IR (infrared) receiver and transmitter
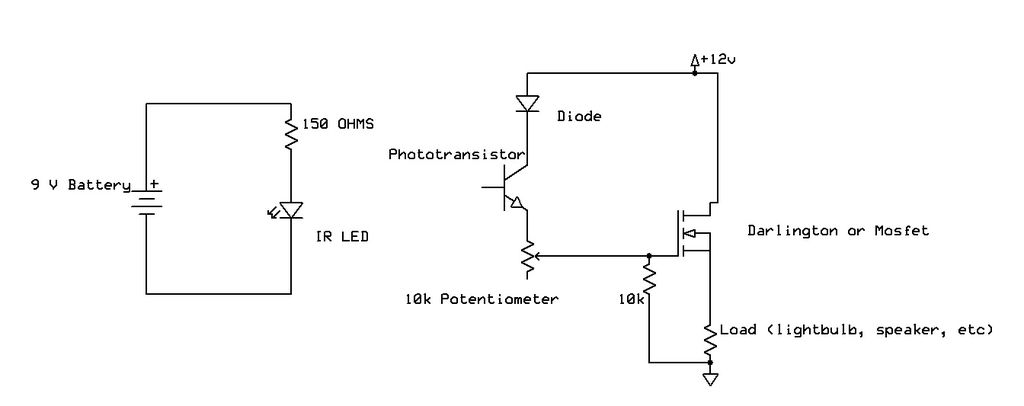
Recently, samples of IR LEDs and a corresponding IR phototransistor were acquired. A project was initiated to utilize these components.
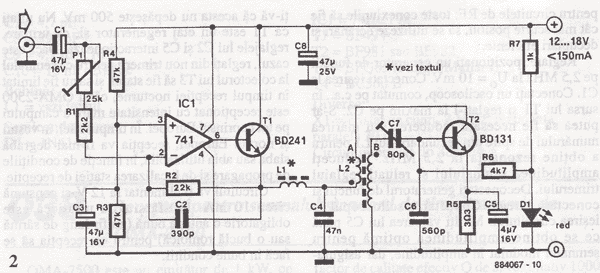
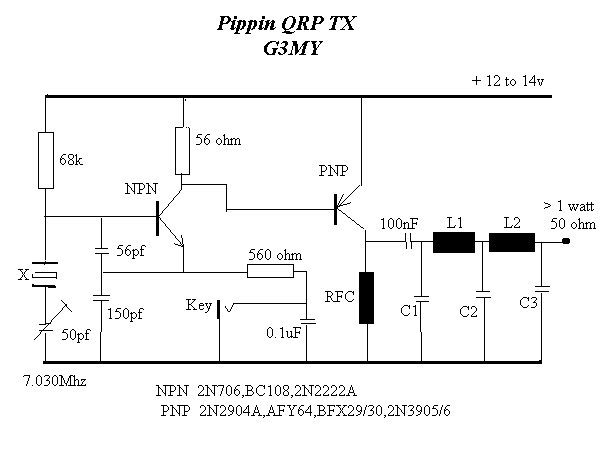
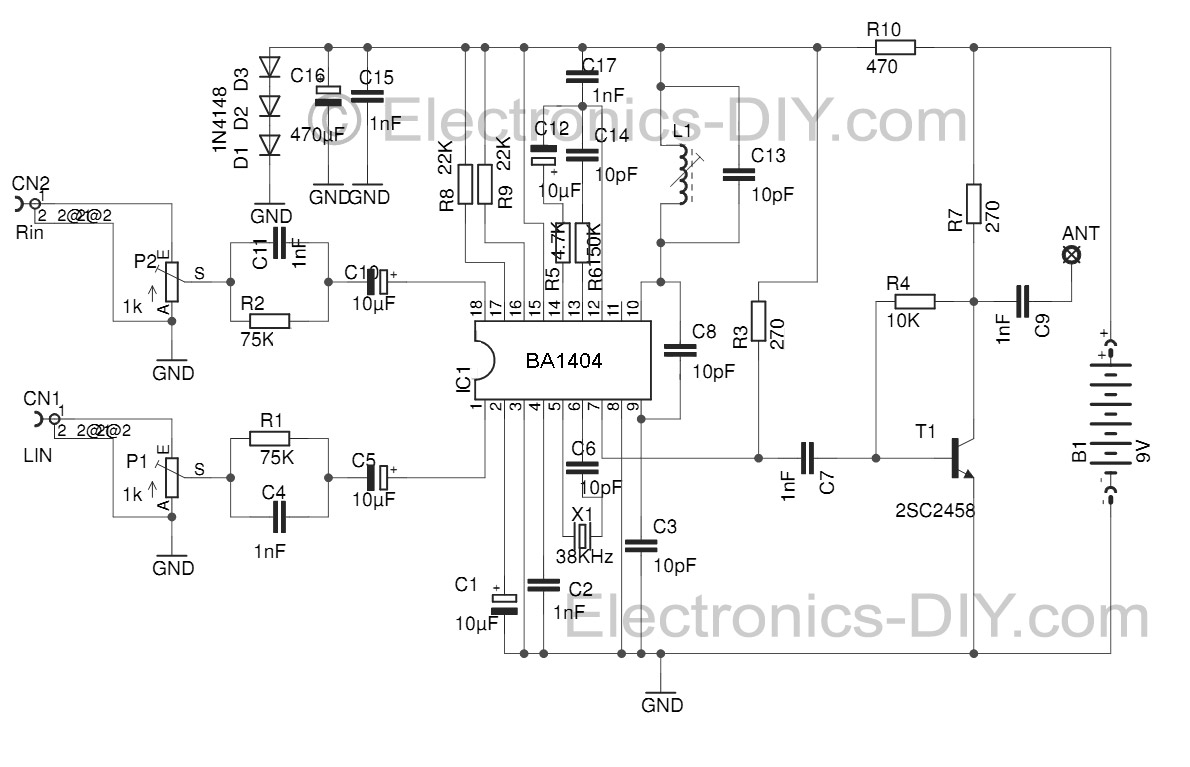
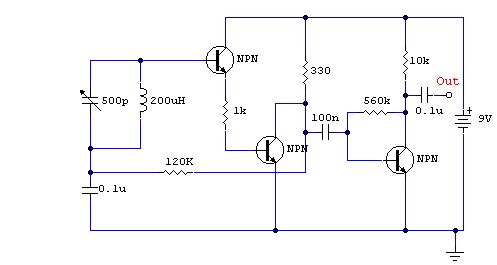
The project involves the integration of infrared (IR) LEDs with an IR phototransistor to create a simple optical communication system or a basic IR sensor circuit. The IR LED emits infrared light, which is typically invisible to the human eye, while the phototransistor detects this emitted light, allowing for the conversion of light signals into electrical signals.
In this circuit, the IR LED is connected in series with a current-limiting resistor to ensure it operates within its specified current range. The anode of the IR LED is connected to the positive terminal of a power supply, while the cathode is connected to one end of the resistor. The other end of the resistor is grounded. This configuration allows the LED to emit infrared light when powered.
The IR phototransistor is connected to a different part of the circuit. Its collector is connected to a positive voltage supply, while the emitter is connected to ground through a load resistor. When the IR LED is activated, it emits infrared light that can be detected by the phototransistor. The phototransistor will conduct when it receives sufficient IR light, allowing current to flow from the collector to the emitter, which can be used to trigger further actions in the circuit, such as activating a relay or lighting an indicator LED.
To enhance the performance of the circuit, it is advisable to use a suitable resistor value for both the IR LED and the phototransistor, depending on their specifications. Additionally, the distance between the IR LED and the phototransistor should be optimized to ensure reliable operation, as the intensity of the emitted infrared light decreases with distance.
This basic circuit can serve as a foundation for various applications, such as remote control systems, simple obstacle detection, or proximity sensors, demonstrating the versatility of IR components in electronic projects.Hello all, Recently I acquired some samples of IR LED`s, and a matching IR Phototransistor. I was bored, and decided to make something with it!.. 🔗 External reference
