC voltage is applied. Avoid condensation, freezing, dust, mist, oil, alcohol, etc. To set up this circuit replace the H14DL with Min Res 22Kohm and Min Res 51Kohm as shown, Acjust RV1 until a voltmeter between output and ground reads 1.40V.
The output will then be as shown in the table to an accuracy of about ~5%.
The humidity sensor described is designed to provide accurate humidity readings while incorporating temperature compensation to enhance measurement precision. The sensor operates optimally when AC voltage is applied, as DC voltage can lead to irreversible damage. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that the circuit is configured to supply AC voltage only, avoiding any direct current conditions.
Environmental conditions must be controlled to maintain sensor accuracy and longevity. Factors such as condensation, freezing temperatures, dust, mist, oil, and alcohol can adversely affect sensor performance. Proper housing or environmental shielding may be necessary to prevent exposure to these elements.
In the circuit setup, the H14DL component should be replaced with two minimum resistors: one with a value of 22 kΩ and another with a value of 51 kΩ. This modification is essential to calibrate the sensor properly. Adjusting the variable resistor (RV1) is a critical step in the setup process. By tuning RV1, the output voltage between the sensor's output and ground should be calibrated to read 1.40V on a voltmeter. This voltage level serves as a baseline for subsequent humidity measurements.
The sensor's output will correlate with humidity levels according to a predefined table, which specifies the output voltage for various humidity percentages. The accuracy of these readings is approximately ±5%, indicating that while the sensor provides reliable data, some variability may occur. Regular calibration and adherence to environmental guidelines will enhance the performance and reliability of the humidity sensor in practical applications.A humidity sensor with temperature compensation built-in. Never apply a DC voltage to the sensor, even measuring the sensor with an ohmmeter will damage the device, always ensure that an AC voltage is applied. Avoid condensation, freezing, dust, mist, oil, alcohol, etc. To set up this circuit replace the H14DL with Min Res 22Kohm and Min Res 51Kohm as shown, Acjust RV1 until a voltmeter between output and ground reads 1.40V.
The output will then be as shown in the table to an accuracy of about ~5%.