
Joule Thief use very low input 0,136 volt
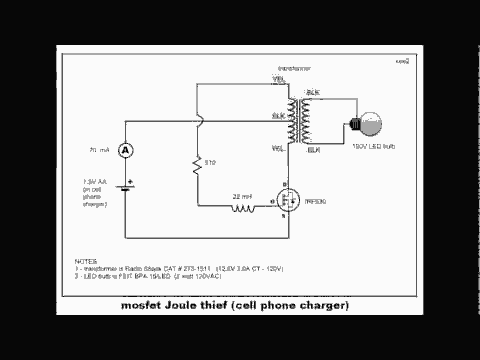
No description available.
Related Circuits
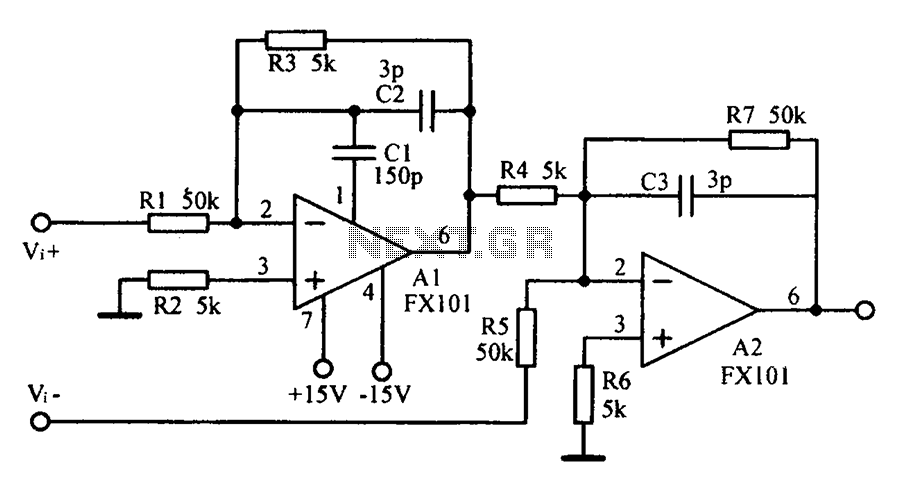
Common mode input voltage up to a difference of 100V enlarged circuit diagram. The circuit diagram described features a design capable of handling a common mode input voltage with a differential range of up to 100V. Such a configuration is...
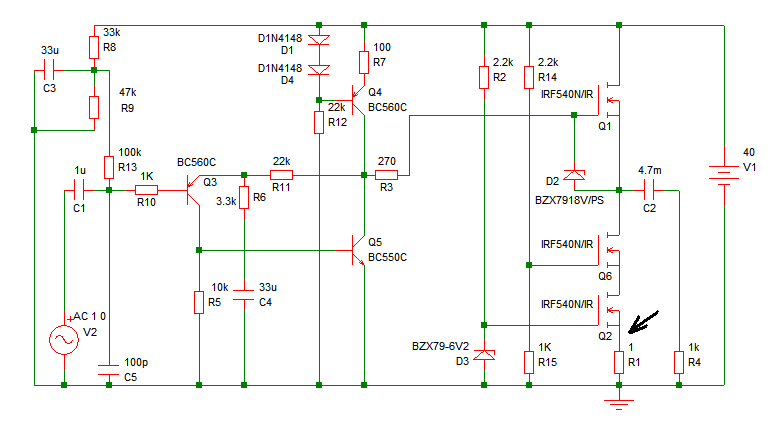
Increasing the quiescent current (Iq) will result in more power output at 4 ohms. It is understood that decreasing the supply voltage affects performance. Increasing the quiescent current (Iq) in a circuit can lead to enhanced power output, particularly when...
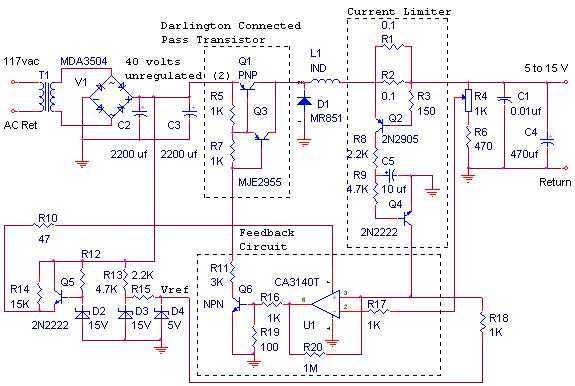
The switching power supply, shown in the schematic, provides 12 volts, at 10 amps, maximum, using a discrete transistor regulator with an op-amp functioning as a comparator in the feedback circuit. The supply was constructed in 1984 and is...