The project involves the integration of infrared (IR) LEDs with an IR phototransistor to create a simple optical communication system or a basic IR sensor circuit. The IR LED emits infrared light, which is typically invisible to the human eye, while the phototransistor detects this emitted light, allowing for the conversion of light signals into electrical signals.
In this circuit, the IR LED is connected in series with a current-limiting resistor to ensure it operates within its specified current range. The anode of the IR LED is connected to the positive terminal of a power supply, while the cathode is connected to one end of the resistor. The other end of the resistor is grounded. This configuration allows the LED to emit infrared light when powered.
The IR phototransistor is connected to a different part of the circuit. Its collector is connected to a positive voltage supply, while the emitter is connected to ground through a load resistor. When the IR LED is activated, it emits infrared light that can be detected by the phototransistor. The phototransistor will conduct when it receives sufficient IR light, allowing current to flow from the collector to the emitter, which can be used to trigger further actions in the circuit, such as activating a relay or lighting an indicator LED.
To enhance the performance of the circuit, it is advisable to use a suitable resistor value for both the IR LED and the phototransistor, depending on their specifications. Additionally, the distance between the IR LED and the phototransistor should be optimized to ensure reliable operation, as the intensity of the emitted infrared light decreases with distance.
This basic circuit can serve as a foundation for various applications, such as remote control systems, simple obstacle detection, or proximity sensors, demonstrating the versatility of IR components in electronic projects.Hello all, Recently I acquired some samples of IR LED`s, and a matching IR Phototransistor. I was bored, and decided to make something with it!.. 🔗 External reference