JG series circuit of a photoelectric relay
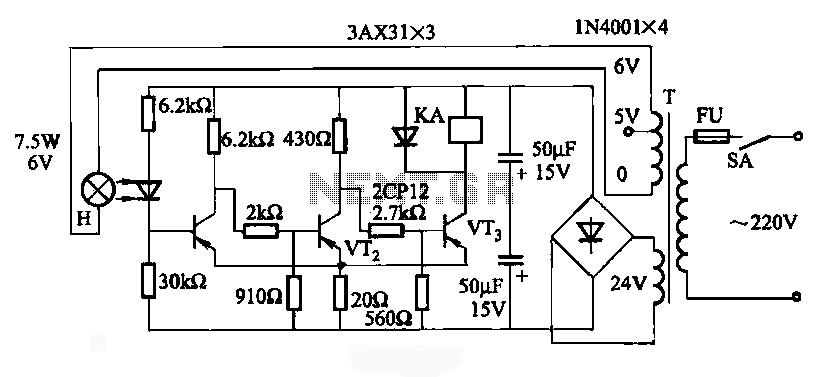
JG series of photoelectric relay circuit. To ensure reliable operation, a Schmitt trigger circuit has been incorporated. These circuits function similarly; when light strikes the photosensitive component, its internal resistance decreases, activating the transistor VT and subsequently energizing the relay KA.
The JG series photoelectric relay circuit is designed to detect light levels and activate a relay based on the presence or absence of light. The core component of this circuit is the photosensitive element, which can be a phototransistor or a photodiode, depending on the specific application requirements. When light hits the photosensitive member, it causes a decrease in internal resistance, allowing current to flow through the circuit.
Incorporating a Schmitt trigger serves to enhance the circuit's reliability by providing hysteresis. This means that the circuit will have distinct threshold levels for turning on and off, preventing false triggering due to noise or fluctuations in light intensity. The Schmitt trigger is typically implemented using a combination of operational amplifiers or dedicated Schmitt trigger ICs.
Once the light level reaches a certain threshold, the photosensitive component activates the transistor VT. This transistor acts as a switch, allowing current to flow to the relay KA. The relay, when energized, can control larger loads or other circuits, making this configuration suitable for various automation and control applications.
The circuit's design should also consider the power supply requirements for the relay and the transistor. Proper biasing of the transistor is essential to ensure it operates within its safe limits. Additionally, protective components such as diodes may be included in the circuit to safeguard against back EMF generated by the relay coil when it is de-energized.
Overall, the JG series photoelectric relay circuit offers a robust solution for applications requiring light detection and control, leveraging the benefits of both the Schmitt trigger and relay technology.JG series of photoelectric relay circuit. For the circuit to work reliably, we have adopted the Schmitt trigger circuit. These circuits are similar, when there is light incident on the photosensitive member, the internal resistance becomes smaller, the transistor VT. Turn, relay KA box together.
The JG series photoelectric relay circuit is designed to detect light levels and activate a relay based on the presence or absence of light. The core component of this circuit is the photosensitive element, which can be a phototransistor or a photodiode, depending on the specific application requirements. When light hits the photosensitive member, it causes a decrease in internal resistance, allowing current to flow through the circuit.
Incorporating a Schmitt trigger serves to enhance the circuit's reliability by providing hysteresis. This means that the circuit will have distinct threshold levels for turning on and off, preventing false triggering due to noise or fluctuations in light intensity. The Schmitt trigger is typically implemented using a combination of operational amplifiers or dedicated Schmitt trigger ICs.
Once the light level reaches a certain threshold, the photosensitive component activates the transistor VT. This transistor acts as a switch, allowing current to flow to the relay KA. The relay, when energized, can control larger loads or other circuits, making this configuration suitable for various automation and control applications.
The circuit's design should also consider the power supply requirements for the relay and the transistor. Proper biasing of the transistor is essential to ensure it operates within its safe limits. Additionally, protective components such as diodes may be included in the circuit to safeguard against back EMF generated by the relay coil when it is de-energized.
Overall, the JG series photoelectric relay circuit offers a robust solution for applications requiring light detection and control, leveraging the benefits of both the Schmitt trigger and relay technology.JG series of photoelectric relay circuit. For the circuit to work reliably, we have adopted the Schmitt trigger circuit. These circuits are similar, when there is light incident on the photosensitive member, the internal resistance becomes smaller, the transistor VT. Turn, relay KA box together.