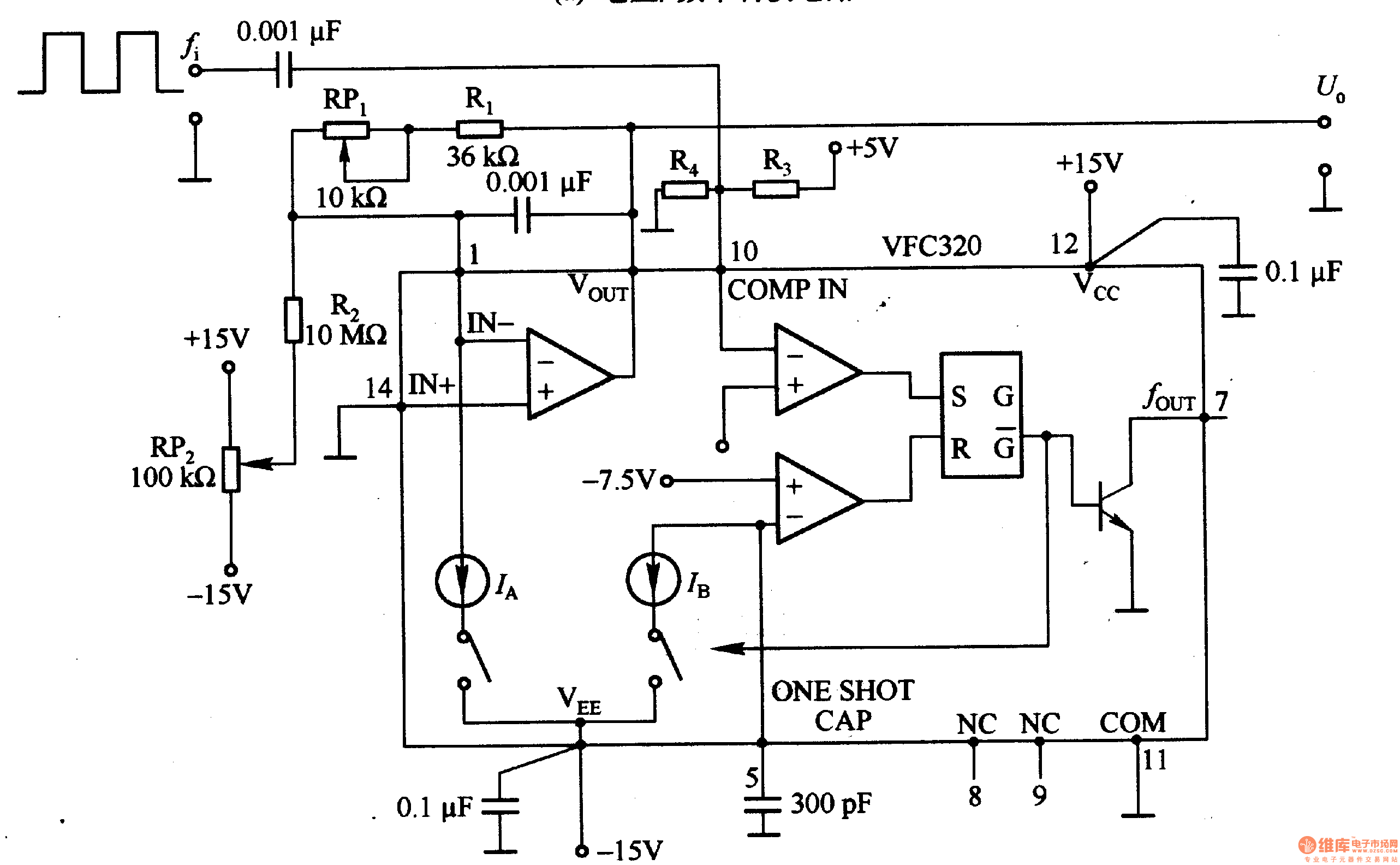
Figure 1-22 (a) illustrates a circuit that converts an input voltage of 0 to +10V (Ui) into a pulse with an output frequency ranging from 0 to 100kHz. In this configuration, pin 7 of the VFC320 is connected to...
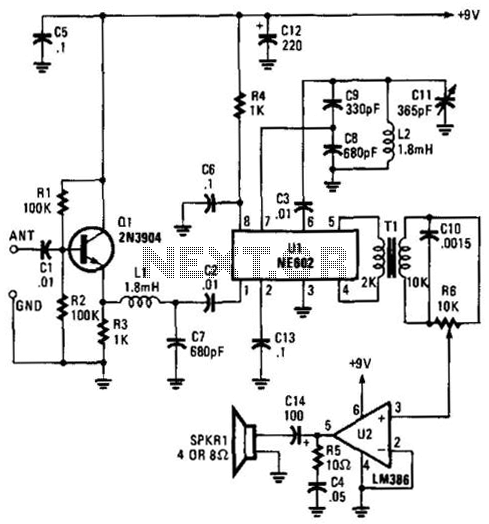
Using an NE602 heterodyne detector and U1 as an RF amplifier, this receiver tunes the middle portion of the low-frequency spectrum from 150 to 250 kHz. U2 is a loudspeaker amplifier. The described circuit employs an NE602 integrated circuit...
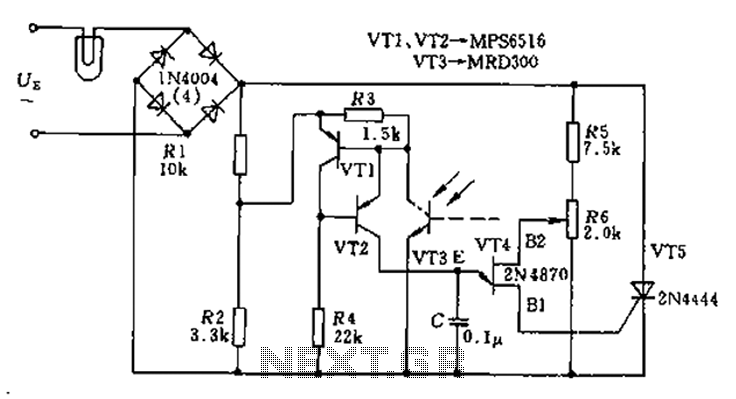
The circuit utilizes a thyristor-based AC automatic voltage regulator to stabilize the brightness of lamp L. A diagonal line connects the thyristor to the T5 bridge. The trigger pulse for the thyristor is generated by a single-junction transistor, VT4....
We use cookies to enhance your experience, analyze traffic, and serve personalized ads. By clicking "Accept", you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more