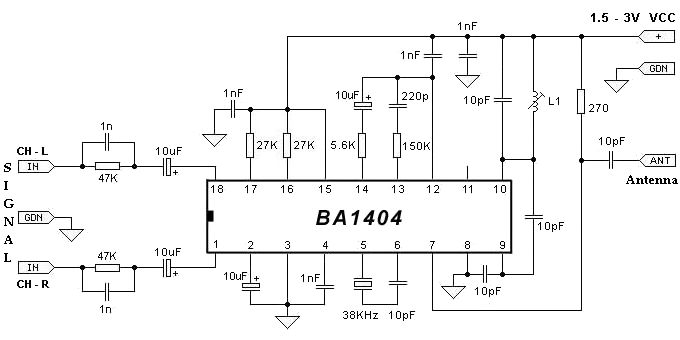
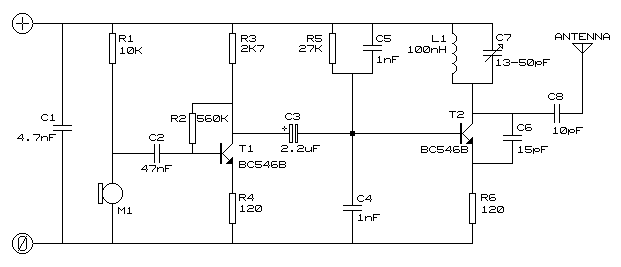
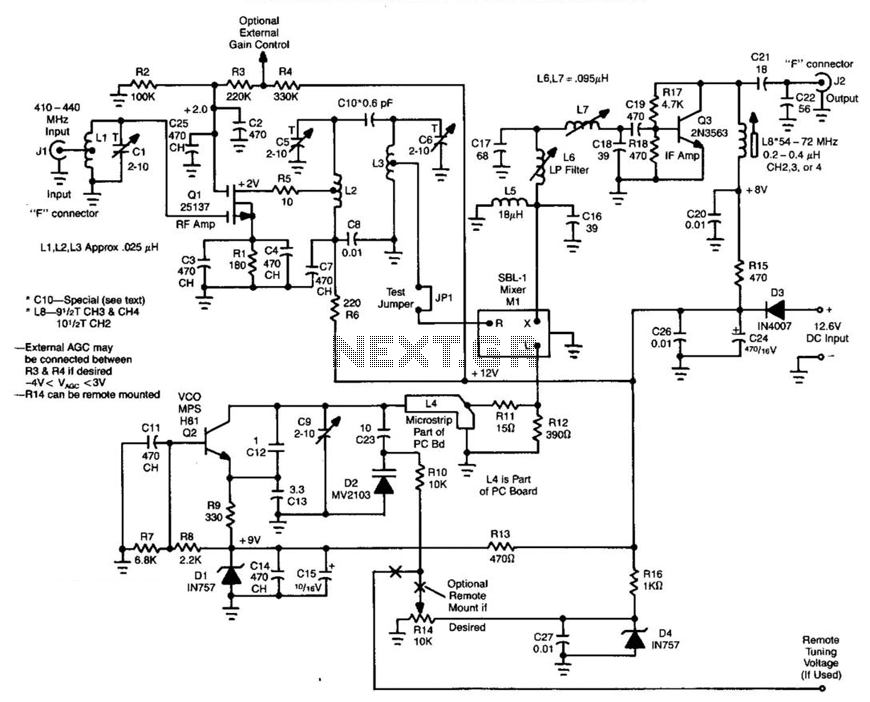
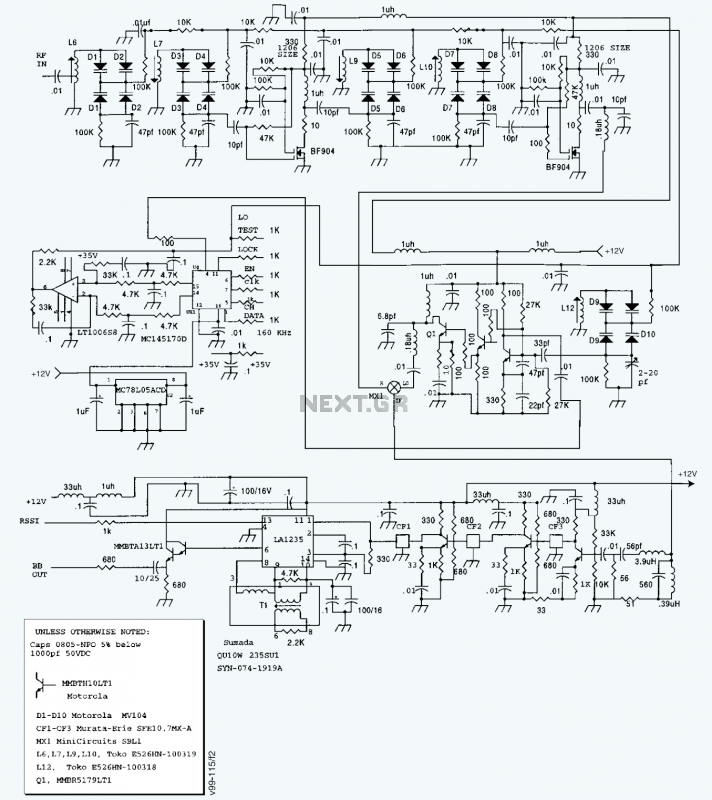
IR transmitter and receiver
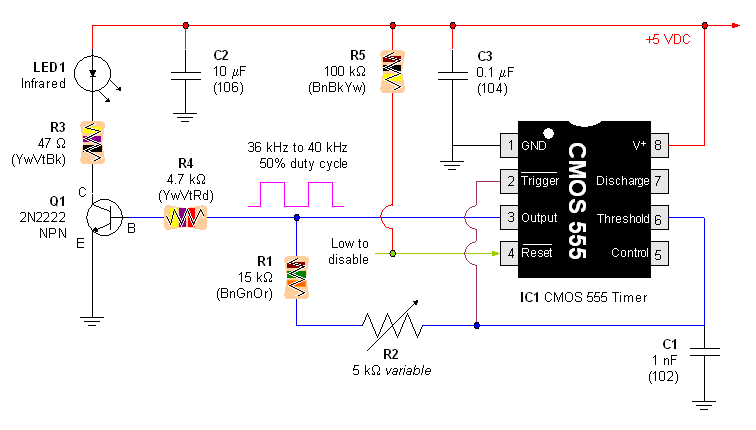
An infrared (IR) transmitter-receiver system is being developed to send signals to a device, specifically a simple blue LED.
The proposed infrared transmitter-receiver system consists of two main components: the IR transmitter and the IR receiver. The transmitter will emit infrared signals modulated to convey information, while the receiver will detect these signals and activate the connected blue LED accordingly.
The IR transmitter can be constructed using an infrared LED, which emits light in the infrared spectrum when a current flows through it. A microcontroller or a simple oscillator circuit can be used to modulate the signal, allowing for the transmission of data. The modulation can be achieved through techniques such as pulse width modulation (PWM) or frequency modulation, depending on the complexity of the signals to be sent.
The IR receiver typically consists of a photodiode or a phototransistor sensitive to infrared light. When the transmitted IR signal is received, the photodiode generates a small current proportional to the intensity of the incoming light. This signal can be amplified using an operational amplifier to ensure it is strong enough to drive the connected blue LED.
To ensure proper operation, the system should include a power supply appropriate for both the transmitter and receiver circuits. The blue LED will require a current-limiting resistor to prevent it from drawing excessive current, which could damage it. The resistor value can be calculated using Ohm's law, considering the forward voltage drop of the LED and the supply voltage.
In summary, this IR transmitter-receiver system is designed to wirelessly control a blue LED using infrared signals, providing a simple yet effective solution for remote signaling applications.Hi, I wanted to build an IR-transmitter-receiver system to send signals to a device . Let`s say the device is a simple blue LED (just to make life.. 🔗 External reference
