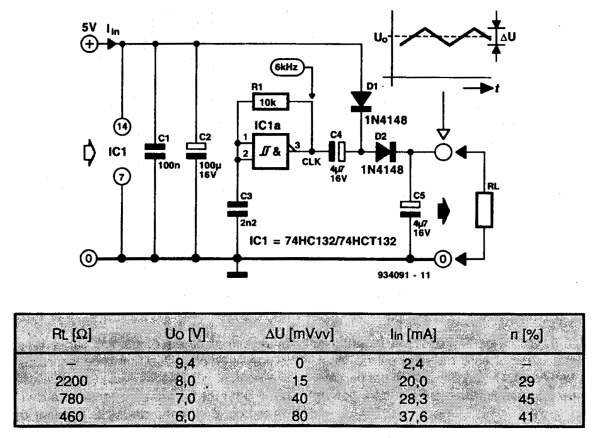
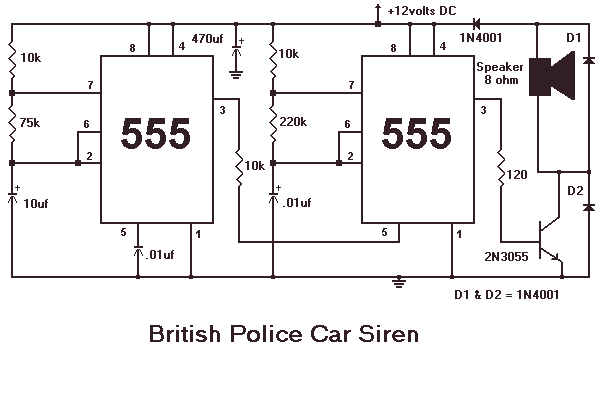
Inductance feedback oscillator circuit
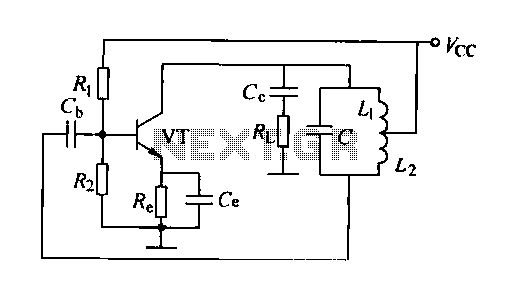
A feedback oscillator circuit utilizing inductance is presented, featuring the 3DG3 transistor. The component parameters reference values include: 1) transistors 3DG6, 2) resistances R1 at 91 kΩ, R2 at 11 kΩ, and R3 unspecified, 3) capacitance values of C at 0.01 µF. The values of capacitors C and inductors L1, L2 are determined by the oscillation frequency. In the AC equivalent circuit, capacitors C and inductors L1, L2 form a selective circuit with the transistor emitter grounded. The output voltage Uo is derived from the input voltage UI, with electrical feedback present. The feedback voltage Uf is defined as the voltage across L2, and the phase difference between Uf and Uo is 180 degrees, fulfilling the positive feedback condition. The three electrodes of the transistor are connected to nodes with inductance, forming an oscillator circuit, which is also characterized as a three-point oscillator due to the voltage across the inductor.
The feedback oscillator circuit described operates by utilizing the properties of inductance and capacitance to generate oscillations. The circuit comprises a transistor (3DG3) that plays a critical role in amplifying the feedback signals. The resistances in the circuit, specifically R1 (91 kΩ) and R2 (11 kΩ), set the biasing conditions and influence the gain of the oscillator. The unspecified resistance R3 may be included for stability or tuning purposes.
Capacitance is provided by a capacitor (C) rated at 0.01 µF, which, together with the inductors L1 and L2, determines the resonant frequency of the oscillator. The selection of these components is crucial, as they dictate the frequency at which the circuit will oscillate. The resonant frequency (f) can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{L \cdot C}} \]
where L is the equivalent inductance of L1 and L2 in series or parallel, depending on their configuration, and C is the capacitance.
The AC equivalent circuit demonstrates how the capacitor and inductors form a selective circuit that allows certain frequencies to pass while attenuating others. With the transistor's emitter grounded, the circuit is configured to provide positive feedback. The output voltage (Uo) is derived from the input voltage (UI), while the feedback voltage (Uf) is taken across L2. The phase difference of 180 degrees between Uf and Uo is essential for sustaining oscillations, as it ensures that the feedback reinforces the input signal.
In summary, this feedback oscillator circuit is a classic example of utilizing transistors, resistors, capacitors, and inductors to create a stable oscillatory output. The careful selection of component values directly influences the performance and frequency of the oscillation, making it suitable for various applications in signal generation and processing.Feedback oscillator circuit inductance shown, transistor 3DG3. Component Parameters Reference values are as follows: 1) transistors 3DG6. 2) Resistance: Rhl 91kfl, RBZ llkfl, R e IkSl. 3) capacitance: C C C 0.OlyF. 4) C and LJ, L2 value is determined by the oscillation frequency. As can be seen from the AC equivalent circuit, a capacitor C and inductance L., Lz constitute a selective circuit, the transistor emitter is grounded. The output voltage Uo - UI], electrical feedback. Voltage Uf -UL2, feedback voltage Uf and the output voltage U
The feedback oscillator circuit described operates by utilizing the properties of inductance and capacitance to generate oscillations. The circuit comprises a transistor (3DG3) that plays a critical role in amplifying the feedback signals. The resistances in the circuit, specifically R1 (91 kΩ) and R2 (11 kΩ), set the biasing conditions and influence the gain of the oscillator. The unspecified resistance R3 may be included for stability or tuning purposes.
Capacitance is provided by a capacitor (C) rated at 0.01 µF, which, together with the inductors L1 and L2, determines the resonant frequency of the oscillator. The selection of these components is crucial, as they dictate the frequency at which the circuit will oscillate. The resonant frequency (f) can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi\sqrt{L \cdot C}} \]
where L is the equivalent inductance of L1 and L2 in series or parallel, depending on their configuration, and C is the capacitance.
The AC equivalent circuit demonstrates how the capacitor and inductors form a selective circuit that allows certain frequencies to pass while attenuating others. With the transistor's emitter grounded, the circuit is configured to provide positive feedback. The output voltage (Uo) is derived from the input voltage (UI), while the feedback voltage (Uf) is taken across L2. The phase difference of 180 degrees between Uf and Uo is essential for sustaining oscillations, as it ensures that the feedback reinforces the input signal.
In summary, this feedback oscillator circuit is a classic example of utilizing transistors, resistors, capacitors, and inductors to create a stable oscillatory output. The careful selection of component values directly influences the performance and frequency of the oscillation, making it suitable for various applications in signal generation and processing.Feedback oscillator circuit inductance shown, transistor 3DG3. Component Parameters Reference values are as follows: 1) transistors 3DG6. 2) Resistance: Rhl 91kfl, RBZ llkfl, R e IkSl. 3) capacitance: C C C 0.OlyF. 4) C and LJ, L2 value is determined by the oscillation frequency. As can be seen from the AC equivalent circuit, a capacitor C and inductance L., Lz constitute a selective circuit, the transistor emitter is grounded. The output voltage Uo - UI], electrical feedback. Voltage Uf -UL2, feedback voltage Uf and the output voltage U