The proposed infrared transmitter-receiver system consists of two main components: the IR transmitter and the IR receiver. The transmitter will emit infrared signals modulated to convey information, while the receiver will detect these signals and activate the connected blue LED accordingly.
The IR transmitter can be constructed using an infrared LED, which emits light in the infrared spectrum when a current flows through it. A microcontroller or a simple oscillator circuit can be used to modulate the signal, allowing for the transmission of data. The modulation can be achieved through techniques such as pulse width modulation (PWM) or frequency modulation, depending on the complexity of the signals to be sent.
The IR receiver typically consists of a photodiode or a phototransistor sensitive to infrared light. When the transmitted IR signal is received, the photodiode generates a small current proportional to the intensity of the incoming light. This signal can be amplified using an operational amplifier to ensure it is strong enough to drive the connected blue LED.
To ensure proper operation, the system should include a power supply appropriate for both the transmitter and receiver circuits. The blue LED will require a current-limiting resistor to prevent it from drawing excessive current, which could damage it. The resistor value can be calculated using Ohm's law, considering the forward voltage drop of the LED and the supply voltage.
In summary, this IR transmitter-receiver system is designed to wirelessly control a blue LED using infrared signals, providing a simple yet effective solution for remote signaling applications.Hi, I wanted to build an IR-transmitter-receiver system to send signals to a device . Let`s say the device is a simple blue LED (just to make life.. 🔗 External reference